Tick-host conflict: immunoglobulin E antibodies to tick proteins in patients with anaphylaxis to tick bite
- PMID: 28423486
- PMCID: PMC5400532
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.15243
Tick-host conflict: immunoglobulin E antibodies to tick proteins in patients with anaphylaxis to tick bite
Abstract
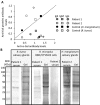
Tick-borne infectious diseases and allergies are a growing problem worldwide. Tick bite allergy has been associated with the direct effect of immunoglobulin E (IgE) response to tick salivary antigens, or secondary to the induction of allergy to red meat consumption through IgE antibodies against the carbohydrate α-Gal (Gal α 1-3Gal β 1-(3)4GlcNAc-R). However, despite the growing burden of this pathology, the proteins associated with anaphylaxis to tick bite have not been characterized. To address this question, a comparative proteomics approach was used to characterize tick proteins producing an IgE antibody response in a healthy individual with record of tick bites, which had not resulted in any allergic reactions, and two patients with anaphylactic reactions to Rhipicephalus bursa or Hyalomma marginatum tick bites. Both patients and the healthy individual were red meat tolerant. The results supported a patient-specific IgE antibody response to tick species responsible for the anaphylaxis to tick bite. Both patients and the healthy individual serologically recognized tick proteins with and without α-Gal modifications, with proteins differentially recognized by patients but not control sera. These proteins could be used as potential antigens for diagnostics, treatment and prevention of tick bite-induced allergies.
Keywords: Immune response; Immunity; Immunology and Microbiology Section; allergy; alpha-Gal; anaphylaxis; immunology; proteomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no commercial or financial conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- de la Fuente J, Estrada-Peña A, Venzal JM, Kocan KM, Sonenshine DE. Overview: Ticks as vectors of pathogens that cause disease in humans and animals. Front Biosci. 2008;13:6938–6946. - PubMed
-
- Estrada-Peña A, Ostfeld RS, Peterson AT, Poulin R, de la Fuente J. Effects of environmental change on zoonotic disease risk: an ecological primer. Trends Parasitol. 2014;30:205–214. - PubMed
-
- Severo MS, Pedra JHF, Ayllón N, Kocan KM, Anaplasma de la Fuente J., Tang In, YW Sussman M, Liu D, Poxton I, Schwartzman J, editors. Molecular Medical Microbiology. 2nd edition. Academic Press, Elsevier; Cambridge: 2015. pp. 2033–2042.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

