Prognostic role of programmed-death ligand 1 (PD-L1) expressing tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in testicular germ cell tumors
- PMID: 28423520
- PMCID: PMC5400624
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.15585
Prognostic role of programmed-death ligand 1 (PD-L1) expressing tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in testicular germ cell tumors
Abstract
Purpose: Testicular germ cell tumors (TGCTs) are nearly universally curable malignancies. Nevertheless, standard cisplatin-based chemotherapy is not curative in a small subgroup of patients. Previously, we showed that PD-L1 overexpression is associated with worse prognosis in TGCTs, while tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) are prognostic in different types of cancer. This study aimed to evaluate the prognostic value of PD-1 and PD-L1 expressing TILs in TGCTs.
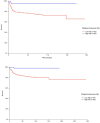
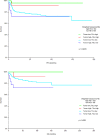
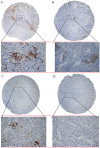
Results: PD-L1 positive TILs were found significantly more often in seminomas (95.9% of patients) and embryonal carcinomas (91.0%) compared to yolk sac tumors (60.0%), choriocarcinomas (54.5%) or teratomas (35.7%) (All p < 0.05). TGCTs patients with high infiltration of PD-L1 positive TILs (HS ≥ 160) had significantly better progression-free survival (HR = 0.17, 95% CI 0.09 - 0.31, p = 0.0006) and overall survival (HR = 0.08, 95% CI 0.04 - 0.16, p = 0.001) opposite to patients with lower expression of PD-L1 (HS < 150). PD-1 expressing TILs were not prognostic in TGCTs.
Materials and methods: Surgical specimens from 240 patients with primary TGCTs were included into this translational study. The PD-1 and PD-L1 expression on tumor and TILs were detected by immunohistochemistry using anti-PD-1 and anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody. Scoring was performed semiquantitatively by weighted histoscore (HS) method.
Conclusions: The prognostic value of PD-L1 expressing TILs in TGCTs was demonstrated for the first time.
Keywords: prognostic factor; programmed cell death protein 1; programmed death-ligand 1; testicular germ cell tumors; tumor infiltrating lymphocytes.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflicts of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prognostic value of programmed-death-1 receptor (PD-1) and its ligand 1 (PD-L1) in testicular germ cell tumors.Ann Oncol. 2016 Feb;27(2):300-5. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdv574. Epub 2015 Nov 23. Ann Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26598537 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic impact of programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) and PD-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression in cancer cells and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in ovarian high grade serous carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2016 Jan 12;7(2):1486-99. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6429. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26625204 Free PMC article.
-
The combination of PD-L1 expression and decreased tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes is associated with a poor prognosis in triple-negative breast cancer.Oncotarget. 2017 Feb 28;8(9):15584-15592. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14698. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28107186 Free PMC article.
-
Significance of evaluating tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) and programmed cell death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression in breast cancer.Med Mol Morphol. 2017 Dec;50(4):185-194. doi: 10.1007/s00795-017-0170-y. Epub 2017 Sep 21. Med Mol Morphol. 2017. PMID: 28936553 Review.
-
Prognostic and clinicopathological value of PD-L1 expression in primary breast cancer: a meta-analysis.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2019 Nov;178(1):17-33. doi: 10.1007/s10549-019-05371-0. Epub 2019 Jul 29. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2019. PMID: 31359214 Review.
Cited by
-
The values of systemic immune-inflammation index and neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in predicting testicular germ cell tumors: A retrospective clinical study.Front Oncol. 2022 Sep 16;12:893877. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.893877. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36185298 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the Immune system and Epigenetic Landscape of Urological Tumors.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 28;21(3):829. doi: 10.3390/ijms21030829. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32012885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increased tumor vascularization is associated with the amount of immune competent PD-1 positive cells in testicular germ cell tumors.Oncol Lett. 2018 Jun;15(6):9852-9860. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8597. Epub 2018 Apr 27. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29928359 Free PMC article.
-
The clinical significance of T cell infiltration and immune checkpoint expression in central nervous system germ cell tumors.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 31;16:1536722. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1536722. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39958339 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic immune-inflammation index in germ-cell tumours.Br J Cancer. 2018 Mar 20;118(6):831-838. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2017.460. Epub 2018 Feb 27. Br J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29485980 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Einhorn LH. Treatment of testicular cancer: a new and improved model. Journal of clinical oncology. 1990;8:1777–1781. - PubMed
-
- Einhorn LH. General Motors Cancer Research Prizewinners Laureates Lectures. Charles F. Kettering Prize. Clinical trials in testicular cancer. Cancer. 1993;71:3182–3184. - PubMed
-
- Motzer RJ, Geller NL, Tan CC, Herr H, Morse M, Fair W, Sheinfeld J, Sogani P, Russo P, Bosl GJ. Salvage chemotherapy for patients with germ cell tumors. The Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center experience (1979-1989). Cancer. 1991;67:1305–1310. - PubMed
-
- Motzer RJ, Sheinfeld J, Mazumdar M, Bains M, Mariani T, Bacik J, Bajorin D, Bosl GJ. Paclitaxel, ifosfamide, and cisplatin second-line therapy for patients with relapsed testicular germ cell cancer. Journal of clinical oncology. 2000;18:2413–2418. - PubMed
-
- Mardiak J, Salek T, Sycova-Mila Z, Obertova J, Hlavata Z, Mego M, Reckova M, Koza I. Paclitaxel plus ifosfamide and cisplatin in second-line treatment of germ cell tumors: a phase II study. Neoplasma. 2005;52:497–501. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

