The combination of circulating long noncoding RNAs AK001058, INHBA-AS1, MIR4435-2HG, and CEBPA-AS1 fragments in plasma serve as diagnostic markers for gastric cancer
- PMID: 28423525
- PMCID: PMC5400602
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.15628
The combination of circulating long noncoding RNAs AK001058, INHBA-AS1, MIR4435-2HG, and CEBPA-AS1 fragments in plasma serve as diagnostic markers for gastric cancer
Abstract
Background: Suitable diagnostic markers for cancers are urgently required in clinical practice. Long non-coding RNAs, which have been reported in many cancer types, are a potential new class of biomarkers for tumor diagnosis.
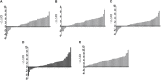
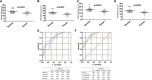
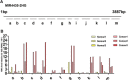
Results: Five lncRNAs, including AK001058, INHBA-AS1, MIR4435-2HG, UCA1 and CEBPA-AS1 were validated to be increased in gastric cancer tissues. Furthermore, we found that plasma level of these five lncRNAs were significantly higher in gastric cancer patients compared with normal controls. By receiver operating characteristic analysis, we found that the combination of plasma lncRNAs with the area under the curve up to 0.921, including AK001058, INHBA-AS1, MIR4435-2HG, and CEBPA-AS1, is a better indicator of gastric cancer than their individual levels or other lncRNA combinations. Simultaneously, we found that the expression levels of a series of MIR4435-2HG fragments are different in gastric cancer plasma samples, but most of them higher than that in healthy control plasma samples.
Materials and methods: LncRNA gene expression profiles were analyzed in two pairs of human gastric cancer and adjacent non-tumor tissues by microarray analysis. Nine gastric cancer-associated lncRNAs were selected and assessed by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction in gastric tissues, and 5 of them were further analyzed in gastric cancer patients' plasma.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrate that certain lncRNAs, such as AK001058, INHBA-AS1, MIR4435-2HG, and CEBPA-AS1, are enriched in human gastric cancer tissues and significantly elevated in the plasma of patients with gastric cancer. These findings indicate that the combination of these four lncRNAs might be used as diagnostic or prognostic markers for gastric cancer patients.
Keywords: RNA fragments; biomarker; gastric cancer; long noncoding RNA; plasma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

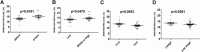
Similar articles
-
Long non-coding RNA UCA1 may be a novel diagnostic and predictive biomarker in plasma for early gastric cancer.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Oct 1;8(10):12936-42. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26722487 Free PMC article.
-
Combined identification of long non-coding RNA XIST and HIF1A-AS1 in serum as an effective screening for non-small cell lung cancer.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Jul 1;8(7):7887-95. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26339353 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Combinations of Plasma lncRNAs and mRNAs as Potential Biomarkers for Precursor Lesions and Early Gastric Cancer.J Oncol. 2022 Feb 11;2022:1458320. doi: 10.1155/2022/1458320. eCollection 2022. J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35186077 Free PMC article.
-
MIR4435-2HG: A newly proposed lncRNA in human cancer.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Jun;150:112971. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112971. Epub 2022 Apr 18. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 35447550 Review.
-
The role of long non-coding RNA AFAP1-AS1 in human malignant tumors.Pathol Res Pract. 2018 Oct;214(10):1524-1531. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2018.08.014. Epub 2018 Aug 20. Pathol Res Pract. 2018. PMID: 30173945 Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging roles of long non-coding RNA FOXP4-AS1 in human cancers: From molecular biology to clinical application.Heliyon. 2024 Oct 26;10(21):e39857. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39857. eCollection 2024 Nov 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39539976 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long non-coding RNAs: Biogenesis, functions, and clinical significance in gastric cancer.Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2021 Nov 11;23:458-476. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2021.11.005. eCollection 2021 Dec 17. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2021. PMID: 34901389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perversely expressed long noncoding RNAs can alter host response and viral proliferation in SARS-CoV-2 infection.Future Virol. 2020 Sep;15(9):577-593. doi: 10.2217/fvl-2020-0188. Future Virol. 2020. PMID: 33224264 Free PMC article.
-
A review of C/EBP α: a potential novel target for solid tumor intervention.J Transl Med. 2025 Aug 11;23(1):894. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06884-7. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40790495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A genome-wide association study in a large community-based cohort identifies multiple loci associated with susceptibility to bacterial and viral infections.Sci Rep. 2022 Feb 16;12(1):2582. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-05838-z. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35173190 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shao Y, Ye M, Jiang X, Sun W, Ding X, Liu Z, Ye G, Zhang X, Xiao B, Guo J. Gastric juice long noncoding RNA used as a tumor marker for screening gastric cancer. Cancer. 2014;120:3320–3328. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

