Identification of long non-coding RNAs GAS5, linc0597 and lnc-DC in plasma as novel biomarkers for systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 28423570
- PMCID: PMC5410334
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.15569
Identification of long non-coding RNAs GAS5, linc0597 and lnc-DC in plasma as novel biomarkers for systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
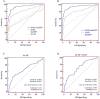
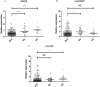
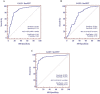
Despite increasing evidence that long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) widely take part in human diseases, the role of lncRNAs in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is largely unknown. In this study, we performed a two-stage study to explore the plasma levels of five lncRNAs (GAS5, linc0949, linc0597, HOTAIRM1 and lnc-DC) and their potential as SLE biomarkers. Compared with healthy controls, plasma levels of GAS5 and lnc-DC were significantly decreased (P < 0.001 and P = 0.002, respectively) while linc0597 were overexpressed in SLE patients (P < 0.001). When SLE patients were divided into SLE without nephritis and lupus nephritis (LN), the levels of lnc-DC were significantly higher in LN compared with SLE without nephritis (P = 0.018), but no significant difference in levels of GAS5 and linc0597 were found between LN and SLE without nephritis; plasma linc0949 level showed no significant difference in all comparisons. Further evaluation on potential biomarkers showed that GAS5, linc0597 and lnc-DC may specifically identify patients with SLE, the combination of GAS5 and linc0597 provided better diagnostic accuracy; lnc-DC may discriminate LN from SLE without nephritis. In summary, GAS5, linc0597 and lnc-DC in plasma could be potential biomarkers for SLE.
Keywords: biomarker; diagnosis; long non-coding RNA; systemic lupus erythematosus.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures

Similar articles
-
Differential Plasma Expression Profiles of Long Non-Coding RNAs Reveal Potential Biomarkers for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Biomolecules. 2019 May 28;9(6):206. doi: 10.3390/biom9060206. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31141998 Free PMC article.
-
Association of long noncoding RNAs expression levels and their gene polymorphisms with systemic lupus erythematosus.Sci Rep. 2017 Nov 9;7(1):15119. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-15156-4. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29123179 Free PMC article.
-
Value of sTNF-R1 and linc0597 as indicators for disease activity and diagnosis of lupus nephritis.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020 May;24(10):5582-5591. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202005_21344. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32495893
-
LncRNA Expression Profiles in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Rheumatoid Arthritis: Emerging Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 23;12:792884. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.792884. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 35003113 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interferon-Inducible Protein 10 and Disease Activity in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Lupus Nephritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 8;20(19):4954. doi: 10.3390/ijms20194954. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31597273 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Long Noncoding RNAs and Circular RNAs in Autoimmune Diseases.Biomolecules. 2020 Jul 14;10(7):1044. doi: 10.3390/biom10071044. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32674342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Mar 2;10:835566. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.835566. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35309937 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decreased H19, GAS5, and linc0597 Expression and Association Analysis of Related Gene Polymorphisms in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Biomolecules. 2019 Dec 29;10(1):55. doi: 10.3390/biom10010055. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31905737 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA growth arrest specific transcript 5 acting as a sponge of MicroRNA-188-5p to regulate SMAD family member 2 expression promotes myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):6674-6686. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1957524. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34632932 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of the Long Noncoding RNA GAS5 Correlates with Liver Fibrosis in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Genes (Basel). 2020 May 13;11(5):545. doi: 10.3390/genes11050545. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32413995 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rahman A, Isenberg DA. Systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:929–939. - PubMed
-
- Cook HT, Botto M. Mechanisms of Disease: the complement system and the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2006;2:330–337. - PubMed
-
- Borchers AT, Leibushor N, Naguwa SM, Cheema GS, Shoenfeld Y, Gershwin ME. Lupus nephritis: a critical review. Autoimmun Rev. 2012;12:174–194. - PubMed
-
- Thomas G, Mancini J, Jourde-Chiche N, Sarlon G, Amoura Z, Harle JR, Jougla E, Chiche L. Mortality associated with systemic lupus erythematosus in France assessed by multiple-cause-of-death analysis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014;66:2503–2511. - PubMed
-
- Chang NH, Li TT, Kim JJ, Landolt-Marticorena C, Fortin PR, Gladman DD, Urowitz MB, Wither JE. Interferon-alpha induces altered transitional B cell signaling and function in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J Autoimmun. 2015;58:100–110. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

