The E3 ubiquitin ligase NEDD4 is translationally upregulated and facilitates pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 28423617
- PMCID: PMC5386762
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.15446
The E3 ubiquitin ligase NEDD4 is translationally upregulated and facilitates pancreatic cancer
Abstract
Aim: To determine the regulation and function of the neural precursor cell expressed developmentally down regulated protein 4 (NEDD4) in PDAC and to determine its dependency on phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) and PI3K/AKT signaling.
Methods: We investigated the expression of NEDD4 and the tumor suppressor PTEN in normal immortalized human pancreatic duct epithelial cell line and pancreatic adenocarcinoma (PDAC) cell lines. We further evaluated whether RNAi-mediated depletion of NEDD4 can attenuate PDAC cell proliferation and migration. We subsequently determined the crosstalk between NEDD4 expression and the PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Finally, we determined the mechanism behind differential NEDD4 protein expression in pancreatic cancer.
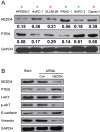
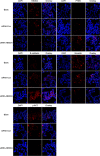
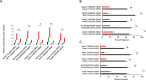
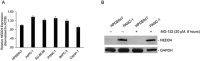
Results: The expression of NEDD4 was heterogeneous in PDAC cells, but was significantly higher compared to normal pancreatic ductal epithelial cells. Analogically, PTEN was decreased in the PDAC cells. A combination of MTT assay, wound healing migration assay, and transwell invasion assays confirmed that depletion of NEDD4 decreased the proliferation and migration ability of PDAC cells. Western blot and immunofluorescence results revealed that NEDD4 could affect PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in PDAC cells. Polysomal profiling revealed that higher NEDD4 protein expression in PDAC cells was due to undefined mechanism involving translational activation.
Conclusions: Our results reveal a novel mechanism of upregulation of NEDD4 expression in PDAC. Our findings indicate that NEDD4 potentially plays a critical role in activating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway by negatively regulating PTEN levels in PDAC cells, which promotes pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and metastasis. Therefore, NEDD4 may be a potential therapeutic target in PDAC.
Keywords: NEDD4; PDAC; PI3K/AKT; PTEN; pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm that they do not have any potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Upregulation of Neural Precursor Cell Expressed Developmentally Downregulated 4-1 is Associated with Poor Prognosis and Chemoresistance in Lung Adenocarcinoma.Chin Med J (Engl). 2018 Jan 5;131(1):16-24. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.221262. Chin Med J (Engl). 2018. PMID: 29271375 Free PMC article.
-
NEDD4 is overexpressed in colorectal cancer and promotes colonic cell growth independently of the PI3K/PTEN/AKT pathway.Cell Signal. 2013 Jan;25(1):12-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2012.08.012. Epub 2012 Sep 5. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 22974840
-
The tumour suppressor PTEN mediates a negative regulation of the E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase Nedd4.Biochem J. 2008 Jun 1;412(2):331-8. doi: 10.1042/BJ20071403. Biochem J. 2008. PMID: 18307411
-
RAKing in AKT: a tumor suppressor function for the intracellular tyrosine kinase FRK.Cell Cycle. 2009 Sep 1;8(17):2728-32. doi: 10.4161/cc.8.17.9389. Epub 2009 Sep 29. Cell Cycle. 2009. PMID: 19652529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NEDD4: The founding member of a family of ubiquitin-protein ligases.Gene. 2015 Feb 25;557(2):113-22. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2014.12.020. Epub 2014 Dec 17. Gene. 2015. PMID: 25527121 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
NEDD4 Plays Roles in the Maintenance of Breast Cancer Stem Cell Characteristics.Front Oncol. 2020 Sep 2;10:1680. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01680. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33014839 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of the PTEN/FOXO3a/PLZF signalling pathway in pancreatic cancer and its significance in tumourigenesis and progression.Invest New Drugs. 2020 Apr;38(2):321-328. doi: 10.1007/s10637-019-00791-7. Epub 2019 May 14. Invest New Drugs. 2020. PMID: 31087222
-
MicroRNA-155-5p in serum derived-exosomes promotes ischaemia-reperfusion injury by reducing CypD ubiquitination by NEDD4.ESC Heart Fail. 2023 Apr;10(2):1144-1157. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.14279. Epub 2023 Jan 11. ESC Heart Fail. 2023. PMID: 36631006 Free PMC article.
-
The E3 ubiquitin ligase NEDD4 regulates chemoresistance to 5-fluorouracil in colorectal cancer cells by altering JNK signalling.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Dec 14;14(12):828. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06349-z. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 38097550 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the Potential Role of NEDD4-like E3 Ligases in Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 16;23(20):12380. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012380. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36293239 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013(63):11–30. - PubMed
-
- Sporn MB. The war on cancer. Lancet. 1996(347):1377–1381. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011(144):646–674. - PubMed
-
- Donovan P, Poronnik P. Nedd4 and Nedd4-2: ubiquitin ligases at work in the neuron. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013(45):706–710. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

