The antitumor activity and preliminary modeling on the potential mechanism of action of human peroxiredoxin-5
- PMID: 28423711
- PMCID: PMC5432328
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.16089
The antitumor activity and preliminary modeling on the potential mechanism of action of human peroxiredoxin-5
Abstract
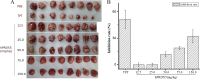
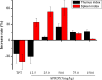
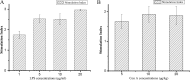
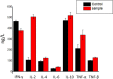
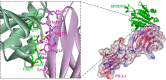
Goat peroxiredoxin-5 (gPRDX5) was verified as a good anti-cancer bioactive peptide (ACBP) against different tumor cell lines. Considering the immunogenicity between species for further therapeutic application, it is necessary to similarly investigate the antitumor activity of human peroxiredoxin-5 (hPRDX5) with 89% similarity in sequence to gPRDX5. In order to evaluate its antitumor activity, the potential anti-neoplastic effect of hPRDX5 on a mouse model was observed directly. The results of its in vivo antitumor activity suggested that hPRDX5 could resist immunosuppression by promoting lymphocyte proliferation and up-regulating the levels of serum cytokines. Meanwhile, PD-L1 was speculated as one of the targets of hPRDX5 to inhibit tumor by enhancing the immune activity according to a preliminary molecular docking study on the interactions between hPRDX5 and PD-L1. The modeling provides a basis for structural modification on hPRDX5/PD-L1 for further biological and biochemical study on the pathway blocking mechanism of hPRDX5. In this work, the results demonstrate that hPRDX5 displays efficient antitumor and immunoregulatory properties in the colon cancer C26/BALB/c and melanoma B16/C57Bl/6 mice tumor models, and suggest the potential of developing peptides from hPRDX5 as low molecular weight drug candidates for corresponding cancer immunotherapy.
Keywords: PD-L1; anti-cancer bioactive peptide; antitumor activity; human peroxiredoxin-5; immunoregulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Discovery of hPRDX5-based peptide inhibitors blocking PD-1/PD-L1 interaction through in silico proteolysis and rational design.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2020 Jan;85(1):185-193. doi: 10.1007/s00280-019-03995-z. Epub 2019 Nov 19. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31745591
-
The antitumor activity of hPRDX5 against pancreatic cancer and the possible mechanisms.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2022 Sep 12;55:e12324. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X2022e12324. eCollection 2022. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2022. PMID: 36102418 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis and evaluation of PD-L1 peptide antagonists as new anticancer agents for immunotherapy.Bioorg Med Chem. 2021 Jan 15;30:115951. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2020.115951. Epub 2020 Dec 15. Bioorg Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33360579
-
Development of the Inhibitors that Target the PD-1/PD-L1 Interaction-A Brief Look at Progress on Small Molecules, Peptides and Macrocycles.Molecules. 2019 May 30;24(11):2071. doi: 10.3390/molecules24112071. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31151293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural Biology of the Immune Checkpoint Receptor PD-1 and Its Ligands PD-L1/PD-L2.Structure. 2017 Aug 1;25(8):1163-1174. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2017.06.011. Structure. 2017. PMID: 28768162 Review.
Cited by
-
Peptides that immunoactivate the tumor microenvironment.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021 Jan;1875(1):188486. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2020.188486. Epub 2020 Dec 1. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33276025 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Su XL, K Y, Yan MR. The experimental research on anti-gastric cancer active peptide. Int J Moden Cancer Ther. 1999;2:26–27.
-
- Quan XH, X L. Effect of anti-gastric cancer biological peptide on mice and induction of TNF. Chin J Cancer Biother. 2005;12:301–302.
-
- Hou JF, Y M, Rong YN, Jiao TM, Su XL. Effect of anticancer bioactive peptide on leukemia mice. Acta Academiae Med Neimongol. 2004;26:3–6.
-
- Yan MR, S X, Liu QP. Effect of anti-gastric cancer biological peptide on lactic dehydrogenase isoenzyme. China J Cancer Prev Treat. 2002;9:382–383.
-
- Su L, Xu GH, Shen J, Tuo Y, Zhang X, Jia S, Chen Z, Su XL. Anticancer bioactive peptide suppresses human gastric cancer growth through modulation of apoptosis and the cell cycle. Oncol Rep. 2010;23:3–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

