Paclitaxel synergizes with exposure time adjusted CD22-targeting immunotoxins against B-cell malignancies
- PMID: 28423727
- PMCID: PMC5458156
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.16141
Paclitaxel synergizes with exposure time adjusted CD22-targeting immunotoxins against B-cell malignancies
Abstract
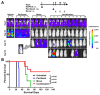
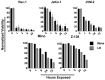
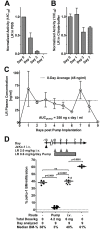
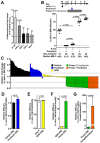
CD22-targeted recombinant immunotoxins (rIT) are active in hairy cell leukemia or acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), but not in mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) patients. The goal was to enhance rIT efficacy in vivo and to define a strong combination treatment. Activity of Moxetumomab pasudotox (Moxe) and LR combined with paclitaxel was tested against MCL cell lines in vitro and as bolus doses or continuous infusion in xenograft models. In the KOPN-8 ALL xenograft, Moxe or paclitaxel alone was active, but all mice died from leukemia; when combined, 60% of the mice achieved a sustained complete remission. Against MCL cells in vitro, LR was more active than Moxe and the cells had to be exposed to rIT for more than 24 hours for them to die. To maintain high blood levels in vivo, LR was administered continuously by 7-day pumps achieving a well-tolerated steady plasma concentration of 45 ng/ml. In JeKo-1 xenografts, continuously administered LR was 14-fold more active than bolus doses and the combination with paclitaxel additionally improved responses by 135-fold. Maintaining high rIT-plasma levels greatly improves responses in the JeKo-1 model and paclitaxel substantially enhances bolus and continuously infused rIT, supporting a clinical evaluation against B-cell malignancies.
Keywords: CD22-targeted immunotoxin; combination therapy; mantle cell lymphoma; paclitaxel; targeted therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
I.P. is a co-inventor on patents assigned to the NIH for the investigational products. F.M., T.C., S.S. and I.P. declare no financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Domain II of Pseudomonas Exotoxin Is Critical for Efficacy of Bolus Doses in a Xenograft Model of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia.Toxins (Basel). 2018 May 21;10(5):210. doi: 10.3390/toxins10050210. Toxins (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29883379 Free PMC article.
-
Wide Variability in the Time Required for Immunotoxins to Kill B Lineage Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Cells: Implications for Trial Design.Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Oct 1;22(19):4913-4922. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-2500. Epub 2016 Apr 25. Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27114443 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the anti-CD22 targeted therapy, moxetumomab pasudotox, for B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2017 Nov;64(11):10.1002/pbc.26604. doi: 10.1002/pbc.26604. Epub 2017 Apr 27. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28449314 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting CD22 in B-cell malignancies: current status and clinical outlook.BioDrugs. 2013 Aug;27(4):293-304. doi: 10.1007/s40259-013-0016-7. BioDrugs. 2013. PMID: 23696252 Review.
-
Antibody fusion proteins: anti-CD22 recombinant immunotoxin moxetumomab pasudotox.Clin Cancer Res. 2011 Oct 15;17(20):6398-405. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-0487. Clin Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 22003067 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Human CD22-Transgenic, Primary Murine Lymphoma Challenges Immunotherapies in Organ-Specific Tumor Microenvironments.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 28;22(19):10433. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910433. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638774 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody-Drug Conjugates for the Treatment of Hematological Malignancies: A Comprehensive Review.Target Oncol. 2018 Jun;13(3):287-308. doi: 10.1007/s11523-018-0558-1. Target Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29556925 Review.
-
Bryostatin Activates CAR T-Cell Antigen-Non-Specific Killing (CTAK), and CAR-T NK-Like Killing for Pre-B ALL, While Blocking Cytolysis of a Burkitt Lymphoma Cell Line.Front Immunol. 2022 Feb 9;13:825364. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.825364. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35222407 Free PMC article.
-
Domain II of Pseudomonas Exotoxin Is Critical for Efficacy of Bolus Doses in a Xenograft Model of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia.Toxins (Basel). 2018 May 21;10(5):210. doi: 10.3390/toxins10050210. Toxins (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29883379 Free PMC article.
-
Antiviral Immunotoxin Against Bovine herpesvirus-1: Targeted Inhibition of Viral Replication and Apoptosis of Infected Cell.Front Microbiol. 2018 Apr 4;9:653. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00653. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29670605 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pastan I, Hassan R, Fitzgerald DJ, Kreitman RJ. Immunotoxin therapy of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:559–565. - PubMed
-
- Mansfield E, Amlot P, Pastan I, FitzGerald DJ. Recombinant RFB4 immunotoxins exhibit potent cytotoxic activity for CD22-bearing cells and tumors. Blood. 1997;90:2020–2026. - PubMed
-
- Kreitman RJ, Squires DR, Stetler-Stevenson M, Noel P, FitzGerald DJ, Wilson WH, Pastan I. Phase I trial of recombinant immunotoxin RFB4(dsFv)-PE38 (BL22) in patients with B-cell malignancies. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:6719–6729. - PubMed
-
- Wayne AS, Kreitman RJ, Findley HW, Lew G, Delbrook C, Steinberg SM, Stetler-Stevenson M, Fitzgerald DJ, Pastan I. Anti-CD22 immunotoxin RFB4(dsFv)-PE38 (BL22) for CD22-positive hematologic malignancies of childhood: preclinical studies and phase I clinical trial. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16:1894–1903. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Salvatore G, Beers R, Margulies I, Kreitman RJ, Pastan I. Improved cytotoxic activity toward cell lines and fresh leukemia cells of a mutant anti-CD22 immunotoxin obtained by antibody phage display. Clin Cancer Res. 2002;8:995–1002. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

