Pneumococcal Capsular Polysaccharide Immunity in the Elderly
- PMID: 28424198
- PMCID: PMC5461380
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00004-17
Pneumococcal Capsular Polysaccharide Immunity in the Elderly
Abstract
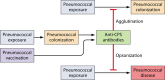
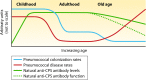
Immunity to pneumococcal infections is impaired in older people, and current vaccines are poorly protective against pneumococcal disease in this population. Naturally acquired immunity to pneumococcal capsular polysaccharides develops during childhood and is robust in young adults but deteriorates with advanced age. In particular, antibody levels and function are reduced in older people. Pneumococcal vaccines are recommended for people >65 years old. However, the benefits of polysaccharide and protein-conjugated vaccines in this population are small, because of both serotype replacement and incomplete protection against vaccine serotype pneumococcal disease. In this review, we overview the immune mechanisms by which naturally acquired and vaccine-induced pneumococcal capsular polysaccharide immunity declines with age, including altered colonization dynamics, reduced opsonic activity of antibodies (particularly IgM), and impaired mucosal immunity.
Keywords: Streptococcus pneumoniae; aging; colonization; immunization; immunoglobulins; mucosal immunity; pneumococcus; pneumonia.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures




References
-
- Jain S, Self WH, Wunderink RG, Fakhran S, Balk R, Bramley AM, Reed C, Grijalva CG, Anderson EJ, Courtney DM, Chappell JD, Qi C, Hart EM, Carroll F, Trabue C, Donnelly HK, Williams DJ, Zhu Y, Arnold SR, Ampofo K, Waterer GW, Levine M, Lindstrom S, Winchell JM, Katz JM, Erdman D, Schneider E, Hicks LA, McCullers JA, Pavia AT, Edwards KM, Finelli L. 2015. Community-acquired pneumonia requiring hospitalization among U.S. adults. N Engl J Med 373:415–427. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1500245. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

