The soy-derived peptide Lunasin inhibits invasive potential of melanoma initiating cells
- PMID: 28424421
- PMCID: PMC5421948
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.16066
The soy-derived peptide Lunasin inhibits invasive potential of melanoma initiating cells
Abstract
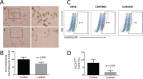
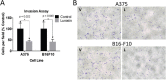
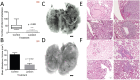
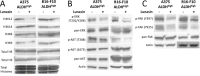
Lunasin is a 44 amino acid peptide with multiple functional domains including an aspartic acid tail, an RGD domain, and a chromatin-binding helical domain. We recently showed that Lunasin induced a phenotype switch of cancer initiating cells (CIC) out of the stem compartment by inducing melanocyte-associated differentiation markers while simultaneously reducing stem-cell-associated transcription factors. In the present study, we advance the hypothesis that Lunasin can reduce pools of melanoma cells with stem cell-like properties, and demonstrate that Lunasin treatment effectively inhibits the invasive potential of CICs in vitro as well as in vivo in a mouse experimental metastasis model. Mice receiving Lunasin treatment had significantly reduced pulmonary colonization after injection of highly metastatic B16-F10 melanoma cells compared to mice in the control group. Mechanistic studies demonstrate that Lunasin reduced activating phosphorylations of the intracellular kinases FAK and AKT as well as reduced histone acetylation of lysine residues in H3 and H4 histones. Using peptides with mutated activity domains, we functionally demonstrated that the RGD domain is necessary for Lunasin uptake and its ability to inhibit oncosphere formation by CICs, thus confirming that Lunasin's ability to affect CICs is at least in part due to the suppression of integrin signaling. Our studies suggest that Lunasin represents a unique anticancer agent that could be developed to help prevent metastasis and patient relapse by reducing the activity of CICs which are known to be resistant to current chemotherapies.
Keywords: Lunasin; cancer stem cells; histone acetylation; integrin signaling; melanoma.
Conflict of interest statement
KRD is listed as an inventor on two issued patents relating to the expression and purification of lunasin peptides and may benefit financially if the technologies described in these patents are licensed or sold. CS, JI and KY declare no conflicts of interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Lunasin is a novel therapeutic agent for targeting melanoma cancer stem cells.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 20;7(51):84128-84141. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11554. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27566591 Free PMC article.
-
Lunasin sensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer cells is linked to suppression of integrin signaling and changes in histone acetylation.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Dec 18;15(12):23705-24. doi: 10.3390/ijms151223705. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25530619 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between lunasin's sequence and its inhibitory activity of histones H3 and H4 acetylation.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2011 Jul;55(7):989-98. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201000632. Epub 2011 May 25. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2011. PMID: 21618425
-
Development of the plant-derived peptide lunasin as an anticancer agent.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2018 Aug;41:27-33. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2018.04.006. Epub 2018 May 22. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29679803 Review.
-
Lunasin as a Promising Plant-Derived Peptide for Cancer Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 23;23(17):9548. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179548. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36076946 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Soy Protein Nanofiber Scaffolds for Uniform Maturation of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Retinal Pigment Epithelium.Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2020 Aug;26(8):433-446. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEC.2020.0072. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2020. PMID: 32635833 Free PMC article.
-
Lunasin and Its Epigenetic Impact in Cancer Chemoprevention.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 24;24(11):9187. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119187. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37298139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Encapsulation of soybean lunasin and amaranth unsaponifiable matter in liposomes induces cell cycle arrest in an allograft melanoma mouse model.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 13;14(1):27858. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-79448-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39537778 Free PMC article.
-
A soy protein Lunasin can ameliorate amyloid-beta 42 mediated neurodegeneration in Drosophila eye.Sci Rep. 2018 Sep 10;8(1):13545. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-31787-7. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30202077 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-92 Expression in CD133+ Melanoma Stem Cells Regulates Immunosuppression in the Tumor Microenvironment via Integrin-Dependent Activation of TGFβ.Cancer Res. 2019 Jul 15;79(14):3622-3635. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-2659. Epub 2019 Apr 23. Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31015227 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McArthur GA, Chapman PB, Robert C, Larkin J, Haanen JB, Dummer R, Ribas A, Hogg D, Hamid O, Ascierto PA, Garbe C, Testori A, Maio M, et al. Safety and efficacy of vemurafenib in BRAF(V600E) and BRAF(V600K) mutation-positive melanoma (BRIM-3): extended follow-up of a phase 3, randomised, open-label study. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:323–32. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hauschild A, Grob JJ, Demidov LV, Jouary T, Gutzmer R, Millward M, Rutkowski P, Blank CU, Miller WH, Jr, Kaempgen E, Martín-Algarra S, Karaszewska B, Mauch C, et al. Dabrafenib in BRAF-mutated metastatic melanoma: a multicentre, open-label, phase 3 randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2012;380:358–65. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

