miRNA and Degradome Sequencing Reveal miRNA and Their Target Genes That May Mediate Shoot Growth in Spur Type Mutant "Yanfu 6"
- PMID: 28424721
- PMCID: PMC5371658
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00441
miRNA and Degradome Sequencing Reveal miRNA and Their Target Genes That May Mediate Shoot Growth in Spur Type Mutant "Yanfu 6"
Abstract
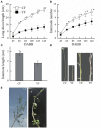
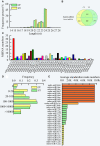
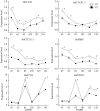
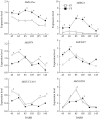
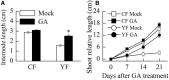
The spur-type growth habit in apple trees is characterized by short internodes, increased number of fruiting spurs, and compact growth that promotes flowering and facilitates management practices, such as pruning. The molecular mechanisms responsible for regulating spur-type growth have not been elucidated. In the present study, miRNAs and the expression of their potential target genes were evaluated in shoot tips of "Nagafu 2" (CF) and spur-type bud mutation "Yanfu 6" (YF). A total of 700 mature miRNAs were identified, including 202 known apple miRNAs and 498 potential novel miRNA candidates. A comparison of miRNA expression in CF and YF revealed 135 differentially expressed genes, most of which were downregulated in YF. YF also had lower levels of GA, ZR, IAA, and ABA hormones, relative to CF. Exogenous applications of GA promoted YF shoot growth. Based on the obtained results, a regulatory network involving plant hormones, miRNA, and their potential target genes is proposed for the molecular mechanism regulating the growth of YF. miRNA164, miRNA166, miRNA171, and their potential targets, and associated plant hormones, appear to regulate shoot apical meristem (SAM) growth. miRNA159, miRNA167, miRNA396, and their potential targets, and associated plant hormones appear to regulate cell division and internode length. This study provides a foundation for further studies designed to elucidate the mechanism underlying spur-type apple architecture.
Keywords: SAM; apple; internode; miRNAs; shoot.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Genome-wide identification of SERK genes in apple and analyses of their role in stress responses and growth.BMC Genomics. 2018 Dec 27;19(1):962. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-5342-1. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 30587123 Free PMC article.
-
Insights on the stem elongation of spur-type bud sport mutant of 'Red Delicious' apple.Planta. 2023 Feb 5;257(3):48. doi: 10.1007/s00425-023-04086-3. Planta. 2023. PMID: 36740622
-
Identification and characterization of microRNAs from in vitro-grown pear shoots infected with Apple stem grooving virus in response to high temperature using small RNA sequencing.BMC Genomics. 2015 Nov 16;16:945. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-2126-8. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26573813 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA and mRNA expression profiling analysis revealed the regulation of plant height in Gossypium hirsutum.BMC Genomics. 2015 Oct 30;16:886. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-2071-6. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26517985 Free PMC article.
-
Signalling between the shoot apical meristem and developing lateral organs.Plant Mol Biol. 2006 Apr;60(6):889-903. doi: 10.1007/s11103-005-1270-y. Plant Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16724259 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide identification of SERK genes in apple and analyses of their role in stress responses and growth.BMC Genomics. 2018 Dec 27;19(1):962. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-5342-1. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 30587123 Free PMC article.
-
The R2R3-type MYB transcription factor MdMYB90-like is responsible for the enhanced skin color of an apple bud sport mutant.Hortic Res. 2021 Jul 1;8(1):156. doi: 10.1038/s41438-021-00590-3. Hortic Res. 2021. PMID: 34193856 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA profiling analysis of developing berries for 'Kyoho' and its early-ripening mutant during berry ripening.BMC Plant Biol. 2018 Nov 16;18(1):285. doi: 10.1186/s12870-018-1516-x. BMC Plant Biol. 2018. PMID: 30445920 Free PMC article.
-
Genome sequencing of 'Fuji' apple clonal varieties reveals genetic mechanism of the spur-type morphology.Nat Commun. 2024 Nov 21;15(1):10082. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-54428-2. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39572540 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-genome resequencing and transcriptome analyses of four generation mutants to reveal spur-type and skin-color related genes in apple (Malus domestica Borkh. Cv. Red delicious).BMC Plant Biol. 2023 Nov 30;23(1):607. doi: 10.1186/s12870-023-04631-y. BMC Plant Biol. 2023. PMID: 38030998 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brown C. L., Sommer H. E. (1992). Shoot growth and histogenesis of trees possessing diverse patterns of shoot development. Am. J. Bot. 79, 335–346. 10.2307/2445024 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

