Catalytic robustness and torque generation of the F1-ATPase
- PMID: 28424741
- PMCID: PMC5380711
- DOI: 10.1007/s12551-017-0262-x
Catalytic robustness and torque generation of the F1-ATPase
Abstract
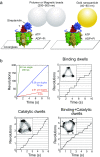
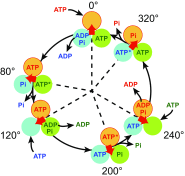
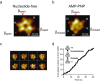
The F1-ATPase is the catalytic portion of the FoF1 ATP synthase and acts as a rotary molecular motor when it hydrolyzes ATP. Two decades have passed since the single-molecule rotation assay of F1-ATPase was established. Although several fundamental issues remain elusive, basic properties of F-type ATPases as motor proteins have been well characterized, and a large part of the reaction scheme has been revealed by the combination of extensive structural, biochemical, biophysical, and theoretical studies. This review is intended to provide a concise summary of the fundamental features of F1-ATPases, by use of the well-described model F1 from the thermophilic Bacillus PS3 (TF1). In the last part of this review, we focus on the robustness of the rotary catalysis of F1-ATPase to provide a perspective on the re-designing of novel molecular machines.
Keywords: ATP synthase; F1-ATPase; Molecular motor; Single-molecule techniques.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
Hiroyuki Noji declares that he has no conflicts of interest. Hiroshi Ueno declares that he has no conflicts of interest. Duncan G. G. McMillan declares that he has no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Figures




Similar articles
-
How Does F1-ATPase Generate Torque?: Analysis From Cryo-Electron Microscopy and Rotational Catalysis of Thermophilic F1.Front Microbiol. 2022 May 6;13:904084. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.904084. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35602057 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rotary properties of hybrid F1-ATPases consisting of subunits from different species.iScience. 2023 Apr 8;26(5):106626. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106626. eCollection 2023 May 19. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37192978 Free PMC article.
-
Catalysis and rotation of F1 motor: cleavage of ATP at the catalytic site occurs in 1 ms before 40 degree substep rotation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Dec 9;100(25):14731-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2434983100. Epub 2003 Dec 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 14657340 Free PMC article.
-
Torque, chemistry and efficiency in molecular motors: a study of the rotary-chemical coupling in F1-ATPase.Q Rev Biophys. 2015 Nov;48(4):395-403. doi: 10.1017/S0033583515000050. Q Rev Biophys. 2015. PMID: 26537397 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A model for the cooperative free energy transduction and kinetics of ATP hydrolysis by F1-ATPase.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Sep 30;100(20):11339-44. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1334188100. Epub 2003 Sep 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 14500780 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Kinetic analysis of the inhibition mechanism of bovine mitochondrial F1-ATPase inhibitory protein using biochemical assay.J Biochem. 2021 Sep 22;170(1):79-87. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvab022. J Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33693769 Free PMC article.
-
How Does F1-ATPase Generate Torque?: Analysis From Cryo-Electron Microscopy and Rotational Catalysis of Thermophilic F1.Front Microbiol. 2022 May 6;13:904084. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.904084. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35602057 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Control of rotation of the F1FO-ATP synthase nanomotor by an inhibitory α-helix from unfolded ε or intrinsically disordered ζ and IF1 proteins.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2018 Oct;50(5):403-424. doi: 10.1007/s10863-018-9773-9. Epub 2018 Sep 28. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2018. PMID: 30267331 Review.
-
Essential Role of the ε Subunit for Reversible Chemo-Mechanical Coupling in F1-ATPase.Biophys J. 2018 Jan 9;114(1):178-187. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2017.11.004. Biophys J. 2018. PMID: 29320685 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitors of ATP Synthase as New Antibacterial Candidates.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Mar 24;12(4):650. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12040650. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37107012 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

