FRET biosensor uncovers cAMP nano-domains at β-adrenergic targets that dictate precise tuning of cardiac contractility
- PMID: 28425435
- PMCID: PMC5411486
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms15031
FRET biosensor uncovers cAMP nano-domains at β-adrenergic targets that dictate precise tuning of cardiac contractility
Abstract
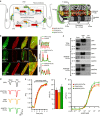
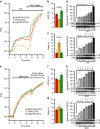
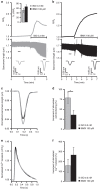
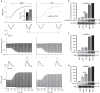
Compartmentalized cAMP/PKA signalling is now recognized as important for physiology and pathophysiology, yet a detailed understanding of the properties, regulation and function of local cAMP/PKA signals is lacking. Here we present a fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET)-based sensor, CUTie, which detects compartmentalized cAMP with unprecedented accuracy. CUTie, targeted to specific multiprotein complexes at discrete plasmalemmal, sarcoplasmic reticular and myofilament sites, reveals differential kinetics and amplitudes of localized cAMP signals. This nanoscopic heterogeneity of cAMP signals is necessary to optimize cardiac contractility upon adrenergic activation. At low adrenergic levels, and those mimicking heart failure, differential local cAMP responses are exacerbated, with near abolition of cAMP signalling at certain locations. This work provides tools and fundamental mechanistic insights into subcellular adrenergic signalling in normal and pathological cardiac function.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Bers D. M. Cardiac excitation-contraction coupling. Nature 415, 198–205 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Zaccolo M. & Pozzan T. Discrete microdomains with high concentration of cAMP in stimulated rat neonatal cardiac myocytes. Science 295, 1711–1715 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Di Benedetto G. et al.. Protein kinase A type I and type II define distinct intracellular signaling compartments. Circ. Res. 103, 836–844 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL138539/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RG/12/18/30088/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- P01 HL080101/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL092097/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL131517/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL030077/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- PG/15/5/31110/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- MR/L006855/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 HL105242/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- PG/10/75/28537/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- R01 HL126802/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL030077/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RG/12/3/29423/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

