A genome-wide association study identifies six novel risk loci for primary biliary cholangitis
- PMID: 28425483
- PMCID: PMC5429142
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms14828
A genome-wide association study identifies six novel risk loci for primary biliary cholangitis
Abstract
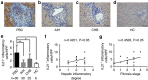
Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) is an autoimmune liver disease with a strong hereditary component. Here, we report a genome-wide association study that included 1,122 PBC cases and 4,036 controls of Han Chinese descent, with subsequent replication in a separate cohort of 907 PBC cases and 2,127 controls. Our results show genome-wide association of 14 PBC risk loci including previously identified 6p21 (HLA-DRA and DPB1), 17q12 (ORMDL3), 3q13.33 (CD80), 2q32.3 (STAT1/STAT4), 3q25.33 (IL12A), 4q24 (NF-κB) and 22q13.1 (RPL3/SYNGR1). We also identified variants in IL21, IL21R, CD28/CTLA4/ICOS, CD58, ARID3A and IL16 as novel PBC risk loci. These new findings and histochemical studies showing enhanced expression of IL21 and IL21R in PBC livers (particularly in the hepatic portal tracks) support a disease mechanism in which the deregulation of the IL21 signalling pathway, in addition to CD4 T-cell activation and T-cell co-stimulation are critical components in the development of PBC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- Selmi C. et al. Primary biliary cirrhosis in monozygotic and dizygotic twins: genetics, epigenetics, and environment. Gastroenterology 127, 485–492 (2004). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

