Hybrid finite difference/finite element immersed boundary method
- PMID: 28425587
- PMCID: PMC5650596
- DOI: 10.1002/cnm.2888
Hybrid finite difference/finite element immersed boundary method
Abstract
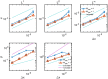
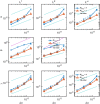
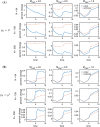
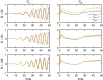
The immersed boundary method is an approach to fluid-structure interaction that uses a Lagrangian description of the structural deformations, stresses, and forces along with an Eulerian description of the momentum, viscosity, and incompressibility of the fluid-structure system. The original immersed boundary methods described immersed elastic structures using systems of flexible fibers, and even now, most immersed boundary methods still require Lagrangian meshes that are finer than the Eulerian grid. This work introduces a coupling scheme for the immersed boundary method to link the Lagrangian and Eulerian variables that facilitates independent spatial discretizations for the structure and background grid. This approach uses a finite element discretization of the structure while retaining a finite difference scheme for the Eulerian variables. We apply this method to benchmark problems involving elastic, rigid, and actively contracting structures, including an idealized model of the left ventricle of the heart. Our tests include cases in which, for a fixed Eulerian grid spacing, coarser Lagrangian structural meshes yield discretization errors that are as much as several orders of magnitude smaller than errors obtained using finer structural meshes. The Lagrangian-Eulerian coupling approach developed in this work enables the effective use of these coarse structural meshes with the immersed boundary method. This work also contrasts two different weak forms of the equations, one of which is demonstrated to be more effective for the coarse structural discretizations facilitated by our coupling approach.
Keywords: finite difference method; finite element method; fluid-structure interaction; immersed boundary method; incompressible elasticity; incompressible flow.
© 2017 The Authors International Journal for Numerical Methods in Biomedical Engineering Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures









Similar articles
-
On the Lagrangian-Eulerian Coupling in the Immersed Finite Element/Difference Method.J Comput Phys. 2022 May 15;457:111042. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2022.111042. Epub 2022 Feb 9. J Comput Phys. 2022. PMID: 35300097 Free PMC article.
-
A sharp interface Lagrangian-Eulerian method for flexible-body fluid-structure interaction.J Comput Phys. 2023 Sep 1;488:112174. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2023.112174. Epub 2023 Apr 24. J Comput Phys. 2023. PMID: 37214277 Free PMC article.
-
Stabilization approaches for the hyperelastic immersed boundary method for problems of large-deformation incompressible elasticity.Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng. 2020 Jun 15;365:112978. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2020.112978. Epub 2020 Apr 18. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng. 2020. PMID: 32483394 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between viscoelasticity and elasticity.Proc Math Phys Eng Sci. 2020 Nov;476(2243):20200419. doi: 10.1098/rspa.2020.0419. Epub 2020 Nov 18. Proc Math Phys Eng Sci. 2020. PMID: 33363441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computational Modeling of Fluidized Beds with a Focus on Pharmaceutical Applications: A Review.J Pharm Sci. 2022 Apr;111(4):1110-1125. doi: 10.1016/j.xphs.2021.09.020. Epub 2021 Sep 20. J Pharm Sci. 2022. PMID: 34555391 Review.
Cited by
-
Fluid-structure interaction in a fully coupled three-dimensional mitral-atrium-pulmonary model.Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2021 Aug;20(4):1267-1295. doi: 10.1007/s10237-021-01444-6. Epub 2021 Mar 26. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2021. PMID: 33770307 Free PMC article.
-
Structural engineering from an inverse problems perspective.Proc Math Phys Eng Sci. 2022 Jan;478(2257):20210526. doi: 10.1098/rspa.2021.0526. Epub 2022 Jan 26. Proc Math Phys Eng Sci. 2022. PMID: 35153609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A sharp interface Lagrangian-Eulerian method for rigid-body fluid-structure interaction.J Comput Phys. 2021 Oct 15;443:110442. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2021.110442. Epub 2021 May 18. J Comput Phys. 2021. PMID: 34149063 Free PMC article.
-
IB2d: a Python and MATLAB implementation of the immersed boundary method.Bioinspir Biomim. 2017 Mar 29;12(3):036003. doi: 10.1088/1748-3190/aa5e08. Bioinspir Biomim. 2017. PMID: 28355146 Free PMC article.
-
The Comparison of Different Constitutive Laws and Fiber Architectures for the Aortic Valve on Fluid-Structure Interaction Simulation.Front Physiol. 2021 Jun 24;12:682893. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.682893. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34248670 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Peskin CS. Flow patterns around heart valves: a numerical method. J Comput Phys. 1972;10(2):252‐271.
-
- Peskin CS. Numerical analysis of blood flow in the heart. J Comput Phys. 1977;25(3):220‐252.
-
- Peskin CS. The immersed boundary method. Acta Numer. 2002;11:479‐517.
-
- Miller LA, Peskin CS. When vortices stick: an aerodynamic transition in tiny insect flight. J Exp Biol. 2004;207(17):3073‐3088. - PubMed
-
- Miller LA, Peskin CS. A computational fluid dynamics of ‘clap and fling’ in the smallest insects. J Exp Biol. 2005;208(2):195‐212. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

