Adult pilocytic astrocytoma of conus medullaris: clinical considerations and review of the literature
- PMID: 28425761
- PMCID: PMC6020877
- DOI: 10.2217/cns-2016-0030
Adult pilocytic astrocytoma of conus medullaris: clinical considerations and review of the literature
Abstract
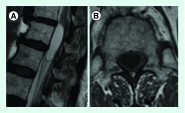
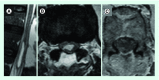
Astrocytomas are responsible for 30% of all primitive intramedullary tumors with cervicothoracic predominance. However, only about one hundred cases of intramedullary pilocytic astrocytomas were described. The authors described the case of a 69 year-old patient presenting with a broad-base gait, bilateral pain and dysesthesia of inferior limbs with a diagnosis of an intra-axial cystic lesion centered to the conus medullaris, diagnosed as pilocytic astrocytoma of conus medullaris (PACM) after surgery. To the best of our knowledge, only two previous reports concerning PACM were made. As benign lesions associated with long survivals, function should be the mainstay of treatment of PACM. Surgical resection should be performed. Adjuvant radiotherapy or chemotherapy has no establish role in pilocytic astrocytic lesions.
Keywords: chemotherapy; conus medullaris; intramedullary spinal cord tumor; pilocytic astrocytoma; radiotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Karikari IO, Nimjee SM, Hodges TR, et al. Impact of tumor histology on resectability and neurological outcome in primary intramedullary spinal cord tumors: a single-center experience with 102 patients. Neurosurgery. 2015;76(Suppl. 1):S4–13. discussion S13. - PubMed
-
- Garcés-Ambrossi GL, McGirt MJ, Mehta VA, et al. Factors associated with progression-free survival and long-term neurological outcome after resection of intramedullary spinal cord tumors: analysis of 101 consecutive cases. J. Neurosurg. Spine. 2009;11(5):591–599. - PubMed
-
- Tobin MK, Geraghty JR, Engelhard HH, et al. Intramedullary spinal cord tumors: a review of current and future treatment strategies. Neurosurg. Focus. 2015;39(2):E14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
