Plasma Micro-RNA Alterations Appear Late in Pancreatic Cancer
- PMID: 28425921
- PMCID: PMC5865497
- DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000002124
Plasma Micro-RNA Alterations Appear Late in Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
Objectives: The aim of this research was to study whether plasma microRNAs (miRNA) can be used for early detection of pancreatic cancer (PC) by analyzing prediagnostic plasma samples collected before a PC diagnosis.
Background: PC has a poor prognosis due to late presenting symptoms and early metastasis. Circulating miRNAs are altered in PC at diagnosis but have not been evaluated in a prediagnostic setting.
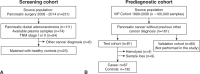
Methods: We first performed an initial screen using a panel of 372 miRNAs in a retrospective case-control cohort that included early-stage PC patients and healthy controls. Significantly altered miRNAs at diagnosis were then measured in an early detection case-control cohort wherein plasma samples in the cases are collected before a PC diagnosis. Carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (Ca 19-9) levels were measured in all samples for comparison.
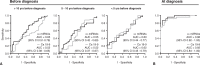
Results: Our initial screen, including 23 stage I-II PC cases and 22 controls, revealed 15 candidate miRNAs that were differentially expressed in plasma samples at PC diagnosis. We combined all 15 miRNAs into a multivariate statistical model, which outperformed Ca 19-9 in receiver-operating characteristics analysis. However, none of the candidate miRNAs, individually or in combination, were significantly altered in prediagnostic plasma samples from 67 future PC patients compared with 132 matched controls. In comparison, Ca 19-9 levels were significantly higher in the cases at <5 years before diagnosis.
Conclusion: Plasma miRNAs are altered in PC patients at diagnosis, but the candidate miRNAs found in this study appear late in the course of the disease and cannot be used for early detection of the disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Plasma miRNAs in diagnosis and prognosis of pancreatic cancer: A miRNA expression analysis.Gene. 2018 Oct 5;673:181-193. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.06.037. Epub 2018 Jun 18. Gene. 2018. PMID: 29913239
-
Plasma miRNAs Effectively Distinguish Patients With Pancreatic Cancer From Controls: A Multicenter Study.Ann Surg. 2016 Jun;263(6):1173-9. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000001345. Ann Surg. 2016. PMID: 26114496
-
Clinical utilization of serum- or plasma-based miRNAs as early detection biomarkers for pancreatic cancer: A meta-analysis up to now.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Aug;97(35):e12132. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000012132. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30170450 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasma microRNA panels to diagnose pancreatic cancer: Results from a multicenter study.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 5;7(27):41575-41583. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9491. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27223429 Free PMC article.
-
Blood circulating miRNAs as pancreatic cancer biomarkers: An evidence from pooled analysis and bioinformatics study.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 May;308(Pt 4):142469. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.142469. Epub 2025 Apr 1. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 40180095 Review.
Cited by
-
Circulating salivary and serum miRNA-182, 320a, 375 and 503 expression levels in type 2 diabetes.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2022 Jul 28;21(2):1469-1478. doi: 10.1007/s40200-022-01082-4. eCollection 2022 Dec. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2022. PMID: 36404826 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating microRNAs as promising diagnostic biomarkers for pancreatic cancer: a systematic review.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 Aug 19;12:6665-6684. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S207963. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 31692495 Free PMC article.
-
miRFA: an automated pipeline for microRNA functional analysis with correlation support from TCGA and TCPA expression data in pancreatic cancer.BMC Bioinformatics. 2019 Jul 16;20(1):393. doi: 10.1186/s12859-019-2974-3. BMC Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 31311505 Free PMC article.
-
Can our experience with surveillance for inherited pancreatic cancer help to identify early pancreatic cancer in the general population?Fam Cancer. 2024 Aug;23(3):399-403. doi: 10.1007/s10689-024-00363-6. Epub 2024 Mar 5. Fam Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38441833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnosis and prognosis of pancreatic cancer with immunoglobulin heavy constant delta blood marker.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Nov;149(14):12977-12992. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05161-8. Epub 2023 Jul 19. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37466798 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bilimoria KY, Bentrem DJ, Ko CY, et al. Validation of the 6th edition AJCC Pancreatic Cancer Staging System: report from the National Cancer Database. Cancer 2007; 110:738–744. - PubMed
-
- Rahib L, Smith BD, Aizenberg R, et al. Projecting cancer incidence and deaths to 2030: the unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and pancreas cancers in the United States. Cancer Res 2014; 74:2913–2921. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

