Studying Lactoferrin N-Glycosylation
- PMID: 28425960
- PMCID: PMC5412451
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms18040870
Studying Lactoferrin N-Glycosylation
Abstract
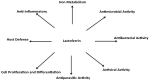
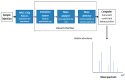
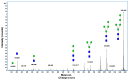
Lactoferrin is a multifunctional glycoprotein found in the milk of most mammals. In addition to its well-known role of binding iron, lactoferrin carries many important biological functions, including the promotion of cell proliferation and differentiation, and as an anti-bacterial, anti-viral, and anti-parasitic protein. These functions differ among lactoferrin homologs in mammals. Although considerable attention has been given to the many functions of lactoferrin, its primary nutritional contribution is presumed to be related to its iron-binding characteristics, whereas the role of glycosylation has been neglected. Given the critical role of glycan binding in many biological processes, the glycan moieties in lactoferrin are likely to contribute significantly to the biological roles of lactoferrin. Despite the high amino acid sequence homology in different lactoferrins (up to 99%), each exhibits a unique glycosylation pattern that may be responsible for heterogeneity of the biological properties of lactoferrins. An important task for the production of biotherapeutics and medical foods containing bioactive glycoproteins is the assessment of the contributions of individual glycans to the observed bioactivities. This review examines how the study of lactoferrin glycosylation patterns can increase our understanding of lactoferrin functionality.
Keywords: N-glycans; bioinfomatic libraries; deglycosylating enzymes; lactoferrin; mass spectrophotometry; structure-activity studies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Sorensen M., Sorensen S. Compte rendu des Travaux du Laboratoire de Carlsberg. Volume 23. Hagerup in Komm; Copenhague, Denmark: 1939. The Proteins in Whey; pp. 55–99.
-
- Johanson B. Isolation of an iron-containing red protein from human milk. Acta Chem. Scand. 1960;14:510–512. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.14-0510. - DOI
-
- Iyer S., Lonnerdal B. Lactoferrin, lactoferrin receptors and iron metabolism. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1993;47:232–241. - PubMed
-
- Levay P.F., Viljoen M. Lactoferrin: A general review. Haematologica. 1995;80:252–267. - PubMed
-
- Steijns J.M. Milk ingredients as nutraceuticals. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2001;54:81–88. doi: 10.1046/j.1364-727x.2001.00019.x. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

