Aneurysm-Specific miR-221 and miR-146a Participates in Human Thoracic and Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms
- PMID: 28425970
- PMCID: PMC5412456
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms18040875
Aneurysm-Specific miR-221 and miR-146a Participates in Human Thoracic and Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms
Abstract
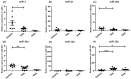
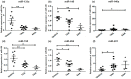
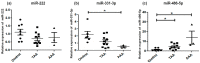
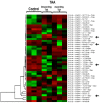
Altered microRNA expression is implicated in cardiovascular diseases. Our objective was to determine microRNA signatures in thoracic aortic aneurysms (TAAs) and abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAAs) compared with control non-aneurysmal aortic specimens. We evaluated the expression of fifteen selected microRNA in human TAA and AAA operative specimens compared to controls. We observed significant upregulation of miR-221 and downregulation of miR-1 and -133 in TAA specimens. In contrast, upregulation of miR-146a and downregulation of miR-145 and -331-3p were found only for AAA specimens. Upregulation of miR-126 and -486-5p and downregulation of miR-30c-2*, -155, and -204 were observed in specimens of TAAs and AAAs. The data reveal microRNA expression signatures unique to aneurysm location and common to both thoracic and abdominal pathologies. Thus, changes in miR-1, -29a, -133a, and -221 are involved in TAAs and miR-145, -146, and -331-3p impact AAAs. This work validates prior studies on microRNA expression in aneurysmal diseases.
Keywords: abdominal aortic aneurysm; microRNA; thoracic aortic aneurysm.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Shared Genetic Risk Factors of Intracranial, Abdominal, and Thoracic Aneurysms.J Am Heart Assoc. 2016 Jul 14;5(7):e002603. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.115.002603. J Am Heart Assoc. 2016. PMID: 27418160 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of microRNAs in vascular smooth muscle cells from patients with abdominal aortic aneurysms.J Vasc Surg. 2014 Jan;59(1):202-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2013.02.244. Epub 2013 Jun 5. J Vasc Surg. 2014. PMID: 23746831
-
Selective microRNA suppression in human thoracic aneurysms: relationship of miR-29a to aortic size and proteolytic induction.Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2011 Dec;4(6):605-13. doi: 10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.111.960419. Epub 2011 Oct 18. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2011. PMID: 22010139 Free PMC article.
-
Synchronous and Metachronous Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms in Patients With Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Am Heart Assoc. 2020 Nov 3;9(21):e017468. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.120.017468. Epub 2020 Oct 26. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020. PMID: 33103575 Free PMC article.
-
The genetic basis for aortic aneurysmal disease.Heart. 2014 Jun;100(12):916-22. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2013-305130. Heart. 2014. PMID: 24842835 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Novel microRNA Profiles Dysregulated in Plasma and Tissue of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Patients.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 28;21(13):4600. doi: 10.3390/ijms21134600. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32605321 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical-pathological correlations of BAV and the attendant thoracic aortopathies. Part 2: Pluridisciplinary perspective on their genetic and molecular origins.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2019 Aug;133:233-246. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2019.05.022. Epub 2019 Jun 6. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 31175858 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-331-3p Inhibits Inflammatory Response after Intracerebral Hemorrhage by Directly Targeting NLRP6.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Jun 7;2020:6182464. doi: 10.1155/2020/6182464. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32596340 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue-Specific miRNAs Regulate the Development of Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm: The Emerging Role of KLF4 Network.J Clin Med. 2019 Oct 3;8(10):1609. doi: 10.3390/jcm8101609. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31623405 Free PMC article.
-
Association of miRNA-145 Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms.In Vivo. 2022 May-Jun;36(3):1120-1125. doi: 10.21873/invivo.12810. In Vivo. 2022. PMID: 35478113 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

