High-resolution esophageal manometry: interpretation in clinical practice
- PMID: 28426462
- PMCID: PMC5568812
- DOI: 10.1097/MOG.0000000000000369
High-resolution esophageal manometry: interpretation in clinical practice
Abstract
Purpose of review: Esophageal high-resolution manometry (HRM) is the current state-of-the-art diagnostic tool to evaluate esophageal motility patterns and, as such, is widely adopted in clinical practice. This article will review the interpretation of esophageal HRM in clinical practice.
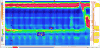
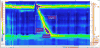
Recent findings: HRM uses a high-resolution catheter to transmit intraluminal pressure data that are subsequently converted into dynamic esophageal pressure topography (EPT) plots. Metric data from EPT plots are synthesized to yield an esophageal motility diagnosis according to the Chicago Classification, a formal analytic scheme for esophageal motility disorders, which is currently in version 3.0. The standard HRM protocol consists of a baseline phase and a series of 10 wet swallows in the supine or reclined position. In addition, data from swallows in the seated position and provocative HRM maneuvers provide useful information about motility properties. Combined high-resolution impedance technology is also clinically available and enables concurrent assessment of bolus transit and postprandial responses. Finally, there is ongoing interest to optimize the training and competency assessment for interpretation of HRM in clinical practice.
Summary: Esophageal HRM is a valuable and sophisticated clinical tool to evaluate esophageal motility patterns. Emerging clinical applications of esophageal HRM include combined impedance technology, provocative maneuvers, and postprandial evaluation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Utility of Esophageal High-Resolution Manometry in Clinical Practice: First, Do HRM.Dig Dis Sci. 2018 Dec;63(12):3178-3186. doi: 10.1007/s10620-018-5300-4. Dig Dis Sci. 2018. PMID: 30276571 Review.
-
Inter-observer agreement for diagnostic classification of esophageal motility disorders defined in high-resolution manometry.Dis Esophagus. 2015 Nov-Dec;28(8):711-9. doi: 10.1111/dote.12278. Epub 2014 Sep 3. Dis Esophagus. 2015. PMID: 25185507 Clinical Trial.
-
The Clinical Utility of Provocative Maneuvers at Esophageal High-resolution Manometry (HRM).J Clin Gastroenterol. 2021 Feb 1;55(2):95-102. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000001466. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 33252559
-
Evaluation of esophageal motor function in clinical practice.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2013 Feb;25(2):99-133. doi: 10.1111/nmo.12071. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2013. PMID: 23336590 Review.
-
Clinical usefulness of esophageal high resolution manometry and adjunctive tests: An update.Dig Liver Dis. 2021 Nov;53(11):1373-1380. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2021.04.007. Epub 2021 May 11. Dig Liver Dis. 2021. PMID: 33994122 Review.
Cited by
-
Spectrum and Clinical Outcome of Motility Disorders on High-Resolution Esophageal Manometry: A Study From a Tertiary Center on Patients With Dysphagia in Pakistan.Cureus. 2020 Dec 14;12(12):e12088. doi: 10.7759/cureus.12088. Cureus. 2020. PMID: 33489506 Free PMC article.
-
Esophageal function and non-acid reflux evaluated by impedance-24 h-pH-metry, high-resolution manometry, and gastroscopy after one-anastomosis gastric bypass-outcomes of a prospective mid-term study.Surg Endosc. 2023 May;37(5):3832-3841. doi: 10.1007/s00464-022-09857-9. Epub 2023 Jan 24. Surg Endosc. 2023. PMID: 36693919 Free PMC article.
-
Utility of Esophageal High-Resolution Manometry in Clinical Practice: First, Do HRM.Dig Dis Sci. 2018 Dec;63(12):3178-3186. doi: 10.1007/s10620-018-5300-4. Dig Dis Sci. 2018. PMID: 30276571 Review.
-
Elevated average maximum intrabolus pressure on high-resolution manometry is associated with esophageal dysmotility and delayed esophageal emptying on timed barium esophagram.BMC Gastroenterol. 2022 Feb 21;22(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s12876-022-02165-5. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 35189822 Free PMC article.
-
Esophageal Dysphagia in the Elderly.Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol. 2019 Dec;17(4):534-553. doi: 10.1007/s11938-019-00264-z. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31741211 Review.
References
-
- Gyawali CP, Patel A. Esophageal motor function: technical aspects of manometry. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2014;24:527–43. - PubMed
-
- Gyawali CP, Bredenoord AJ, Conklin JL, et al. Evaluation of esophageal motor function in clinical practice. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2013;25:99–133. - PubMed
-
- Clouse RE, Prakash C. Topographic esophageal manometry: an emerging clinical and investigative approach. Dig Dis. 2000;18:64–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

