Pharmacokinetics and relative bioavailability of an oral amoxicillin-apramycin combination in pigs
- PMID: 28426744
- PMCID: PMC5398684
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176149
Pharmacokinetics and relative bioavailability of an oral amoxicillin-apramycin combination in pigs
Abstract
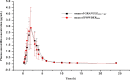
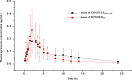
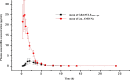
A new compound granular premix of amoxicillin (20% w/w dry mass)/apramycin (5% w/w dry mass) was developed, and its pharmacokinetics and relative bioavailability were determined in pigs following oral administration following a cross-over study design. The pharmacokinetic parameters of amoxicillin (t1/2λ = 6.43 ± 4.85h, Cmax = 3.2 ± 1.35 μg·mL-1, Tmax = 1.92 ± 0.58, AUCINF = 8.98 ± 2.11 h·μg·mL-1) and apramycin (t1/2λ = 8.67±4.4h, Cmax = 0.23 ± 0.12 μg·mL-1, Tmax = 2.25 ± 0.82 h, AUCINF = 12.37 ± 8.64h·μg·mL-1) when administered as the amoxicillin-apramycin granular premix did not significantly differ from those for the single-ingredient powder form of each component. The relative bioavailability of amoxicillin following oral administration of the amoxicillin-apramycin granular premix was 22.62% when compared to the intramuscular administration of commercial amoxicillin sodium-powder. This is the first report of a new amoxicillin-apramycin combination which has a potential veterinary application the for prevention and treatment digestive tract infections in pigs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Development of an amoxicillin-radix scutellaria extract formulation and evaluation of its pharmacokinetics in pigs.BMC Vet Res. 2023 Sep 19;19(1):164. doi: 10.1186/s12917-023-03713-1. BMC Vet Res. 2023. PMID: 37726783 Free PMC article.
-
Relative oral bioavailability of microgranulated amoxicillin in pigs.J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2002 Oct;25(5):329-34. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2885.2002.00428.x. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2002. PMID: 12423222
-
Pharmacokinetics of amoxicillin trihydrate in cultured olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus).J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Feb;38(1):86-92. doi: 10.1111/jvp.12155. Epub 2014 Sep 17. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2015. PMID: 25229401 Clinical Trial.
-
Influence of a pig respiratory disease on the pharmacokinetic behaviour of amoxicillin after oral ad libitum administration in medicated feed.J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2011 Jun;34(3):265-76. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2885.2010.01220.x. Epub 2010 Aug 24. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2011. PMID: 21492192
-
Kinetic disposition, systemic bioavailability and tissue distribution of apramycin in broiler chickens.Res Vet Sci. 1997 May-Jun;62(3):249-52. doi: 10.1016/s0034-5288(97)90199-5. Res Vet Sci. 1997. PMID: 9300543
Cited by
-
Qualitative risk assessment of homogeneity, stability, and residual concentrations of antimicrobials in medicated feed and drinking water in pig rearing.BMC Vet Res. 2023 Jan 13;19(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s12917-022-03555-3. BMC Vet Res. 2023. PMID: 36639815 Free PMC article.
-
Development of an amoxicillin-radix scutellaria extract formulation and evaluation of its pharmacokinetics in pigs.BMC Vet Res. 2023 Sep 19;19(1):164. doi: 10.1186/s12917-023-03713-1. BMC Vet Res. 2023. PMID: 37726783 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Breakpoint of Apramycin to Swine Salmonella and Its Effect on Ileum Flora.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 26;23(3):1424. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031424. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163350 Free PMC article.
-
Maximum levels of cross-contamination for 24 antimicrobial active substances in non-target feed. Part 2: Aminoglycosides/aminocyclitols: apramycin, paromomycin, neomycin and spectinomycin.EFSA J. 2021 Oct 26;19(10):e06853. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2021.6853. eCollection 2021 Oct. EFSA J. 2021. PMID: 34729082 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Streptococcus suis Isolated from Diseased Pigs in Thailand, 2018-2020.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Mar 18;11(3):410. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11030410. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35326873 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Soliman AM, Abu-Basha EA, Youssef SA, Amer AM, Murphy PA, Hauck CC, et al. Effect of chronic lead intoxication on the distribution and elimination of amoxicillin in goats. Journal of veterinary science. 2013;14(4):395–403. PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3885732. doi: 10.4142/jvs.2013.14.4.395 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Papich MG. Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic values for amoxicillin in pigs. American journal of veterinary research. 2014;75(4):316 doi: 10.2460/ajvr.75.4.316 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Darras-Joly C, Bedos JP, Sauve C, Moine P, Vallee E, Carbon C, et al. Synergy between amoxicillin and gentamicin in combination against a highly penicillin-resistant and -tolerant strain of Streptococcus pneumoniae in a mouse pneumonia model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1996;40(9):2147–51. PubMed Central PMCID: PMC163489. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Opriessnig T, Halbur PG. Concurrent infections are important for expression of porcine circovirus associated disease. Virus research. 2012;164(1–2):20–32. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2011.09.014 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

