Pharmacokinetics and relative bioavailability of an oral amoxicillin-apramycin combination in pigs
- PMID: 28426744
- PMCID: PMC5398684
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176149
Pharmacokinetics and relative bioavailability of an oral amoxicillin-apramycin combination in pigs
Abstract
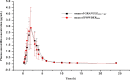
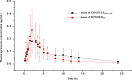
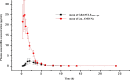
A new compound granular premix of amoxicillin (20% w/w dry mass)/apramycin (5% w/w dry mass) was developed, and its pharmacokinetics and relative bioavailability were determined in pigs following oral administration following a cross-over study design. The pharmacokinetic parameters of amoxicillin (t1/2λ = 6.43 ± 4.85h, Cmax = 3.2 ± 1.35 μg·mL-1, Tmax = 1.92 ± 0.58, AUCINF = 8.98 ± 2.11 h·μg·mL-1) and apramycin (t1/2λ = 8.67±4.4h, Cmax = 0.23 ± 0.12 μg·mL-1, Tmax = 2.25 ± 0.82 h, AUCINF = 12.37 ± 8.64h·μg·mL-1) when administered as the amoxicillin-apramycin granular premix did not significantly differ from those for the single-ingredient powder form of each component. The relative bioavailability of amoxicillin following oral administration of the amoxicillin-apramycin granular premix was 22.62% when compared to the intramuscular administration of commercial amoxicillin sodium-powder. This is the first report of a new amoxicillin-apramycin combination which has a potential veterinary application the for prevention and treatment digestive tract infections in pigs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Soliman AM, Abu-Basha EA, Youssef SA, Amer AM, Murphy PA, Hauck CC, et al. Effect of chronic lead intoxication on the distribution and elimination of amoxicillin in goats. Journal of veterinary science. 2013;14(4):395–403. PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3885732. doi: 10.4142/jvs.2013.14.4.395 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Papich MG. Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic values for amoxicillin in pigs. American journal of veterinary research. 2014;75(4):316 doi: 10.2460/ajvr.75.4.316 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Darras-Joly C, Bedos JP, Sauve C, Moine P, Vallee E, Carbon C, et al. Synergy between amoxicillin and gentamicin in combination against a highly penicillin-resistant and -tolerant strain of Streptococcus pneumoniae in a mouse pneumonia model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1996;40(9):2147–51. PubMed Central PMCID: PMC163489. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Opriessnig T, Halbur PG. Concurrent infections are important for expression of porcine circovirus associated disease. Virus research. 2012;164(1–2):20–32. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2011.09.014 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

