Ex vivo cultures combined with vivo-morpholino induced gene knockdown provide a system to assess the role of WT1 and GATA4 during gonad differentiation
- PMID: 28426816
- PMCID: PMC5398674
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176296
Ex vivo cultures combined with vivo-morpholino induced gene knockdown provide a system to assess the role of WT1 and GATA4 during gonad differentiation
Abstract
Gonad morphogenesis relies on the correct spatiotemporal expression of a number of genes that together fulfill the differentiation of the bipotential gonad into testes or ovaries. As such, the transcription factors WT1 and GATA4 are pivotal for proper gonadal development. Here we address the contributions of GATA4 and WT1 to the sex differentiation phase in testes and ovaries. We applied an ex vivo technique for cultivating gonads in hanging droplets of media that were supplemented with vivo-morpholinos to knockdown WT1 and GATA4 either alone or in combination at the same developmental stage. We show that WT1 is equally important for both, the initial establishment and the maintenance of the sex-specific gene expression signature in testes and ovaries. We further identified Foxl2 as a novel putative downstream target gene of WT1. Moreover, knockdown of WT1 reduced mRNA levels of several molecular components of the hedgehog signaling pathway in XY gonads, whereas Gata4 vivo-morpholino treatment increased transcripts of Dhh and Ptch1 in embryonic testes. The data suggest that for its proper function, WT1 relies on the correct expression of the GATA4 protein. Furthermore, GATA4 down-regulates several ovarian promoting genes in testes, such as Ctnnb1, Fst, and Bmp2, suggesting that this repression is required for maintaining the male phenotype. In conclusion, this study provides novel insights into the role of WT1 and GATA4 during the sex differentiation phase and represents an approach that can be applied to assess other proteins with as yet unknown functions during gonadal development.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

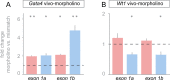

Similar articles
-
Wilms tumor protein-dependent transcription of VEGF receptor 2 and hypoxia regulate expression of the testis-promoting gene Sox9 in murine embryonic gonads.J Biol Chem. 2017 Dec 8;292(49):20281-20291. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.816751. Epub 2017 Oct 17. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 29042436 Free PMC article.
-
WT1-mediated gene regulation in early urogenital ridge development.Sex Dev. 2007;1(4):238-54. doi: 10.1159/000104774. Sex Dev. 2007. PMID: 18391535
-
Correct dosage of Fog2 and Gata4 transcription factors is critical for fetal testis development in mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Sep 18;104(38):14994-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0701677104. Epub 2007 Sep 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17848526 Free PMC article.
-
Genes promoting and disturbing testis development.Histol Histopathol. 2012 Nov;27(11):1361-83. doi: 10.14670/HH-27.1361. Histol Histopathol. 2012. PMID: 23018237 Review.
-
Control of sex development.Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010 Apr;24(2):163-86. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2009.12.002. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010. PMID: 20541146 Review.
Cited by
-
GATA4/6 regulate DHH transcription in rat adrenocortical autografts.Sci Rep. 2020 Jan 16;10(1):446. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-57351-5. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 31949236 Free PMC article.
-
Whole exome sequencing identified a rare WT1 loss-of-function variant in a non-syndromic POI patient.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2022 Jan;10(1):e1820. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.1820. Epub 2021 Nov 29. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2022. PMID: 34845858 Free PMC article.
-
Disorders of sex development.Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2018 Apr;48:90-102. doi: 10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2017.11.005. Epub 2017 Nov 22. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2018. PMID: 29503125 Free PMC article. Review.
-
46,XX DSD: Developmental, Clinical and Genetic Aspects.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Jul 30;11(8):1379. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11081379. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34441313 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Probing GATA factor function in mouse Leydig cells via testicular injection of adenoviral vectors.Reproduction. 2017 Oct;154(4):455-467. doi: 10.1530/REP-17-0311. Epub 2017 Jul 14. Reproduction. 2017. PMID: 28710293 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bunce C, Capel B. Cycling in the Cell Fate Landscape. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2016;116: 153–165. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2015.10.001 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Munger SC, Capel B. Sex and the circuitry: Progress toward a systems-level understanding of vertebrate sex determination. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2012;4: 401–412. doi: 10.1002/wsbm.1172 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kreidberg JA, Sariola H, Loring JM, Maeda M, Pelletier J, Housman D, et al. WT-1 is required for early kidney development. Cell. 1993;74: 679–691. - PubMed
-
- Molkentin JD, Lin Q, Duncan SA, Olson EN. Requirement of the transcription factor GATA4 for heart tube formation and ventral morphogenesis. Genes Dev. 1997;11: 1061–1072. - PubMed
-
- Watt AJ, Battle MA, Li J, Duncan SA. GATA4 is essential for formation of the proepicardium and regulates cardiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101: 12573–8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0400752101 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

