Joint genetic analysis using variant sets reveals polygenic gene-context interactions
- PMID: 28426829
- PMCID: PMC5398484
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006693
Joint genetic analysis using variant sets reveals polygenic gene-context interactions
Abstract
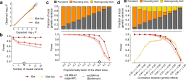
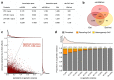
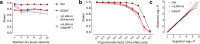
Joint genetic models for multiple traits have helped to enhance association analyses. Most existing multi-trait models have been designed to increase power for detecting associations, whereas the analysis of interactions has received considerably less attention. Here, we propose iSet, a method based on linear mixed models to test for interactions between sets of variants and environmental states or other contexts. Our model generalizes previous interaction tests and in particular provides a test for local differences in the genetic architecture between contexts. We first use simulations to validate iSet before applying the model to the analysis of genotype-environment interactions in an eQTL study. Our model retrieves a larger number of interactions than alternative methods and reveals that up to 20% of cases show context-specific configurations of causal variants. Finally, we apply iSet to test for sub-group specific genetic effects in human lipid levels in a large human cohort, where we identify a gene-sex interaction for C-reactive protein that is missed by alternative methods.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Analytical strategies to include the X-chromosome in variance heterogeneity analyses: Evidence for trait-specific polygenic variance structure.Genet Epidemiol. 2019 Oct;43(7):815-830. doi: 10.1002/gepi.22247. Epub 2019 Jul 22. Genet Epidemiol. 2019. PMID: 31332826
-
Underestimation of heritability using a mixed model with a polygenic covariance structure in a genome-wide association study for complex traits.Eur J Hum Genet. 2014 Jun;22(6):851-4. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2013.236. Epub 2013 Oct 23. Eur J Hum Genet. 2014. PMID: 24149545 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient Prioritization of Multiple Causal eQTL Variants via Sparse Polygenic Modeling.Genetics. 2017 Dec;207(4):1301-1312. doi: 10.1534/genetics.117.300435. Epub 2017 Oct 26. Genetics. 2017. PMID: 29074555 Free PMC article.
-
Complex-Trait Prediction in the Era of Big Data.Trends Genet. 2018 Oct;34(10):746-754. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2018.07.004. Epub 2018 Aug 20. Trends Genet. 2018. PMID: 30139641 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Detecting epistatic interactions contributing to quantitative traits.Genet Epidemiol. 2004 Sep;27(2):141-52. doi: 10.1002/gepi.20006. Genet Epidemiol. 2004. PMID: 15305330 Review.
Cited by
-
Joint Analysis of Multiple Interaction Parameters in Genetic Association Studies.Genetics. 2019 Feb;211(2):483-494. doi: 10.1534/genetics.118.301394. Epub 2018 Dec 21. Genetics. 2019. PMID: 30578273 Free PMC article.
-
sn-spMF: matrix factorization informs tissue-specific genetic regulation of gene expression.Genome Biol. 2020 Sep 11;21(1):235. doi: 10.1186/s13059-020-02129-6. Genome Biol. 2020. PMID: 32912314 Free PMC article.
-
eQTL discovery and their association with severe equine asthma in European Warmblood horses.BMC Genomics. 2018 Aug 2;19(1):581. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-4938-9. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 30071827 Free PMC article.
-
Genotype × environment interactions in gene regulation and complex traits.Nat Genet. 2024 Jun;56(6):1057-1068. doi: 10.1038/s41588-024-01776-w. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Nat Genet. 2024. PMID: 38858456 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modeling Cell-Cell Interactions from Spatial Molecular Data with Spatial Variance Component Analysis.Cell Rep. 2019 Oct 1;29(1):202-211.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.08.077. Cell Rep. 2019. PMID: 31577949 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kang HM, Sul JH, Service SK, Zaitlen NA, Kong SY, Freimer NB, et al. Variance component model to account for sample structure in genome-wide association studies. Nature genetics. 2010;42(4):348–54. PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3092069. doi: 10.1038/ng.548 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yang J, Zaitlen NA, Goddard ME, Visscher PM, Price AL. Advantages and pitfalls in the application of mixed-model association methods. Nature genetics. 2014;46(2):100–6. PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3989144. doi: 10.1038/ng.2876 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fusi N, Stegle O, Lawrence ND. Joint modelling of confounding factors and prominent genetic regulators provides increased accuracy in genetical genomics studies. PLoS computational biology. 2012;8(1):e1002330 PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3252274. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002330 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Listgarten J, Kadie C, Schadt EE, Heckerman D. Correction for hidden confounders in the genetic analysis of gene expression. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2010;107(38):16465–70. PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2944732. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1002425107 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

