Metaplasticity as a Neural Substrate for Adaptive Learning and Choice under Uncertainty
- PMID: 28426971
- PMCID: PMC5515734
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2017.03.044
Metaplasticity as a Neural Substrate for Adaptive Learning and Choice under Uncertainty
Abstract
Value-based decision making often involves integration of reward outcomes over time, but this becomes considerably more challenging if reward assignments on alternative options are probabilistic and non-stationary. Despite the existence of various models for optimally integrating reward under uncertainty, the underlying neural mechanisms are still unknown. Here we propose that reward-dependent metaplasticity (RDMP) can provide a plausible mechanism for both integration of reward under uncertainty and estimation of uncertainty itself. We show that a model based on RDMP can robustly perform the probabilistic reversal learning task via dynamic adjustment of learning based on reward feedback, while changes in its activity signal unexpected uncertainty. The model predicts time-dependent and choice-specific learning rates that strongly depend on reward history. Key predictions from this model were confirmed with behavioral data from non-human primates. Overall, our results suggest that metaplasticity can provide a neural substrate for adaptive learning and choice under uncertainty.
Keywords: decision making; learning rate; metaplasticity; reward; sub-optimality; uncertainty; volatility.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

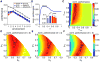
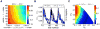
References
-
- Abraham WC. Metaplasticity: tuning synapses and networks for plasticity. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2008;9:387–399. - PubMed
-
- Abraham WC, Bear MF. Metaplasticity: the plasticity of synaptic plasticity. Trends Neurosci. 1996;19:126–130. - PubMed
-
- Aston-Jones G, Cohen JD. An integrative theory of locus coeruleusnorepinephrine function: adaptive gain and optimal performance. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2005;28:403–450. - PubMed
-
- Behrens TEJ, Woolrich MW, Walton ME, Rushworth MFS. Learning the value of information in an uncertain world. Nat Neurosci. 2007;10:1214–1221. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

