Metformin inhibits ALK1-mediated angiogenesis via activation of AMPK
- PMID: 28427181
- PMCID: PMC5464828
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.15825
Metformin inhibits ALK1-mediated angiogenesis via activation of AMPK
Abstract
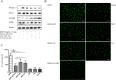
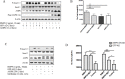
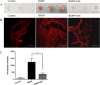
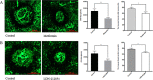
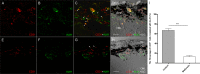
Anti-VEGF therapy has been proven to be effective in the treatment of pathological angiogenesis. However, therapy resistance often occurs, leading to development of alternative approaches. The present study examines if AMPK negatively regulates ALK1-mediated signaling events and associated angiogenesis. Thus, we treated human umbilical vein endothelial cells with metformin as well as other pharmacological AMPK activators and showed that activation of AMPK inhibited Smad1/5 phosphorylation and tube formation induced by BMP9. This event was mimicked by expression of the active mutant of AMPKα1 and prevented by the dominant negative AMPKα1. Metformin inhibition of BMP9 signaling is possibly mediated by upregulation of Smurf1, leading to degradation of ALK1. Furthermore, metformin suppressed BMP9-induced angiogenesis in mouse matrigel plug. In addition, laser photocoagulation was employed to evaluate the effect of metformin. The data revealed that metformin significantly reduced choroidal neovascularization to a level comparable to LDN212854, an ALK1 specific inhibitor. In conjunction, metformin diminished expression of ALK1 in endothelium of the lesion area. Collectively, our study for the first time demonstrates that AMPK inhibits ALK1 and associated angiogenesis/neovascularization. This may offer us a new avenue for the treatment of related diseases using clinically used pharmacological AMPK activators like metformin in combination with other strategies to enhance the treatment efficacy or in the case of anti-VEGF resistance.
Keywords: ALK1; AMPK; tumor angiogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Targeting activin receptor-like kinase 1 inhibits angiogenesis and tumorigenesis through a mechanism of action complementary to anti-VEGF therapies.Cancer Res. 2011 Feb 15;71(4):1362-73. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-1451. Epub 2011 Jan 6. Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21212415 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated circulating BMP9 aggravates pulmonary angiogenesis in hepatopulmonary syndrome rats through ALK1-Endoglin-Smad1/5/9 signalling.Eur J Clin Invest. 2024 Aug;54(8):e14212. doi: 10.1111/eci.14212. Epub 2024 Apr 9. Eur J Clin Invest. 2024. PMID: 38591651
-
Identification of BMP9 and BMP10 as functional activators of the orphan activin receptor-like kinase 1 (ALK1) in endothelial cells.Blood. 2007 Mar 1;109(5):1953-61. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-07-034124. Epub 2006 Oct 26. Blood. 2007. PMID: 17068149
-
Activin receptor-like kinase 1 as a target for anti-angiogenesis therapy.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2013 Nov;22(11):1371-83. doi: 10.1517/13543784.2013.837884. Epub 2013 Sep 21. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2013. PMID: 24053899 Review.
-
ALK1-Smad1/5 signaling pathway in fibrosis development: friend or foe?Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013 Dec;24(6):523-37. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2013.08.002. Epub 2013 Sep 13. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013. PMID: 24055043 Review.
Cited by
-
In vivo photoacoustic imaging for monitoring treatment outcome of corneal neovascularization with metformin eye drops.Biomed Opt Express. 2021 May 21;12(6):3597-3606. doi: 10.1364/BOE.423982. eCollection 2021 Jun 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2021. PMID: 34221681 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Protective Effects of Traditional Antidiabetic Medications and Novel Antihyperglycemic Agents in Diabetic Rodent Models.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 May 1;18(5):670. doi: 10.3390/ph18050670. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40430489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maturation and Protection Effect of Retinal Tissue-Derived Bioink for 3D Cell Printing Technology.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Jun 23;13(7):934. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13070934. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34201702 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin inhibits pathological retinal neovascularization but promotes retinal fibrosis in experimental neovascular age-related macular degeneration.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 20;16:1547492. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1547492. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40183100 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin suppresses proliferation and differentiation induced by BMP9 via AMPK signaling in human fetal lung fibroblast-1.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 24;13:984730. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.984730. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36091775 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jin Y, Kaluza D, Jakobsson L. VEGF, Notch and TGFbeta/BMPs in regulation of sprouting angiogenesis and vascular patterning. Biochemical Society transactions. 2014;42:1576–1583. - PubMed
-
- de Vinuesa AG, Bocci M, Pietras K, Ten Dijke P. Targeting tumour vasculature by inhibiting activin receptor-like kinase (ALK)1 function. Biochemical Society transactions. 2016;44:1142–1149. - PubMed
-
- Li W, Salmon RM, Jiang H, Morrell NW. Regulation of the ALK1 ligands, BMP9 and BMP10. Biochemical Society transactions. 2016;44:1135–1141. - PubMed
-
- Roelen BA, van Rooijen MA, Mummery CL. Expression of ALK-1, a type 1 serine/threonine kinase receptor, coincides with sites of vasculogenesis and angiogenesis in early mouse development. Dev Dyn. 1997;209:418–430. - PubMed
-
- Wu X, Robinson CE, Fong HW, Crabtree JS, Rodriguez BR, Roe BA, Gimble JM. Cloning and characterization of the murine activin receptor like kinase-1 (ALK-1) homolog. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995;216:78–83. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

