Conditioned taste avoidance, conditioned place preference and hyperthermia induced by the second generation 'bath salt' α-pyrrolidinopentiophenone (α-PVP)
- PMID: 28427995
- PMCID: PMC6155479
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pbb.2017.04.003
Conditioned taste avoidance, conditioned place preference and hyperthermia induced by the second generation 'bath salt' α-pyrrolidinopentiophenone (α-PVP)
Abstract
Background: α-Pyrrolidinopentiophenone (α-PVP) has been reported to be rewarding in a variety of pre-clinical models. Given that a number of drugs of abuse have both rewarding and aversive effects, the balance of which influences addiction potential, the present study examined the aversive properties of α-PVP by assessing its ability to induce taste avoidance. This assessment was made in a combined taste avoidance/place conditioning design that also allowed an evaluation of the relationship between α-PVP's aversive and rewarding effects.
Methods: Male Sprague-Dawley rats were exposed to a novel saccharin solution, injected with one of four doses of α-PVP (0, 0.3, 1.0 and 3.0mg/kg) (IP) and placed on one side of a place conditioning apparatus. The next day, they were injected with vehicle, given access to water and placed on the other side. Following four conditioning cycles, saccharin avoidance and place preferences were then assessed. The effects of α-PVP on body temperature were also examined.
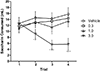
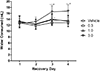
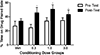
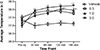
Results: α-PVP induced dose-dependent taste avoidance as well as significant increases in time spent on the drug-paired side (although this effect was not dependent on dose). α-PVP also induced dose- and time-dependent hyperthermia.
Conclusions: α-PVP induced significant taste avoidance whose strength relative to the psychostimulants methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV) and cocaine paralleled their relative binding to the dopamine transporter. Similar to other drugs of abuse, α-PVP has both aversive and rewarding effects. It will be important to assess how various experiential and subject variables impact these effects and their balance to predict abuse liability.
Keywords: Bath salts; Conditioned place preference; Conditioned taste avoidance; Hyperthermia; α-PVP.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Stereoselective effects of the second-generation synthetic cathinone α-pyrrolidinopentiophenone (α-PVP): assessments of conditioned taste avoidance in rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019 Mar;236(3):1067-1077. doi: 10.1007/s00213-018-5070-x. Epub 2018 Oct 17. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019. PMID: 30334086 Free PMC article.
-
Sex differences in α-pyrrolidinopentiophenone (α-PVP)-induced taste avoidance, place preference, hyperthermia and locomotor activity in rats.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2019 Oct;185:172762. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2019.172762. Epub 2019 Aug 21. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2019. PMID: 31445057 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanol pre-exposure differentially impacts the rewarding and aversive effects of α-pyrrolidinopentiophenone (α-PVP): Implications for drug use and abuse.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2021 Dec;211:173286. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2021.173286. Epub 2021 Oct 8. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2021. PMID: 34634300 Free PMC article.
-
Conditioned taste avoidance and conditioned place preference induced by the third-generation synthetic cathinone eutylone in female sprague-dawley rats.Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2023 Dec;31(6):1069-1079. doi: 10.1037/pha0000657. Epub 2023 May 25. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37227884
-
Neurobiology of 3,4-methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV) and α-pyrrolidinovalerophenone (α-PVP).Brain Res Bull. 2016 Sep;126(Pt 1):111-126. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2016.04.011. Epub 2016 Apr 29. Brain Res Bull. 2016. PMID: 27142261 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Serial Polydrug Use on the Rewarding and Aversive Effects of the Novel Synthetic Cathinone Eutylone.Brain Sci. 2023 Sep 7;13(9):1294. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13091294. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 37759895 Free PMC article.
-
Stereoselective neurochemical, behavioral, and cardiovascular effects of α-pyrrolidinovalerophenone enantiomers in male rats.Addict Biol. 2020 Nov;25(6):e12842. doi: 10.1111/adb.12842. Epub 2019 Nov 13. Addict Biol. 2020. PMID: 31724254 Free PMC article.
-
Stereoselective effects of the second-generation synthetic cathinone α-pyrrolidinopentiophenone (α-PVP): assessments of conditioned taste avoidance in rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019 Mar;236(3):1067-1077. doi: 10.1007/s00213-018-5070-x. Epub 2018 Oct 17. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019. PMID: 30334086 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of the Aversive Effects of Drugs on Their Use and Abuse.Behav Neurol. 2022 Apr 20;2022:8634176. doi: 10.1155/2022/8634176. eCollection 2022. Behav Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35496768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Abuse potential and toxicity of the synthetic cathinones (i.e., "Bath salts").Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2020 Mar;110:150-173. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2018.07.015. Epub 2019 May 14. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2020. PMID: 31101438 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baumann MH, Partilla JS, Lehner KR, Thorndike EB, Hoffman AF, Holy M, Rothman RB, Goldberg SR, Lupica CR, Sitte HH, Brandt SD, Tella SR, Cozzi NV, Schindler CW. Powerful cocaine-like actions of 3,4-methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV), a principal constituent of psychoactive ‘bath salts’ products. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013;38:552–562. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berman RF, Cannon DS. The effect of prior ethanol experience on ethanol-induced saccharin aversions. Physiol Behav. 1974;12:1041–1044. - PubMed
-
- Brockwell NT, Eikelboom R, Beninger RJ. Caffeine-induced place and taste conditioning: production of dose-dependent preference and aversion. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1991;38:513–517. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

