Whither Radioimmunotherapy: To Be or Not To Be?
- PMID: 28428282
- PMCID: PMC5413412
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-2523
Whither Radioimmunotherapy: To Be or Not To Be?
Abstract
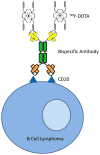
Therapy of cancer with radiolabeled monoclonal antibodies has produced impressive results in preclinical experiments and in clinical trials conducted in radiosensitive malignancies, particularly B-cell lymphomas. Two "first-generation," directly radiolabeled anti-CD20 antibodies, 131iodine-tositumomab and 90yttrium-ibritumomab tiuxetan, were FDA-approved more than a decade ago but have been little utilized because of a variety of medical, financial, and logistic obstacles. Newer technologies employing multistep "pretargeting" methods, particularly those utilizing bispecific antibodies, have greatly enhanced the therapeutic efficacy of radioimmunotherapy and diminished its toxicities. The dramatically improved therapeutic index of bispecific antibody pretargeting appears to be sufficiently compelling to justify human clinical trials and reinvigorate enthusiasm for radioimmunotherapy in the treatment of malignancies, particularly lymphomas. Cancer Res; 77(9); 2191-6. ©2017 AACR.
©2017 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure of COI: The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Scott AM, Wolchok JD, Old LJ. Antibody therapy of cancer. Nature reviews Cancer. 2012;12:278–87. - PubMed
-
- Lokhorst HM, Plesner T, Laubach JP, Nahi H, Gimsing P, Hansson M, et al. Targeting CD38 with Daratumumab Monotherapy in Multiple Myeloma. N Engl J Med. 2015 - PubMed
-
- Lonial S, Dimopoulos M, Palumbo A, White D, Grosicki S, Spicka I, et al. Elotuzumab Therapy for Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:621–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

