Triglyceride Rich Lipoprotein -LPL-VLDL Receptor and Lp(a)-VLDL Receptor Pathways for Macrophage Foam Cell Formation
- PMID: 28428482
- PMCID: PMC5453679
- DOI: 10.5551/jat.RV17004
Triglyceride Rich Lipoprotein -LPL-VLDL Receptor and Lp(a)-VLDL Receptor Pathways for Macrophage Foam Cell Formation
Abstract
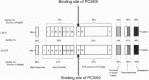
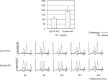
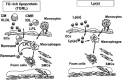
Very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) receptor is a member of the low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor family. It binds triglyceride rich lipoprotein (TGRL) but not LDL, because it recognizes apolipoprotein (apo)E only but not apoB. The VLDL receptor functions as a peripheral lipoprotein receptor in concert with lipoprotein lipase (LPL) in heart, muscle, adipose tissue and macrophages. In contrast to the LDL receptor, VLDL receptor binds apo E2/2 VLDL and apoE3/3 VLDL particles, and its expression is not down-regulated by intracellular lipoproteins. It has been reported that both LDL-cholesterol (LDL-C) and postprandial triglyceride (chyromicron and VLDL remnants) are risk factors for human atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD). True ligands such as lipoprotein particles of the VLDL receptor are chyromicron remnant (CMR) and VLDL remnant (postprandial hyperlipidemia). Although the oxidized LDL (oxLDL)-scavenger receptors pathway is considered to be the main mechanism for macrophage foam cell formation, it seems that the TGRL-LPL-VLDL receptor pathway is also involved. Since Lp(a) is one of the ligands for the VLDL receptor, the Lp(a)-VLDL receptor pathway is another potential alternative. The expression of VLDL receptor protein in mouse macrophages is modest compared to that in rabbit and human macrophages, both in vitro and in vivo. Therefore, we need to elucidate the mechanism of human ASCVD not by using the mouse model and scavenger receptors pathway but instead using the rabbit model and VLDL receptor pathway, respectively.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Lipoprotein lipase; Lp(a); Macrophage foam cell formation; VLDL receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ross R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis: a perspective for the 1990s. Nature, 1993; 362: 801-809 - PubMed
-
- Manning-Tobin JJ, Moore KJ, Seimon TA, Bell SA, Sharuk M, Alvarez-Leite JI, de Winther MP, Tabas I, Freeman MW. Loss of SR-A and CD36 activity reduces atherosclerotic lesion complexity without abrogating foam cell formation in hyperlipidemic mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2009; 29: 19-26 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

