Comparative Study of Two ELISA Kits for Estimation of Antibodies to Hepatitis B Virus in Human Normal Immunoglobulin and Specific Immunoglobulin Intended for Intravenous or Intramuscular Use
- PMID: 28428703
- PMCID: PMC5382075
- DOI: 10.1007/s12291-016-0590-9
Comparative Study of Two ELISA Kits for Estimation of Antibodies to Hepatitis B Virus in Human Normal Immunoglobulin and Specific Immunoglobulin Intended for Intravenous or Intramuscular Use
Abstract
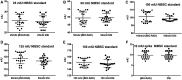
Current study is conducted to evaluate method verification of two locally available kits manufactured by DSI & BIORAD for quantitative estimation of Hepatitis B virus antibodies in human normal immunoglobulin by using International standard of National Institute of Biological Standards and Control. Four analyst perform five sets of test in duplicate analysing accuracy, precision, and limit of detection, sensitivity and specificity. Our results suggest that both DSI and BIORAD kits fulfil the validation criteria and are sensitive to detect up to 10 mIU concentration precisely and accurately. DSI kit is more precise at concentration 100 mIU and economically 4-5 times cheaper in local market; on the other hand, BIORAD kits provide larger detection range up to 1000 mIU.
Keywords: Accuracy; Hepatitis B virus; Immunoglobulin; Limit of detection; Precision; Sensitivity; Specificity.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal participants performed by any of the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Sensitivity and specificity of 4 domestic ELISA kits for detection of hepatitis B virus markers].Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2008 Sep;29(9):915-8. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2008. PMID: 19173858 Chinese.
-
[Diagnostic kits in parasitology: which controls?].Parassitologia. 2004 Jun;46(1-2):145-9. Parassitologia. 2004. PMID: 15305705 Review. Italian.
-
Time course of hepatitis A antibody production after active, passive and active/passive immunisation: the results are highly dependent on the antibody test system used.J Virol Methods. 1993 Aug;43(3):287-97. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(93)90147-j. J Virol Methods. 1993. PMID: 8408443
-
Assessment of assay sensitivity and precision in a malaria antibody ELISA.J Immunoassay Immunochem. 2003;24(1):89-112. doi: 10.1081/IAS-120018471. J Immunoassay Immunochem. 2003. PMID: 12680609
-
[Development of sera reference panels for quality control of ELISA diagnostic kits in Russia].Vestn Ross Akad Med Nauk. 1998;(3):47-51. Vestn Ross Akad Med Nauk. 1998. PMID: 9608278 Review. Russian.
References
-
- Cooper MA, Pommering TL, Korányi K. Primary immunodeficiencies. Am Fam Physician. 2011;2003(68):2001–2008. - PubMed
-
- Isabelle SA, Isabelle P, Wael A, Katherine C, Cassandra RG, Janelle DO, Milene V, Denis S, Renee B. Brain bioavailability of human intravenous immunoglobulin and its transport through the murine blood–brain barrier. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2013;33:1983–1992. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2013.160. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
