Cullin 4A is associated with epithelial to mesenchymal transition and poor prognosis in perihilar cholangiocarcinoma
- PMID: 28428711
- PMCID: PMC5385398
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i13.2318
Cullin 4A is associated with epithelial to mesenchymal transition and poor prognosis in perihilar cholangiocarcinoma
Abstract
Aim: To explore the functional role of cullin 4A (CUL4A), a core subunit of E3 ubiquitin ligase, in perihilar cholangiocarcinoma (PHCC).
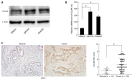
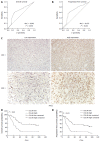
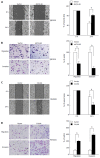
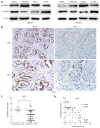
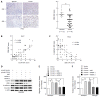
Methods: The expression of CUL4A in PHCC cell lines was evaluated by Western blot and quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) was adopted to investigate the relationship between CUL4A expression and clinicopathological characteristics of PHCC. Univariate analysis and multivariate regression analysis were performed to analyze the risk factors related to overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) of PHCC patients. Wound healing, Transwell and Matrigel assays were utilized to explore the function of CUL4A in PHCC metastasis. Furthermore, expression of epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) markers was verified in cells with CUL4A knockdown or overexpression. The relationship between CUL4A expression and E-cadherin expression was also analyzed by IHC assay. Finally, the role of ZEB1 in regulating CUL4A mediated PHCC was detected by IHC, Western blot, Transwell and Matrigel assays.
Results: CUL4A overexpression was detected in PHCC cell lines and clinical specimens. Clinicopathological analysis revealed a close correlation between CUL4A overexpression and tumour differentiation, T, N and TNM stages in PHCC. Kaplan-Meier analysis revealed that high CUL4A expression was correlated with poor OS and PFS of PHCC patients. Univariate analysis identified the following four parameters as risk factors related to OS rate of PHCC: T, N, TNM stages and high CUL4A expression; as well as three related to PFS: N stage, TNM stage and high CUL4A expression. Further multivariate logistic regression analysis identified high CUL4A expression as the only independent prognostic factor for PHCC. Moreover, CUL4A silencing in PHCC cell lines dramatically inhibited metastasis and the EMT. Conversely, CUL4A overexpression promoted these processes. Mechanistically, ZEB1 was discovered to regulate the function of CUL4A in promoting the EMT and metastasis.
Conclusion: CUL4A is an independent prognostic factor for PHCC, and it can promote the EMT by regulating ZEB1 expression. CUL4A may be a potential therapeutic target for PHCC.
Keywords: Cullin 4A; Epithelial to mesenchymal transition; Metastasis; Perihilar cholangiocarcinoma; Prognosis; ZEB1.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: To the best of our knowledge, no conflict of interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
High Expressions of CUL4A and TP53 in Colorectal Cancer Predict Poor Survival.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;51(6):2829-2842. doi: 10.1159/000496013. Epub 2018 Dec 18. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30562757
-
Effect of CUL4A on the metastatic potential of lung adenocarcinoma to the bone.Oncol Rep. 2020 Feb;43(2):662-670. doi: 10.3892/or.2019.7448. Epub 2019 Dec 27. Oncol Rep. 2020. PMID: 31894344
-
ZEB1 expression is associated with prognosis of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.J Clin Pathol. 2016 Jul;69(7):593-9. doi: 10.1136/jclinpath-2015-203115. Epub 2015 Dec 15. J Clin Pathol. 2016. PMID: 26670746
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cholangiocarcinoma: From clinical evidence to regulatory networks.J Hepatol. 2017 Feb;66(2):424-441. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.09.010. Epub 2016 Sep 26. J Hepatol. 2017. PMID: 27686679 Review.
-
The CUL4A ubiquitin ligase is a potential therapeutic target in skin cancer and other malignancies.Chin J Cancer. 2013 Sep;32(9):478-82. doi: 10.5732/cjc.012.10279. Epub 2013 Jul 12. Chin J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23845142 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting Cullin-RING E3 Ubiquitin Ligase 4 by Small Molecule Modulators.J Cell Signal. 2021;2(3):195-205. doi: 10.33696/Signaling.2.051. J Cell Signal. 2021. PMID: 34604860 Free PMC article.
-
CUL4A expression is associated with tumor stage and prognosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Dec;98(51):e18036. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000018036. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31860954 Free PMC article.
-
CUL4A regulates endometrial cancer cell proliferation, invasion and migration by interacting with CSN6.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Jan;23(1):23. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11661. Epub 2020 Nov 12. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 33179082 Free PMC article.
-
Non-apoptotic activity of the mitochondrial protein SMAC/Diablo in lung cancer: Novel target to disrupt survival, inflammation, and immunosuppression.Front Oncol. 2022 Sep 14;12:992260. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.992260. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36185255 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging role for Cullin 4 family of E3 ligases in tumorigenesis.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2019 Jan;1871(1):138-159. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2018.11.007. Epub 2018 Dec 30. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30602127 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kang MJ, Jang JY, Chang J, Shin YC, Lee D, Kim HB, Kim SW. Actual Long-Term Survival Outcome of 403 Consecutive Patients with Hilar Cholangiocarcinoma. World J Surg. 2016;40:2451–2459. - PubMed
-
- Brito AF, Abrantes AM, Encarnação JC, Tralhão JG, Botelho MF. Cholangiocarcinoma: from molecular biology to treatment. Med Oncol. 2015;32:245. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

