MicroRNA-145 exerts tumor-suppressive and chemo-resistance lowering effects by targeting CD44 in gastric cancer
- PMID: 28428713
- PMCID: PMC5385400
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i13.2337
MicroRNA-145 exerts tumor-suppressive and chemo-resistance lowering effects by targeting CD44 in gastric cancer
Abstract
Aim: To determine the potential roles of CD4 and microRNA (miR)-145 in gastric cancer.
Methods: The levels of CD44 and miR-145 were determined in gastric cancer cells. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction was used to measure to the level of CD44 mRNA. A luciferase reporter assay and western blotting were performed to examine the effect of miR-145 on CD44 expression. Tumor sphere and MTT assays were carried out to evaluate the self-renewal and chemo-resistance properties of gastric cancer cells.
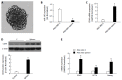
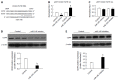
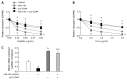
Results: The expression of CD44 was greatly increased and miR-145 was decreased in gastric cancer cells that were highly enriched in cancer stem cells (CSCs). The results demonstrated that miR-145 regulated CD44 by targeting directly the CD44 3'-untranslated region (3'-UTR). In gastric cancer cells, overexpression of miR-145 repressed the activity of the CD44 3'-UTR, and disruption of miR-145/CD44 3'-UTR interactions abrogated the silencing effects. In addition, miR-145 inhibition stimulated CD44 3'-UTR activity and disruption of miR-145/CD44 3'-UTR interactions abrogated this stimulatory effect. Enforced CD44 expression greatly increased tumor sphere formation and chemo-resistance in gastric cancer cells. Furthermore, the inhibition of CSCs and the chemo-sensitivity of gastric cancer cells treated with miR-145 were significantly abrogated by overexpression of CD44.
Conclusion: miR-145 targeting of CD44 plays critical roles in the regulation of tumor growth and chemo-resistance in gastric cancer.
Keywords: CD44; Chemo-resistance; Gastric cancer stem cells; miR-145.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that there are no potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-199a targets CD44 to suppress the tumorigenicity and multidrug resistance of ovarian cancer-initiating cells.FEBS J. 2012 Jun;279(11):2047-59. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2012.08589.x. Epub 2012 Apr 24. FEBS J. 2012. PMID: 22498306
-
Expression of microRNA-328 Functions as a Biomarker for Recurrence of Early Gastric Cancer (EGC) After Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (ESD) by Modulating CD44.Med Sci Monit. 2016 Dec 6;22:4779-4785. doi: 10.12659/msm.896225. Med Sci Monit. 2016. PMID: 27923017 Free PMC article.
-
Altered Expression of CD44, SIRT1, CXCR4, miR-21, miR-34a, and miR-451 Genes in MKN-45 Cell Line After Docetaxel Treatment.J Gastrointest Cancer. 2020 Jun;51(2):520-526. doi: 10.1007/s12029-019-00274-1. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31273630
-
Unravelling the role of Silibinin in targeting CD44+ cancer stem cells: Therapeutic implications, effective strategies and approaches.Phytother Res. 2024 Apr;38(4):1830-1837. doi: 10.1002/ptr.8150. Epub 2024 Feb 14. Phytother Res. 2024. PMID: 38353369 Review.
-
[Advances in tumor chemo-resistance regulated by MicroRNA].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2014 Oct 20;17(10):741-9. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2014.10.06. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25342041 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
MiR-145 Regulates the Chemoresistance of Hepatic Carcinoma Cells Against 5-Fluorouracil by Targeting Toll-Like Receptor 4.Cancer Manag Res. 2020 Jul 22;12:6165-6175. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S257598. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. Retraction in: Cancer Manag Res. 2023 Sep 15;15:1013-1014. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S440059. PMID: 32801865 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Targeting the Hippo Pathway in Gastric Cancer and Other Malignancies in the Digestive System: From Bench to Bedside.Biomedicines. 2022 Oct 8;10(10):2512. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10102512. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36289774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circular RNA circMAN2B2 promotes growth and migration of gastric cancer cells by down-regulation of miR-145.J Clin Lab Anal. 2020 Jun;34(6):e23215. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23215. Epub 2020 Feb 5. J Clin Lab Anal. 2020. PMID: 32020674 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor cell stemness in gastrointestinal cancer: regulation and targeted therapy.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Feb 22;10:1297611. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1297611. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38455361 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Down-regulation of long noncoding RNA PVT1 inhibits esophageal carcinoma cell migration and invasion and promotes cell apoptosis via microRNA-145-mediated inhibition of FSCN1.Mol Oncol. 2019 Dec;13(12):2554-2573. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12555. Epub 2019 Sep 8. Mol Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31369196 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87–108. - PubMed
-
- Wilke H, Stahl M. [Therapy in gastric cancer. From an oncological perspective] Chirurg. 2009;80:1023–1027. - PubMed
-
- Robb WB, Mariette C. Predicting the response to chemotherapy in gastric adenocarcinoma: who benefits from neoadjuvant chemotherapy? Recent Results Cancer Res. 2012;196:241–268. - PubMed
-
- Saikawa Y, Fukuda K, Takahashi T, Nakamura R, Takeuchi H, Kitagawa Y. Gastric carcinogenesis and the cancer stem cell hypothesis. Gastric Cancer. 2010;13:11–24. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

