High Salt Intake Augments Excitability of PVN Neurons in Rats: Role of the Endoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+ Store
- PMID: 28428739
- PMCID: PMC5382644
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2017.00182
High Salt Intake Augments Excitability of PVN Neurons in Rats: Role of the Endoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+ Store
Abstract
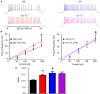
High salt (HS) intake sensitizes central autonomic circuitry leading to sympathoexcitation. However, its underlying mechanisms are not fully understood. We hypothesized that inhibition of PVN endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Ca2+ store function would augment PVN neuronal excitability and sympathetic nerve activity (SNA). We further hypothesized that a 2% (NaCl) HS diet for 5 weeks would reduce ER Ca2+ store function and increase excitability of PVN neurons with axon projections to the rostral ventrolateral medulla (PVN-RVLM) identified by retrograde label. PVN microinjection of the ER Ca2+ ATPase inhibitor thapsigargin (TG) increased SNA and mean arterial pressure (MAP) in a dose-dependent manner in rats with a normal salt (NS) diet (0.4%NaCl). In contrast, sympathoexcitatory responses to PVN TG were significantly (p < 0.05) blunted in HS treated rats compared to NS treatment. In whole cell current-clamp recordings from PVN-RVLM neurons, graded current injections evoked graded increases in spike frequency. Maximum discharge was significantly augmented (p < 0.05) by HS diet compared to NS group. Bath application of TG (0.5 μM) increased excitability of PVN-RVLM neurons in NS (p < 0.05), yet had no significant effect in HS rats. Our data indicate that HS intake augments excitability of PVN-RVLM neurons. Inhibition of the ER Ca2+-ATPase and depletion of Ca2+ store likely plays a role in increasing PVN neuronal excitability, which may underlie the mechanisms of sympathoexcitation in rats with chronic HS intake.
Keywords: endoplasmic reticulum; high salt diet; hypertension; paraventricular nucleus; sympathetic nerve activity.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Long-Term High Salt Intake Involves Reduced SK Currents and Increased Excitability of PVN Neurons with Projections to the Rostral Ventrolateral Medulla in Rats.Neural Plast. 2017;2017:7282834. doi: 10.1155/2017/7282834. Epub 2017 Dec 6. Neural Plast. 2017. PMID: 29362678 Free PMC article.
-
Hypertension induced by angiotensin II and a high salt diet involves reduced SK current and increased excitability of RVLM projecting PVN neurons.J Neurophysiol. 2010 Nov;104(5):2329-37. doi: 10.1152/jn.01013.2009. Epub 2010 Aug 18. J Neurophysiol. 2010. PMID: 20719931 Free PMC article.
-
Sympathoexcitation in ANG II-salt hypertension involves reduced SK channel function in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015 Jun 15;308(12):H1547-55. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00832.2014. Epub 2015 Apr 10. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25862832 Free PMC article.
-
Sympathoexcitation by hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus neurons projecting to the rostral ventrolateral medulla.J Physiol. 2018 Oct;596(19):4581-4595. doi: 10.1113/JP276223. Epub 2018 Aug 18. J Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30019338 Free PMC article.
-
Sympathoexcitatory input from hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus neurons projecting to rostral ventrolateral medulla is enhanced after myocardial infarction.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2020 Dec 1;319(6):H1197-H1207. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00273.2020. Epub 2020 Sep 18. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32946261
Cited by
-
Effects of a high salt diet on blood pressure dipping and the implications on hypertension.Front Neurosci. 2023 Jul 3;17:1212208. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1212208. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37465583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Caveolin-1 regulates medium spiny neuron structural and functional plasticity.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2020 Sep;237(9):2673-2684. doi: 10.1007/s00213-020-05564-2. Epub 2020 Jun 2. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2020. PMID: 32488350 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological acetic acid concentrations from ethanol metabolism stimulate accumbens shell medium spiny neurons via NMDAR activation in a sex-dependent manner.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2024 Apr;49(5):885-892. doi: 10.1038/s41386-023-01752-8. Epub 2023 Oct 16. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2024. PMID: 37845488 Free PMC article.
-
The ethanol metabolite acetic acid activates mouse nucleus accumbens shell medium spiny neurons.J Neurophysiol. 2021 Feb 1;125(2):620-627. doi: 10.1152/jn.00659.2020. Epub 2021 Jan 6. J Neurophysiol. 2021. PMID: 33405999 Free PMC article.
-
High-Salt Diet Impairs the Neurons Plasticity and the Neurotransmitters-Related Biological Processes.Nutrients. 2021 Nov 17;13(11):4123. doi: 10.3390/nu13114123. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34836378 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

