A Possible Role for Idiotype/Anti-idiotype B-T Cell Interactions in Maintaining Immune Memory
- PMID: 28428787
- PMCID: PMC5382190
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00409
A Possible Role for Idiotype/Anti-idiotype B-T Cell Interactions in Maintaining Immune Memory
Abstract
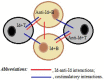
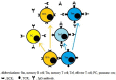
Variable regions of both B-cell receptors (BCRs) and T-cell receptors (TCRs) are completely formed in the postnatal period, and, consequently, no innate immune tolerance against these structures exists in adulthood. Indeed, antibodies (Abs) specific to TCRs have been found in both animals and humans. These facts clearly indicate the existence of B cells able to directly interact with T cells through binding of BCRs to TCRs without implicating major histocompatibility complex molecules. A novel paradigm is proposed in that the immune memory is based on idiotype/anti-idiotype interactions occurring between BCRs and TCRs following clearance of the antigen that elicited immune responses. It is envisaged that direct contact between memory T and B cells could provide co-stimulatory signals needed to sustain viability, growth, and differentiation of the interacting immune cells. In contrast, plasma cells originating from memory B-cells could produce anti-TCR Abs that inhibit direct BCR-to-TCR interactions, thereby downregulating the B- to T-cell contact-based immune memory via a negative feedback mechanism.
Keywords: B-cell receptor; T-cell receptor; idiotype/anti-idiotype interaction; immune memory; memory B-cell; memory T cell.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Direct receptor:receptor interactions between T and B lymphocytes: idiotypic restriction in the antibody response to a cloned helper T cell receptor.J Mol Cell Immunol. 1987;3(2):83-94. J Mol Cell Immunol. 1987. PMID: 2978239
-
Idiotype-specific T helper cells are required to induce idiotype-positive B memory cells to secrete antibody.Eur J Immunol. 1978 Aug;8(8):600-6. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080812. Eur J Immunol. 1978. PMID: 308883
-
Human anti-idiotypic T lymphocyte clones are activated by autologous anti-rabies virus antibodies presented in association with HLA-DQ molecules.J Mol Cell Immunol. 1987;3(3):145-55. J Mol Cell Immunol. 1987. PMID: 2908179
-
Immune Response Regulation by Antigen Receptors' Clone-Specific Nonself Parts.Front Immunol. 2018 Jun 25;9:1471. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01471. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30034389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
T cell antigen receptor recognition of antigen-presenting molecules.Annu Rev Immunol. 2015;33:169-200. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-032414-112334. Epub 2014 Dec 10. Annu Rev Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25493333 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanism(s) of prolonged attenuation of allergic responses after modulation of idiotypic regulatory network.Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2019 Dec 4;15:79. doi: 10.1186/s13223-019-0393-7. eCollection 2019. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31827543 Free PMC article.
-
The dynamic interface of genetics and immunity: toward future horizons in health & disease.Genes Immun. 2023 Aug;24(4):155-158. doi: 10.1038/s41435-023-00213-y. Genes Immun. 2023. PMID: 37464025 No abstract available.
-
Tumor-Associated Disialylated Glycosphingolipid Antigen-Revealing Antibodies Found in Melanoma Patients' Immunoglobulin Repertoire Suggest a Two-Direction Regulation Mechanism Between Immune B Cells and the Tumor.Front Immunol. 2019 Apr 5;10:650. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00650. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31024530 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

