A cross-circulated bicephalic model of head transplantation
- PMID: 28429535
- PMCID: PMC6492697
- DOI: 10.1111/cns.12700
A cross-circulated bicephalic model of head transplantation
Abstract
Aims: A successful cephalosomatic anastomosis ("head transplant") requires, among others, the ability to control long-term immune rejection and avoidance of ischemic events during the head transference phase. We developed a bicephalic model of head transplantation to study these aspects.
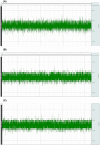
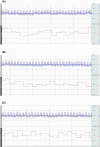
Methods and results: The thoracic aorta and superior vena cava of a donor rat were anastomosed with the carotid artery and extracorporeal veins of a recipient rat by vascular grafts. Before thoracotomy in the donor rat, the axillary artery and vein of the donor were connected to the carotid and the extracranial vein of the third rat through a silicone tube. The silicone tube was passed through a peristaltic pump to ensure donor brain tissue blood supply. There is no ischemia reperfusion injury in donor brain tissue analyzed by electroencephalogram. Postoperative donor has pain reflex and corneal reflex.
Conclusions: Peristaltic pump application can guarantee the blood supply of donor brain tissue per unit time, while the application of temperature change device to the silicone tube can protect the brain tissue hypothermia, postoperative experimental data show that there is no brain tissue ischemia during the whole operation. The application of vascular grafting can also provide the possibility of long-term survival of the model.
Keywords: head transplantation; immune rejection; ischemia reperfusion injury; rat model.
© 2017 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Head Transplantation in Mouse Model.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2015 Aug;21(8):615-8. doi: 10.1111/cns.12422. Epub 2015 Jun 20. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2015. PMID: 26096690 Free PMC article.
-
Blood as the carrier of ischemic tolerance in rat brain.J Neurosci Res. 2015 Aug;93(8):1250-7. doi: 10.1002/jnr.23580. Epub 2015 Mar 18. J Neurosci Res. 2015. PMID: 25787695
-
Allogeneic head and body reconstruction: mouse model.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2014 Dec;20(12):1056-60. doi: 10.1111/cns.12341. Epub 2014 Nov 4. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2014. PMID: 25367718 Free PMC article.
-
Central Pain Following Cord Severance for Cephalosomatic Anastomosis.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2016 Apr;22(4):271-4. doi: 10.1111/cns.12527. Epub 2016 Feb 16. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2016. PMID: 26880305 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Technical guidelines for porcine liver allo-transplantation: a review of literature.Ann Transplant. 2012 Apr-Jun;17(2):101-10. doi: 10.12659/aot.883228. Ann Transplant. 2012. PMID: 22743728 Review.
Cited by
-
First cephalosomatic anastomosis in a human model.Surg Neurol Int. 2017 Nov 17;8:276. doi: 10.4103/sni.sni_415_17. eCollection 2017. Surg Neurol Int. 2017. PMID: 29279793 Free PMC article.
-
First Human Head Transplantation: Surgically Challenging, Ethically Controversial and Historically Tempting – an Experimental Endeavor or a Scientific Landmark?Maedica (Bucur). 2019 Mar;14(1):5-11. doi: 10.26574/maedica.2019.14.1.5. Maedica (Bucur). 2019. PMID: 31123505 Free PMC article. Greek, Modern.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

