Noninvasive neuromodulation and thalamic mapping with low-intensity focused ultrasound
- PMID: 28430035
- PMCID: PMC7032074
- DOI: 10.3171/2016.11.JNS16976
Noninvasive neuromodulation and thalamic mapping with low-intensity focused ultrasound
Abstract
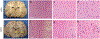
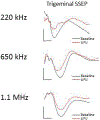
OBJECTIVE Ultrasound can be precisely focused through the intact human skull to target deep regions of the brain for stereotactic ablations. Acoustic energy at much lower intensities is capable of both exciting and inhibiting neural tissues without causing tissue heating or damage. The objective of this study was to demonstrate the effects of low-intensity focused ultrasound (LIFU) for neuromodulation and selective mapping in the thalamus of a large-brain animal. METHODS Ten Yorkshire swine ( Sus scrofa domesticus) were used in this study. In the first neuromodulation experiment, the lemniscal sensory thalamus was stereotactically targeted with LIFU, and somatosensory evoked potentials (SSEPs) were monitored. In a second mapping experiment, the ventromedial and ventroposterolateral sensory thalamic nuclei were alternately targeted with LIFU, while both trigeminal and tibial evoked SSEPs were recorded. Temperature at the acoustic focus was assessed using MR thermography. At the end of the experiments, all tissues were assessed histologically for damage. RESULTS LIFU targeted to the ventroposterolateral thalamic nucleus suppressed SSEP amplitude to 71.6% ± 11.4% (mean ± SD) compared with baseline recordings. Second, we found a similar degree of inhibition with a high spatial resolution (∼ 2 mm) since adjacent thalamic nuclei could be selectively inhibited. The ventromedial thalamic nucleus could be inhibited without affecting the ventrolateral nucleus. During MR thermography imaging, there was no observed tissue heating during LIFU sonications and no histological evidence of tissue damage. CONCLUSIONS These results suggest that LIFU can be safely used to modulate neuronal circuits in the central nervous system and that noninvasive brain mapping with focused ultrasound may be feasible in humans.
Keywords: FUS = focused ultrasound; H & E = hematoxylin and eosin; HIFU = high-intensity focused ultrasound; ISA = spatial average intensity; LFB = Luxol fast blue; LIFU = low-intensity focused ultrasound; PRFS = proton resonance frequency shift; SSEP = somatosensory evoked potential; VPL = ventroposterolateral thalamic nucleus; VPM = ventroposteromedial thalamic nucleus; brain mapping; functional neurosurgery; low intensity focused ultrasound; neuromodulation; noninvasive; somatosensory evoked potentials; thalamus.
Figures

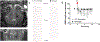
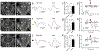
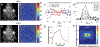
References
-
- Adrianov OS, Vykhodtseva NI, Fokin VF, Uranova NA, Avirom VM: [Reversible functional shutdown of the optic tract on exposure to focused ultrasound]. Biull Eksp Biol Med 97:760–762, 1984 - PubMed
-
- Chang WS, Jung HH, Kweon EJ, Zadicario E, Rachmilevitch I, Chang JW: Unilateral magnetic resonance guided focused ultrasound thalamotomy for essential tremor: practices and clinicoradiological outcomes. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 86:257–264, 2015 - PubMed
-
- Clement GT, Hynynen K: A non-invasive method for focusing ultrasound through the human skull. Physics in Medicine & Biology 47:1219–1236, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Clement GT, Sun J, Giesecke T, Hynynen K: A hemisphere array for non-invasive ultrasound brain therapy and surgery. Phys Med Biol 45:3707–3719, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Clement GT, White J, Hynynen K: Investigation of a large-area phased array for focused ultrasound surgery through the skull. Phys Med Biol 45:1071–1083., 2000 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

