Enhancing Insights into Pulmonary Vascular Disease through a Precision Medicine Approach. A Joint NHLBI-Cardiovascular Medical Research and Education Fund Workshop Report
- PMID: 28430547
- PMCID: PMC5476915
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.201701-0150WS
Enhancing Insights into Pulmonary Vascular Disease through a Precision Medicine Approach. A Joint NHLBI-Cardiovascular Medical Research and Education Fund Workshop Report
Abstract
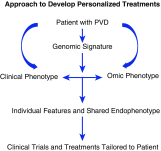
The Division of Lung Diseases of the NHLBI and the Cardiovascular Medical Education and Research Fund held a workshop to discuss how to leverage the anticipated scientific output from the recently launched "Redefining Pulmonary Hypertension through Pulmonary Vascular Disease Phenomics" (PVDOMICS) program to develop newer approaches to pulmonary vascular disease. PVDOMICS is a collaborative, protocol-driven network to analyze all patient populations with pulmonary hypertension to define novel pulmonary vascular disease (PVD) phenotypes. Stakeholders, including basic, translational, and clinical investigators; clinicians; patient advocacy organizations; regulatory agencies; and pharmaceutical industry experts, joined to discuss the application of precision medicine to PVD clinical trials. Recommendations were generated for discussion of research priorities in line with NHLBI Strategic Vision Goals that include: (1) A national effort, involving all the stakeholders, should seek to coordinate biosamples and biodata from all funded programs to a web-based repository so that information can be shared and correlated with other research projects. Example programs sponsored by NHLBI include PVDOMICS, Pulmonary Hypertension Breakthrough Initiative, the National Biological Sample and Data Repository for PAH, and the National Precision Medicine Initiative. (2) A task force to develop a master clinical trials protocol for PVD to apply precision medicine principles to future clinical trials. Specific features include: (a) adoption of smaller clinical trials that incorporate biomarker-guided enrichment strategies, using adaptive and innovative statistical designs; and (b) development of newer endpoints that reflect well-defined and clinically meaningful changes. (3) Development of updated and systematic variables in imaging, hemodynamic, cellular, genomic, and metabolic tests that will help precisely identify individual and shared features of PVD and serve as the basis of novel phenotypes for therapeutic interventions.
Keywords: Pulmonary Vascular Disease Phenomics; master protocol; precision medicine; pulmonary hypertension; pulmonary vascular disease.
Figures

Comment in
-
Pulmonary Hypertension and Precision Medicine through the "Omics" Looking Glass.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017 Jun 15;195(12):1558-1560. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201704-0750ED. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017. PMID: 28617089 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Moore WC, Meyers DA, Wenzel SE, Teague WG, Li H, Li X, D’Agostino R, Jr, Castro M, Curran-Everett D, Fitzpatrick AM, et al. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute’s Severe Asthma Research Program. Identification of asthma phenotypes using cluster analysis in the Severe Asthma Research Program. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010;181:315–323. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dweik RA, Rounds S, Erzurum SC, Archer S, Fagan K, Hassoun PM, Hill NS, Humbert M, Kawut SM, Krowka M, et al. ATS Committee on Pulmonary Hypertension Phenotypes. An official American Thoracic Society statement: pulmonary hypertension phenotypes. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014;189:345–355. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U01 HL125218/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL060917/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL138473/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL122596/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL109250/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087118/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R24 HL123767/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL125215/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL107393/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL124021/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL122887/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL125212/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL074186/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R24 HL105333/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

