Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR): A rising star in the era of precision medicine of lung cancer
- PMID: 28430586
- PMCID: PMC5564844
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.16854
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR): A rising star in the era of precision medicine of lung cancer
Abstract
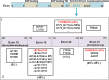
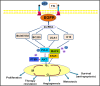
Lung cancer is a leading cause of cancer mortality worldwide. In tumors, the important role of noncoding RNA regulatory networks has been more and more reveal. EGFR has been identified as an oncogenic driver of NSCLC, especially activating mutations EGFR and its inhibition with specific TKIs can generate dramatic tumor responses. Studies have shown that EGFR plays significant roles in the progression of NSCLC. Subset analysis of the small proportion of patients with EGFR-mutant lung cancer showed a disease-free survival benefit, but was underpowered to detect a survival advantage. Herein, we highlight the progression of EGFR, noncoding RNA, and their roles in carcinogenesis. We also focus on anti-lung cancer drug development and EGFR-related drug resistance.
Keywords: epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR); lung cancer; noncoding RNA; precision medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87–108. - PubMed
-
- Tsao MS, Sakurada A, Cutz JC, Zhu CQ, Kamel-Reid S, Squire J, Lorimer I, Zhang T, Liu N, Daneshmand M, Marrano P, da Cunha Santos G, Lagarde A, et al. Erlotinib in lung cancer - molecular and clinical predictors of outcome. The New England journal of medicine. 2005;353:133–144. - PubMed
-
- Shaw AT, Kim DW, Nakagawa K, Seto T, Crino L, Ahn MJ, De Pas T, Besse B, Solomon BJ, Blackhall F, Wu YL, Thomas M, O'Byrne KJ, et al. Crizotinib versus chemotherapy in advanced ALK-positive lung cancer. The New England journal of medicine. 2013;368:2385–2394. - PubMed
-
- Yoshida T, Zhang G, Haura EB. Targeting epidermal growth factor receptor: central signaling kinase in lung cancer. Biochemical pharmacology. 2010;80:613–623. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

