TAK1 inhibitor 5Z-7-oxozeaenol sensitizes cervical cancer to doxorubicin-induced apoptosis
- PMID: 28430599
- PMCID: PMC5464900
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.16895
TAK1 inhibitor 5Z-7-oxozeaenol sensitizes cervical cancer to doxorubicin-induced apoptosis
Abstract
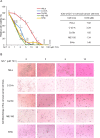
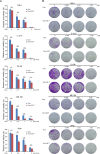
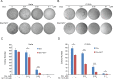
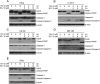
Aberrant activation of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) allows cancer cells to escape chemotherapy-induced cell death and acts as one of the major mechanisms of acquired chemoresistance in cervical cancer. TAK1, a crucial mediator that upregulates NF-κB activation in response to cellular genotoxic stress, is required for tumor cell viability and survival. Herein, we examined whether TAK1 inhibition is a potential therapeutic strategy for treating cervical cancer. We found that TAK1 inhibitor 5Z-7-oxozeaenol significantly augmented the cytotoxic effects of Dox in a panel of cervical cancer cell lines. Treatment with 5Z-7-oxozeaenol hindered Dox-induced NF-κB activation and promoted Dox-induced apoptosis in cervical cancer cells. Moreover, 5Z-7-oxozeaenol showed similar effects in both positive and negative human papillomavirus-infected cervical cancer cells. Taken together, our results provide evidence that TAK1 inhibition significantly sensitizes cervical cancer cells to chemotherapy-induced cell death and supports the use of TAK1 inhibitor with current chemotherapies in the clinic for patients with refractory cervical cancer.
Keywords: 5Z-7-oxozeaenol; TAK1 inhibitor; cervical cancer; chemotherapy; doxorubicin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TAK1 inhibitor 5Z-7-oxozeaenol sensitizes neuroblastoma to chemotherapy.Apoptosis. 2013 Oct;18(10):1224-34. doi: 10.1007/s10495-013-0864-0. Apoptosis. 2013. PMID: 23700229 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic action of 5Z-7-oxozeaenol and bortezomib in inducing apoptosis of Burkitt lymphoma cell line Daudi.Tumour Biol. 2016 Jan;37(1):531-9. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3832-1. Epub 2015 Aug 1. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26227222
-
Mechanism and in vitro pharmacology of TAK1 inhibition by (5Z)-7-Oxozeaenol.ACS Chem Biol. 2013 Mar 15;8(3):643-50. doi: 10.1021/cb3005897. Epub 2013 Jan 7. ACS Chem Biol. 2013. PMID: 23272696
-
Semisynthesis of Hypothemycin Analogues Targeting the C8-C9 Diol.J Nat Prod. 2022 Aug 26;85(8):2018-2025. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.2c00434. Epub 2022 Jul 14. J Nat Prod. 2022. PMID: 35834411 Free PMC article. Review.
-
(5Z)-7-Oxozeaenol: A novel and potent resorcylic acid lactone kinase inhibitor with a cis-enone Michael acceptor.Chirality. 2019 Feb;31(2):110-117. doi: 10.1002/chir.23040. Epub 2018 Dec 19. Chirality. 2019. PMID: 30565749 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Anti-Inflammatory Activities of an Anti-Histamine Drug, Loratadine, by Suppressing TAK1 in AP-1 Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 3;23(7):3986. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073986. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409346 Free PMC article.
-
TAK1 signaling is a potential therapeutic target for pathological angiogenesis.Angiogenesis. 2021 Aug;24(3):453-470. doi: 10.1007/s10456-021-09787-5. Epub 2021 May 10. Angiogenesis. 2021. PMID: 33973075 Review.
-
Inhibition of the MAP2K7-JNK pathway with 5Z-7-oxozeaenol induces apoptosis in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Oncotarget. 2021 Aug 31;12(18):1787-1801. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.28040. eCollection 2021 Aug 31. Oncotarget. 2021. PMID: 34504651 Free PMC article.
-
Tbx5 overexpression in embryoid bodies increases TAK1 expression but does not enhance the differentiation of sinoatrial node cardiomyocytes.Biol Open. 2023 Jun 15;12(6):bio059881. doi: 10.1242/bio.059881. Epub 2023 Jun 5. Biol Open. 2023. PMID: 37272627 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome Analysis of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Cells Inducibly Expressing MyD88 L265P Mutation Identifies Upregulated CD44, LGALS3, NFKBIZ, and BATF as Downstream Targets of Oncogenic NF-κB Signaling.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 15;24(6):5623. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065623. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982699 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Shen MR, Hsu YM, Hsu KF, Chen YF, Tang MJ, Chou CY. Insulin-like growth factor 1 is a potent stimulator of cervical cancer cell invasiveness and proliferation that is modulated by alphavbeta3 integrin signaling. Carcinogenesis. 2006;27:962–971. - PubMed
-
- Cornelio DB, Roesler R, Schwartsmann G. Emerging therapeutic agents for cervical cancer. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2009;4:196–206. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

