Simulated weightlessness affects the expression and activity of neuronal nitric oxide synthase in the rat brain
- PMID: 28430607
- PMCID: PMC5458159
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.15407
Simulated weightlessness affects the expression and activity of neuronal nitric oxide synthase in the rat brain
Abstract
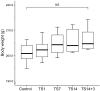
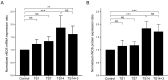
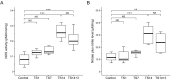
Spaceflight induces pathophysiological alterations in various organs. To study pathophysiological adaptations to weightlessness on the ground, the tail suspension (TS) rat model has been used to simulate the effects of weightlessness. There is currently little information on the effect of TS on the expression and activity of nitric oxide synthase (NOS) in the brain. In this study, we examined time-dependent alterations in the expression and activity of neuronal NOS (nNOS) in the brains of TS rats. Male Sprague-Dawley rats were tail-suspended for 1 (TS1), 7 (TS7), and 14 (TS14) days or rested on the ground for 3 days after 14 days of TS. TS1 and TS7 rats exhibited no significant alterations in the expression of nNOS compared to control rats, whereas nNOS expression in TS14 rats was significantly upregulated compared to control rats. Normalized expression of nNOS mRNA and protein in TS14 rats (1.86 ± 0.48 and 1.84 ± 0.29, respectively) were significantly higher than that of control rats (P < 0.001 and P < 0.001, respectively). Consistent with these results, significant elevations in NOS activity and NO production were observed in TS14 rats. Thus, we demonstrated a significant upregulation of nNOS expression, accompanied by significant increases in NOS activity and NO production, in the brain of rats exposed to simulated weightlessness.
Keywords: Pathology Section; brain; neuronal nitric oxide synthase; rat; simulated weightlessness; tail suspension.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Increased nitric oxide synthase activity and expression in the hypothalamus of hindlimb unloaded rats.Brain Res. 2006 Oct 18;1115(1):65-74. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2006.07.078. Epub 2006 Aug 30. Brain Res. 2006. PMID: 16938283
-
Down-regulation of neuronal nitric oxide synthase by nitric oxide after oxygen-glucose deprivation in rat forebrain slices.J Neurochem. 1999 Jan;72(1):248-54. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1999.0720248.x. J Neurochem. 1999. PMID: 9886076
-
Amyloid-beta (25-35) increases activity of neuronal NO-synthase in rat brain.Neurochem Int. 2008 May;52(6):1114-24. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2007.11.009. Epub 2007 Dec 8. Neurochem Int. 2008. PMID: 18207612
-
Functional Roles of Neuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase in Neurodegenerative Diseases and Mood Disorders.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2021;18(10):831-840. doi: 10.2174/1567205018666211022164025. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2021. PMID: 34719364 Review.
-
Regulation of neuronal nitric oxide synthase and identification of novel nitric oxide signaling pathways.Prog Brain Res. 1998;118:3-11. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)63196-9. Prog Brain Res. 1998. PMID: 9932430 Review.
Cited by
-
Hindlimb unloading-induced reproductive suppression via Downregulation of hypothalamic Kiss-1 expression in adult male rats.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2021 Mar 4;19(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s12958-021-00694-4. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2021. PMID: 33663539 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance and Aerobic Preconditioning Delays Unloading-Induced Multisystemic Physiological Changes: The NEBULA Project.FASEB J. 2025 Jul 15;39(13):e70759. doi: 10.1096/fj.202501128R. FASEB J. 2025. PMID: 40614062 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of microgravity on spontaneous calcium activity of primary hippocampal neurons grown in microfluidic chips.NPJ Microgravity. 2024 Feb 6;10(1):15. doi: 10.1038/s41526-024-00355-x. NPJ Microgravity. 2024. PMID: 38321051 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of ginsenosides Rg1 and Rb1 against cognitive impairment induced by simulated microgravity in rats.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Apr 24;14:1167398. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1167398. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37168997 Free PMC article.
References
-
- De Santo NG, Christensen NJ, Drummer C, Kramer HJ, Regnard J, Heer M, Cirillo M, Norsk P. Fluid balance and kidney function in space: introduction. Am J Kidney Dis. 2001;38:664–667. - PubMed
-
- Fishman RA. Philadelphia, USA: Saunders; 1992. Cerebrospinal fluid in disease of the nervous system.
-
- Morey-Holton ER, Globus RK. Hindlimb unloading rodent model: technical aspects. J Appl Physiol. 2002;92:1367–1377. - PubMed
-
- Hargens AR, Steskal J, Johansson C, Tipton CM. Tissue fluid shift, forelimb loading, and tail tension in tail-suspended rats. Physiologist. 1984;27:S37–38.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

