Clinical efficacy of icotinib in lung cancer patients with different EGFR mutation status: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 28430623
- PMCID: PMC5464926
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.15475
Clinical efficacy of icotinib in lung cancer patients with different EGFR mutation status: a meta-analysis
Abstract
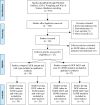
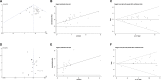
Icotinib is a novel and the third listed epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs), which exerts a good anti-tumor efficacy on non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The efficacy of EGFR-TKIs has been shown to be associated with the EGFR mutation status, especially exon 19 deletion (19Del) and exon 21 L858R mutation. Therefore, a meta-analysis was performed to assess the efficacy of icotinib in NSCLC patients harboring EGFR mutations (19Del or L858R) and wild type (19Del and L858R loci wild type). A total of 24 studies were included for comparing the objective response rate (ORR) in the EGFR wild type and mutant patients treated with icotinib. The ORRs of EGFR mutant patients (19Del or L858R) are better than those of EGFR wild type patients (OR = 7.03(5.09-9.71), P < 0.00001). The pooling ORs from 21 studies on the disease control rate (DCR) in EGFR mutant patients are better than those of EGFR wild type patients (OR = 10.54(5.72-19.43), P < 0.00001). Moreover, the ORRs of EGFR 19Del patients are better than those of EGFR L858R patients after pooling ORs of 12 studies (OR = 2.04(1.12-3.73), P = 0.019). However, there was no significant difference on DCRs of EGFR 19Del patients and those of EGFR L858R patients (OR = 2.01(0.94-4.32), P = 0.072). Our findings indicated that compared with EGFR wild type patients, EGFR mutant patients have better ORRs and DCRs after icotinib treatment; EGFR 19Del patients treated with icotinib have better ORRs than EGFR L858R patients. EGFR mutation status is a useful biomarker for the evaluation of icotinib efficacy in NSCLC patients.
Keywords: disease control rate; epidermal growth factor receptor; icotinib; meta-analysis; objective response rate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effects of icotinib on advanced non-small cell lung cancer with different EGFR phenotypes.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014 Sep;70(1):553-8. doi: 10.1007/s12013-014-9955-y. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014. PMID: 24777808
-
Efficacy of Icotinib, an EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients with Exon 19 Deletion and Exon 21 L858R: A Retrospective Analysis in China.Pharmacology. 2021;106(11-12):658-666. doi: 10.1159/000519847. Epub 2021 Oct 21. Pharmacology. 2021. PMID: 34673645
-
A single-arm, multicenter, safety-monitoring, phase IV study of icotinib in treating advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).Lung Cancer. 2014 Nov;86(2):207-12. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2014.08.014. Epub 2014 Sep 16. Lung Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25261231
-
Icotinib, a selective EGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, for the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer.Future Oncol. 2015;11(3):385-97. doi: 10.2217/fon.14.249. Future Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25675121 Review.
-
Effectiveness of EGFR-TKIs in a Patient with Lung Adenocarcinoma Harboring an EGFR-RAD51 Fusion.Oncologist. 2019 Aug;24(8):1027-1030. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2018-0732. Epub 2019 May 7. Oncologist. 2019. PMID: 31064887 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Recent advances in the pharmacological diversification of quinazoline/quinazolinone hybrids.RSC Adv. 2020 Nov 12;10(68):41353-41392. doi: 10.1039/d0ra06642g. eCollection 2020 Nov 11. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35516563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SNCA Is a Functionally Low-Expressed Gene in Lung Adenocarcinoma.Genes (Basel). 2018 Jan 4;9(1):16. doi: 10.3390/genes9010016. Genes (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29300342 Free PMC article.
-
Case report: Efficacy of icotinib treatment in lung adenocarcinoma with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a rare case of double primary malignant tumors.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Mar 28;11:1266062. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1266062. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38606154 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer Metastases from Lung Adenocarcinoma Disappeared After Molecular Targeted Therapy: A Successfully Clinical Treatment Experience.Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2022 May 26;15:539-546. doi: 10.2147/PGPM.S367978. eCollection 2022. Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 35651533 Free PMC article.
-
EYA2 promotes lung cancer cell proliferation by downregulating the expression of PTEN.Oncotarget. 2017 Dec 2;8(67):110837-110848. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.22860. eCollection 2017 Dec 19. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29340020 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60:277–300. - PubMed
-
- Socinski MA, Crowell R, Hensing TE, Langer CJ, Lilenbaum R, Sandler AB, Morris D. American College of Chest P. Treatment of non-small cell lung cancer, stage IV: ACCP evidence-based clinical practice guidelines (2nd edition) Chest. 2007;132:277S–289S. - PubMed
-
- Zhou C, Wu YL, Chen G, Feng J, Liu XQ, Wang C, Zhang S, Wang J, Zhou S, Ren S, Lu S, Zhang L, Hu C, et al. Erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12:735–742. - PubMed
-
- Mitsudomi T, Morita S, Yatabe Y, Negoro S, Okamoto I, Tsurutani J, Seto T, Satouchi M, Tada H, Hirashima T, Asami K, Katakami N, Takada M, et al. Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): an open label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11:121–128. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

