Spatiotemporal Regulation of Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 and Its Receptor in the Brain: Is There a Role for Growth Hormone?
- PMID: 28430923
- PMCID: PMC5413082
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2016-1884
Spatiotemporal Regulation of Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 and Its Receptor in the Brain: Is There a Role for Growth Hormone?
Figures
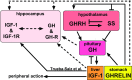
Comment on
-
Circulating Insulin-Like Growth Factor I Regulates Its Receptor in the Brain of Male Mice.Endocrinology. 2017 Feb 1;158(2):349-355. doi: 10.1210/en.2016-1468. Endocrinology. 2017. PMID: 27792405
Similar articles
-
Administration of growth hormone and nandrolone decanoate alters mRNA expression of the GABAB receptor subunits as well as of the GH receptor, IGF-1, and IGF-2 in rat brain.Growth Horm IGF Res. 2014 Apr-Jun;24(2-3):60-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ghir.2014.01.002. Epub 2014 Jan 16. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2014. PMID: 24480470
-
A novel dominant negative mutation in the intracellular domain of GHR is associated with growth hormone insensitivity.Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2016 Oct;85(4):669-71. doi: 10.1111/cen.13116. Epub 2016 Jun 30. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2016. PMID: 27234692 No abstract available.
-
The role of growth hormone in neural development.Horm Res. 2005;64 Suppl 3:66-72. doi: 10.1159/000089320. Epub 2006 Jan 20. Horm Res. 2005. PMID: 16439847 Review.
-
Targeting the growth hormone axis as a therapeutic strategy in oncology.Growth Horm IGF Res. 2000 Apr;10 Suppl A:S45-6. doi: 10.1016/s1096-6374(00)90022-4. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2000. PMID: 10984291 Review. No abstract available.
-
'Paresis of facial and abducens nerves in a patient with growth-hormone receptor deficiency treated with insulin-like growth factor I'.Dev Med Child Neurol. 1999 Apr;41(4):285. doi: 10.1017/s0012162299220609. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1999. PMID: 10355817 No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Oligodendrocyte Response to Pathophysiological Conditions Triggered by Episode of Perinatal Hypoxia-Ischemia: Role of IGF-1 Secretion by Glial Cells.Mol Neurobiol. 2020 Oct;57(10):4250-4268. doi: 10.1007/s12035-020-02015-z. Epub 2020 Jul 21. Mol Neurobiol. 2020. PMID: 32691304 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of a Csf1r enhancer selectively impacts CSF1R expression and development of tissue macrophage populations.Nat Commun. 2019 Jul 19;10(1):3215. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11053-8. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31324781 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nishijima T, Piriz J, Duflot S, Fernandez AM, Gaitan G, Gomez-Pinedo U, Verdugo JMG, Leroy F, Soya H, Nuñez A, Torres-Aleman I. Neuronal activity drives localized blood-brain-barrier transport of serum insulin-like growth factor-I into the CNS. Neuron. 2010;67(5):834–846. - PubMed
-
- Beilharz EJ, Russo VC, Butler G, Baker NL, Connor B, Sirimanne ES, Dragunow M, Werther GA, Gluckman PD, Williams CE, Scheepens A. Co-ordinated and cellular specific induction of the components of the IGF/IGFBP axis in the rat brain following hypoxic-ischemic injury. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1998;59(2):119–134. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

