Field Trial Performance of Herculex XTRA (Cry34Ab1/Cry35Ab1) and SmartStax (Cry34Ab1/Cry35Ab1 + Cry3Bb1) Hybrids and Soil Insecticides Against Western and Northern Corn Rootworms (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae)
- PMID: 28430986
- PMCID: PMC5444676
- DOI: 10.1093/jee/tox099
Field Trial Performance of Herculex XTRA (Cry34Ab1/Cry35Ab1) and SmartStax (Cry34Ab1/Cry35Ab1 + Cry3Bb1) Hybrids and Soil Insecticides Against Western and Northern Corn Rootworms (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae)
Abstract
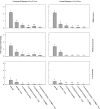
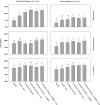
Western corn rootworm, Diabrotica virgifera virgifera LeConte (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae), and northern corn rootworm, Diabrotica barberi Smith and Lawrence (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae), are important insect pests in corn, Zea mays L. For more than a decade, growers have been using transgenic plants expressing proteins from the bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) to protect corn roots from feeding. In 2011, western corn rootworm populations were reported to have developed resistance to Bt hybrids expressing Cry3Bb1 and later found to be cross-resistant to hybrids expressing mCry3A and eCry3.1Ab. The identification of resistance to Cry3 (Cry3Bb1, mCry3A, and eCry3.1Ab) hybrids led to concerns about durability and efficacy of products with single traits and of products containing a pyramid of a Cry3 protein and the binary Bt proteins Cry34Ab1 and Cry35Ab1. From 2012 to 2014, 43 field trials were conducted across the central United States to estimate root protection provided by plants expressing Cry34Ab1/Cry35Ab1 alone (Herculex RW) or pyramided with Cry3Bb1 (SmartStax). These technologies were evaluated with and without soil-applied insecticides to determine if additional management measures provided benefit where Cry3 performance was reduced. Trials were categorized for analysis based on rootworm damage levels on Cry3-expressing hybrids and rootworm feeding pressure within each trial. Across scenarios, Cry34Ab1/Cry35Ab1 hybrids provided excellent root protection. Pyramided traits provided greater root and yield protection than non-Bt plus a soil-applied insecticide, and only in trials where larval feeding pressure exceeded two nodes of damage did Cry34Ab1/Cry35Ab1 single-trait hybrids and pyramided hybrids show greater root protection from the addition of soil-applied insecticides.
Keywords: Cry34Ab1/Cry35Ab1; Cry3Bb1; SmartStax; northern corn rootworm; western corn rootworm.
© The Authors 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Entomological Society of America. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of corn hybrids expressing Cry34Ab1/Cry35Ab1 and Cry3BbL against the western corn rootworm (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae).J Econ Entomol. 2013 Apr;106(2):823-9. doi: 10.1603/ec12392. J Econ Entomol. 2013. PMID: 23786070
-
Transgenic Bt Corn, Soil Insecticide, and Insecticidal Seed Treatment Effects on Corn Rootworm (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) Beetle Emergence, Larval Feeding Injury, and Corn Yield in North Dakota.J Econ Entomol. 2018 Feb 9;111(1):348-360. doi: 10.1093/jee/tox297. J Econ Entomol. 2018. PMID: 29186516
-
Evaluation of corn hybrids expressing Cry1F, cry1A.105, Cry2Ab2, Cry34Ab1/Cry35Ab1, and Cry3Bb1 against southern United States insect pests.J Econ Entomol. 2012 Oct;105(5):1825-34. doi: 10.1603/ec12155. J Econ Entomol. 2012. PMID: 23156183
-
Safety considerations derived from Cry34Ab1/Cry35Ab1 structure and function.J Invertebr Pathol. 2017 Jan;142:27-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2016.07.019. Epub 2016 Jul 29. J Invertebr Pathol. 2017. PMID: 27480405 Review.
-
Resistance to Bt maize by western corn rootworm: insights from the laboratory and the field.Curr Opin Insect Sci. 2016 Jun;15:111-5. doi: 10.1016/j.cois.2016.04.001. Epub 2016 Apr 13. Curr Opin Insect Sci. 2016. PMID: 27436740 Review.
Cited by
-
Resistance management and integrated pest management insights from deployment of a Cry3Bb1+ Gpp34Ab1/Tpp35Ab1 pyramid in a resistant western corn rootworm landscape.PLoS One. 2024 Mar 8;19(3):e0299483. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0299483. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38457466 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the Spectrum of Activity of IPD079Ea: A Protein Derived From Ophioglossum pendulum (Ophioglossales: Ophioglossaceae) With Activity Against Western Corn Rootworm [Diabrotica virgifera virgifera (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae)].J Econ Entomol. 2022 Oct 12;115(5):1531-1538. doi: 10.1093/jee/toac079. J Econ Entomol. 2022. PMID: 35640234 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the Spectrum of Insecticidal Activity for IPD072Aa: A Protein Derived from Pseudomonas chlororaphis with Activity Against Diabrotica virgifera virgifera (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae).J Econ Entomol. 2019 May 22;112(3):1190-1196. doi: 10.1093/jee/toz029. J Econ Entomol. 2019. PMID: 30817816 Free PMC article.
-
Risk Assessment of RNAi-Based Potential Pesticide dsNlAtg3 and Its Homologues for Nilaparvata lugens and Non-Target Organisms.Insects. 2025 Feb 19;16(2):225. doi: 10.3390/insects16020225. Insects. 2025. PMID: 40003854 Free PMC article.
-
Recent progress on the interaction between insects and Bacillus thuringiensis crops.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2019 Mar 4;374(1767):20180316. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2018.0316. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30967027 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bergman M. K., Ellis C. R., Bledsoe L. W.. 1991. Influence of wind speed and placement of soil insecticides against corn rootworm (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 84: 256–259.
-
- Dunn J. P., Frommelt K.. 1998. Effects of below ground herbivory by Diabrotica virgifera virgifera (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) on biomass allocation and carbohydrate storage of maize. Appl. Soil Ecol. 7: 213–218.
-
- Dun Z., Mitchell P. D., Agosti M.. 2010. Estimating Diabrotica virgifera virgifera damage functions with field trial data: Applying an unbalanced nested error component model. J. Appl. Entomol. 134: 409–419.
-
- Estes R. E., Tinsley N. A., Gray M. E.. 2015. Evaluation of soil-applied insecticides with Bt maize for managing corn rootworm larval injury. J. Econ. Entomol. 140: 19–27.
-
- (U. S. EPA) U. S. Environmental Protection Agency. 2016. Current and previously registered section 3 PIP registrations. (https://www.epa.gov/ingredients-used-pesticide-products/current-and-prev...) (accessed 23 February 2017).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

