Serum C-reactive protein, procalcitonin, and lactate dehydrogenase for the diagnosis of pancreatic necrosis
- PMID: 28431197
- PMCID: PMC6478063
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD012645
Serum C-reactive protein, procalcitonin, and lactate dehydrogenase for the diagnosis of pancreatic necrosis
Abstract
Background: The treatment of people with pancreatic necrosis differs from that of people with oedematous pancreatitis. It is important to know the diagnostic accuracy of serum C-reactive protein (CRP), serum procalcitonin, and serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) as a triage test for the detection of pancreatic necrosis in people with acute pancreatitis, so that an informed decision can be made as to whether the person with pancreatic necrosis needs further investigations such as computed tomography (CT) scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan and treatment for pancreatic necrosis started. There is currently no standard clinical practice, although CRP, particularly an increasing trend of CRP, is often used as a triage test to determine whether the person requires further imaging. There is also currently no systematic review of the diagnostic test accuracy of CRP, procalcitonin, and LDH for the diagnosis of pancreatic necrosis in people with acute pancreatitis.
Objectives: To compare the diagnostic accuracy of CRP, procalcitonin, or LDH (index test), either alone or in combination, in the diagnosis of necrotising pancreatitis in people with acute pancreatitis and without organ failure.
Search methods: We searched MEDLINE, Embase, Science Citation Index Expanded, National Institute for Health Research (NIHR HTA and DARE), and other databases until March 2017. We searched the references of the included studies to identify additional studies. We did not restrict studies based on language or publication status, or whether data were collected prospectively or retrospectively. We also performed a 'related search' and 'citing reference' search in MEDLINE and Embase.
Selection criteria: We included all studies that evaluated the diagnostic test accuracy of CRP, procalcitonin, and LDH for the diagnosis of pancreatic necrosis in people with acute pancreatitis using the following reference standards, either alone or in combination: radiological features of pancreatic necrosis (contrast-enhanced CT or MRI), surgeon's judgement of pancreatic necrosis during surgery, or histological confirmation of pancreatic necrosis. Had we found case-control studies, we planned to exclude them because they are prone to bias; however, we did not locate any. Two review authors independently identified the relevant studies from the retrieved references.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently extracted data, including methodological quality assessment, from the included studies. As the included studies reported CRP, procalcitonin, and LDH on different days of admission and measured at different cut-off levels, it was not possible to perform a meta-analysis using the bivariate model as planned. We have reported the sensitivity, specificity, post-test probability of a positive and negative index test along with 95% confidence interval (CI) on each of the different days of admission and measured at different cut-off levels.
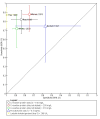
Main results: A total of three studies including 242 participants met the inclusion criteria for this review. One study reported the diagnostic performance of CRP for two threshold levels (> 200 mg/L and > 279 mg/L) without stating the day on which the CRP was measured. One study reported the diagnostic performance of procalcitonin on day 1 (1 day after admission) using a threshold level of 0.5 ng/mL. One study reported the diagnostic performance of CRP on day 3 (3 days after admission) using a threshold level of 140 mg/L and LDH on day 5 (5 days after admission) using a threshold level of 290 U/L. The sensitivities and specificities varied: the point estimate of the sensitivities ranged from 0.72 to 0.88, while the point estimate of the specificities ranged from 0.75 to 1.00 for the different index tests on different days of hospital admission. However, the confidence intervals were wide: confidence intervals of sensitivities ranged from 0.51 to 0.97, while those of specificities ranged from 0.18 to 1.00 for the different tests on different days of hospital admission. Overall, none of the tests assessed in this review were sufficiently accurate to suggest that they could be useful in clinical practice.
Authors' conclusions: The paucity of data and methodological deficiencies in the studies meant that it was not possible to arrive at any conclusions regarding the diagnostic test accuracy of the index test because of the uncertainty of the results. Further well-designed diagnostic test accuracy studies with prespecified index test thresholds of CRP, procalcitonin, LDH; appropriate follow-up (for at least two weeks to ensure that the person does not have pancreatic necrosis, as early scans may not indicate pancreatic necrosis); and clearly defined reference standards (of surgical or radiological confirmation of pancreatic necrosis) are important to reliably determine the diagnostic accuracy of CRP, procalcitonin, and LDH.
Conflict of interest statement
This report is independent research funded by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR Cochrane Programme Grants, 13/89/03 ‐ Evidence‐based diagnosis and management of upper digestive, hepato‐biliary, and pancreatic disorders). The views expressed in this publication are those of the author(s) and not necessarily those of the National Health Service, the NIHR, or the Department of Health.
OK: none known.
SPP: none known.
BRD: none known.
KSG: none known.
Figures
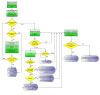
Acute pancreatitis is usually confirmed by consensus criteria (Banks 2013).
Irrespective of the CT scan findings and presence or absence of necrosis, people with organ failure will require organ support and will receive a CT scan.
CT scan may also be performed in people without organ failure if there is clinical deterioration (not amounting to organ failure) or in some centres based on an elevated CRP.
Necrotising pancreatitis is usually confirmed by the findings on the CT scan and by histopathological examination of the biopsy obtained during necrosectomy if early necrosectomy is performed.
Infected necrotising pancreatitis is usually confirmed by the findings on the CT scan and by microbiological examination of fluid aspirated under radiological guidance or from the tissue biopsy obtained during necrosectomy if early necrosectomy is performed.
Organ failure is diagnosed on the basis of clinical examination and blood tests (urea, creatinine, blood pressure, pulse rate, respiratory rate, arterial blood gas analysis).


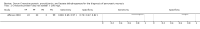



Similar articles
-
Serum amylase and lipase and urinary trypsinogen and amylase for diagnosis of acute pancreatitis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 21;4(4):CD012010. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012010.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28431198 Free PMC article.
-
Amylase in drain fluid for the diagnosis of pancreatic leak in post-pancreatic resection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 7;4(4):CD012009. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012009.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28386958 Free PMC article.
-
Regional cerebral blood flow single photon emission computed tomography for detection of Frontotemporal dementia in people with suspected dementia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jun 23;2015(6):CD010896. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010896.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26102272 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Blood biomarkers for the non-invasive diagnosis of endometriosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 1;2016(5):CD012179. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012179. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27132058 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Evaluation of Inflammatory Biomarkers in Predicting Progression of Acute Pancreatitis to Pancreatic Necrosis: A Diagnostic Test Accuracy Review.Healthcare (Basel). 2022 Dec 22;11(1):27. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11010027. Healthcare (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36611486 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum Level of Lactate Dehydrogenase is Associated with Cardiovascular Disease Risk as Determined by the Framingham Risk Score and Arterial Stiffness in a Health-Examined Population in China.Int J Gen Med. 2022 Jan 4;15:11-17. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S337517. eCollection 2022. Int J Gen Med. 2022. PMID: 35018110 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Validation of a Nomogram for Predicting the Severity of the First Episode of Hyperlipidemic Acute Pancreatitis.J Inflamm Res. 2024 May 20;17:3211-3223. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S459258. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 38800592 Free PMC article.
-
Factors associated with increased pancreatic enzymes in septic patients: a prospective study.J Intensive Care. 2017 Jul 14;5:44. doi: 10.1186/s40560-017-0243-y. eCollection 2017. J Intensive Care. 2017. PMID: 28725436 Free PMC article.
-
Acute necrotising pancreatitis: measurements of necrosis volume and mean CT attenuation help early prediction of organ failure and need for intervention.Eur Radiol. 2021 Oct;31(10):7705-7714. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-07840-x. Epub 2021 Mar 23. Eur Radiol. 2021. PMID: 33758956
References
References to studies included in this review
Alfonso 2003 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Alfonso V, Gomez F, Lopez A, Moreno‐Osset E, Valle R, Anton MD, et al. C‐reactive protein level in the detection of necrosis in acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterologia y Hepatologia 2003;26(5):288‐93. - PubMed
Bertsch 1997 {published data only}
-
- Bertsch T, Richter A, Hofheinz H, Bohm C, Hartel M, Aufenanger J. Procalcitonin ‐ a new marker for the acute‐phase reaction in acute pancreatitis. Langenbecks Archiv fur Chirurgie 1997;382(6):367‐72. - PubMed
Rau 1998 {published data only}
-
- Rau B, Cebulla M, Uhl W, Schoenberg MH, Beger HG. The clinical value of human pancreas‐specific protein procarboxypeptidase B as an indicator of necrosis in acute pancreatitis : Comparison to CRP and LDH. Pancreas 1998;17(2):134‐9. - PubMed
-
- Rau B, Steinbach G, Baumgart K, Gansauge F, Grunert A, Beger HG. Serum amyloid A versus C‐reactive protein in acute pancreatitis: Clinical value of an alternative acute‐phase reactant. Critical Care Medicine 2000;28(3):736‐42. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Abishek 2014 {published data only}
-
- Abishek V, Babu V, Muthukumaran, Ramkumar, Balamurali, Murali A, et al. Role of C‐reactive protein in predicting severity of acute pancreatitis. Indian Journal of Gastroenterology 2014;33(Suppl 1):A92.
Aggelopoulos 1996 {published data only}
-
- Aggelopoulos C, Aloizos S, Touliatou A, Papanastasopoulos C, Tsaglis B, Papanastasopoulous B. APACHE III and CRP as early predictive indexes in acute pancreatitis. HPB Surgery 1996;9(Supp 2):121. [P200]
Ammori 2003 {published data only}
-
- Ammori BJ, Becker KL, Kite P, Snider RH, Nylen ES, White JC, et al. Calcitonin precursors in the prediction of severity of acute pancreatitis on the day of admission. British Journal of Surgery 2003;90(2):197‐204. - PubMed
Appasani 2011a {published data only}
-
- Appasani S, Thandassery RB, Dixit P, Yadav TD, Attri SV, Rana SV, et al. Serum ADA levels in predicting the severity in acute pancreatitis. Indian Journal of Gastroenterology 2011;1:A87.
Appasani 2011b {published data only}
-
- Appasani S, Thandassery RB, Varma N, Yadav TD, Attri SV, Rana SV, et al. D‐dimer as a single marker for early prediction of severity, necrosis, organ failure and mortality in acute pancreatitis. Indian Journal of Gastroenterology 2011;1:A12.
Appasani 2012 {published data only}
-
- Appasani S, Rana S, Babu Thandassery R, Basha J, Yadav TD, Attri SV, et al. Serum ADA levels in predicting the severity in acute pancreatitis. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2012;27:374‐5.
Bajec 2010 {published data only}
-
- Bajec D, Gunjic D, Radenkovic D, Gregoric P, Karadzic B, Pejovic I. Evaluation of Glasgow and APACHE II scores and CRP in prediction of severity of acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2010;10(2‐3):349.
Bapat 1986 {published data only}
-
- Bapat RD, Nazareth HM, Kulkarni AG, Shah AB. Prognostic markers in acute pancreatitis ‐ a prospective study. Indian Journal of Gastroenterology 1986;5(2):113‐5. - PubMed
Barauskas 2004 {published data only}
-
- Barauskas G, Svagzdys S, Maleckas A. C‐reactive protein in early prediction of pancreatic necrosis. Medicina 2004;40(2):135‐40. - PubMed
Bassi 1994 {published data only}
-
- Bassi C. Infected pancreatic necrosis. International Journal of Pancreatology 1994;16(1):1‐10. - PubMed
Beger 1989 {published data only}
-
- Beger HG, Buchler M. C‐reactive protein and acute pancreatitis. British Journal of Surgery 1989;76(8):877. - PubMed
Berry 1982 {published data only}
-
- Berry AR, Taylor TV, Davies GC. Diagnostic tests and prognostic indicators in acute pancreatitis. Journal of the Royal College of Surgeons of Edinburgh 1982;27(6):345‐52. - PubMed
Bezmarevic 2012a {published data only}
-
- Bezmarevic M, Kostic Z, Jovanovic M, Mickovic S, Mirkovic D, Soldatovic I, et al. Procalcitonin and BISAP score versus C‐reactive protein and APACHE II score in early assessment of severity and outcome of acute pancreatitis. Vojnosanitetski Pregled 2012;69(5):425‐31. - PubMed
Bezmarevic 2012b {published data only}
-
- Bezmarevic M, Mirkovic D, Mickovic S, Perisic N. BISAP score and procalcitonin versus APACHE II score and C‐reactive protein in early assessment of the severity and outcome of acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2012;12(6):534. - PubMed
Bezmarevic 2012c {published data only}
-
- Bezmarevic M, Mirkovic D, Soldatovic I, Stamenkovic D, Mitrovic N, Perisic N, et al. Correlation between procalcitonin and intra‐abdominal pressure and their role in prediction of the severity of acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2012;12(4):337‐43. - PubMed
Bihari 2004 {published data only}
Blum 2001 {published data only}
-
- Blum T, Maisonneuve P, Lowenfels AB, Lankisch PG. Fatal outcome in acute pancreatitis: Its occurrence and early prediction. Pancreatology 2001;1(3):237‐41. - PubMed
Boskovic 2014 {published data only}
-
- Boskovic A, Pasic S, Soldatovic I, Milinic N, Stankovic I. The role of D‐dimer in prediction of the course and outcome in paediatric acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2014;14(5):330‐4. - PubMed
Brailski 1975 {published data only}
-
- Brailski KH. Acute pancreatitis (etiology, pathogenesis and pathobiochemistry). Vutreshni Bolesti 1975;14(4):1‐11. - PubMed
Brand 2014 {published data only}
-
- Brand M, Gotz A, Zeman F, Behrens G, Leitzmann M, Brunnler T, et al. Acute necrotizing pancreatitis: Laboratory, clinical, and imaging findings as predictors of patient outcome. American Journal of Roentgenology 2014;202(6):1215‐31. - PubMed
Brisinda 1999 {published data only}
-
- Brisinda G, Maria G, Ferrante A, Civello IM. Evaluation of prognostic factors in patients with acute pancreatitis. Hepato‐Gastroenterology 1999;46(27):1990‐7. - PubMed
Buchler 1986a {published data only}
-
- Buchler M, Malfertheiner P, Schoetensack C, Uhl W, Beger HG. Sensitivity of antiproteases, complement factors and C‐reactive protein in detecting pancreatic necrosis ‐ results of a prospective clinical‐study. International Journal of Pancreatology 1986;1(3‐4):227‐35. - PubMed
Buchler 1986b {published data only}
-
- Buchler M, Malfertheiner P, Schoetensack C, Uhl W, Scherbaum W, Beger HG. Value of biochemical and imaging procedures for the diagnosis and prognosis of acute pancreatitis ‐ results of a prospective clinical study. Zeitschrift Fur Gastroenterologie 1986;24(2):100‐9. - PubMed
Buchler 1986c {published data only}
-
- Buchler M, Malfertheiner P, Uhl W, Beger HG. A new staging system in patients with acute‐pancreatitis using serum alpha‐2‐macroglobulin and C‐reactive protein. Gastroenterology 1986;90(5):1361.
Buchler 1987 {published data only}
-
- Buchler M, Malfertheiner P, Uhl W, Beger HG. C‐reactive protein as a marker of inflammation and necrosis in gastroenterology. Medizinische Klinik 1987;82(5):180‐5. - PubMed
Buchler 1991 {published data only}
-
- Buchler M. Objectification of the severity of acute‐pancreatitis. Hepato‐Gastroenterology 1991;38(2):101‐8. - PubMed
Bulbuller 2006 {published data only}
-
- Bulbuller N, Dogru O, Ayten R, Akbulut H, Ilhan YS, Cetinkaya Z. Procalcitonin is a predictive marker for severe acute pancreatitis. Ulusal Travma ve Acil Cerrahi Dergisi [Turkish Journal of Trauma & Emergency Surgery: TJTES] 2006;12(2):115‐20. - PubMed
Cai 2014 {published data only}
-
- Cai YY, Ee J, Liew YX, Lee WN, Chlebicki MP, Goh YC, et al. A procalcitonin‐based guideline promotes shorter duration of antibiotic use safely in acute pancreatitis. Journal of Infection 2014;69(4):412‐5. - PubMed
Cardoso 2011 {published data only}
-
- Cardoso F, Ricardo L, Oliveira A, Rodrigues C, Horta D, Figueiredo A, et al. Value of C‐reactive protein in predicting organ failure, complications and mortality in acute pancreatitis. Pancreas 2011;40(8):1315.
Cardoso 2013 {published data only}
-
- Cardoso FS, Ricardo LB, Oliveira AM, Canena JM, Horta DV, Papoila AL, et al. C‐reactive protein prognostic accuracy in acute pancreatitis: Timing of measurement and cutoff points. European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology 2013;25(7):784‐9. - PubMed
Cardoso 2015 {published data only}
-
- Cardoso FS, Ricardo L, Gondar P, Deus JR, Horta D. C‐reactive protein may influence decisively the prescription of prophylactic antibiotics in acute pancreatitis: a population‐based cohort study. Pancreas 2015;44(3):404‐8. - PubMed
Chen 1992 {published data only}
-
- Chen CC, Wang SS, Chao Y, Lu CW, Lee SD, Tsal YT, et al. C‐reactive protein and lactate‐dehydrogenase isoenzymes in the assessment of the prognosis of acute‐pancreatitis. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 1992;7(4):363‐6. - PubMed
Chen 2004 {published data only}
-
- Chen CC. Serum markers in the early assessment of severity of acute pancreatitis: Which is the most useful?. Journal of the Chinese Medical Association: JCMA 2004;67(9):439‐41. - PubMed
Chen 2012 {published data only}
-
- Chen D, Lu S, Xu F. Study for the value of serum lactate dehydrogenase in predicting multiple organ dysfunction syndrome caused by acute pancreatitis. Chinese Journal of Critical Care Medicine 2012;32(4):349‐51.
Choi 2012 {published data only}
-
- Choi JS, Cho JH, Jeon TJ, Kim HM, Kim YJ, Han KJ, et al. Prognostic value of procalcitonin, CRP, BISAP, RANSON'S, APACHE II and CTSI scores according to the various etiologies of acute pancreatitis. Pancreas 2012;41(8):1353.
Choi 2013 {published data only}
-
- Choi JS, Cho JH, Jeon TJ, Kim HM, Kim YJ, Han KJ, et al. Prognostic value of procalcitonin, CRP, BISAP RANSON'S, APACHE II and CTSI scores according to the various etiologies of acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2013;13(2):e20.
Chooklin 2010 {published data only}
-
- Chooklin S, Lyba M, Bihalskyy I. Pancreatic necrosis markers in severe acute pancreatitis. European Journal of Clinical Investigation 2010;40:14.
Choudhary 2012 {published data only}
-
- Choudhary RK, Choudhary M. A useful diagnostic and prognostic tool for acute appendicitis and acute pancreatitis. BMJ 2012;344:e1404; author reply e9. - PubMed
Cooper 1981 {published data only}
-
- Cooper MJ, Whicher JT, Walters G, Williamson RCN. Predictive value of C‐reactive protein and complement in acute‐pancreatitis. Gastroenterologie Clinique Et Biologique 1981;5(10):920‐1.
Cravo 1988 {published data only}
-
- Cravo M, Santos P, Marques A, Deus J, Santos ML, Geada H, et al. Antiproteases and C‐reactive protein in the early assessment of severity of acute‐pancreatitis. Digestion 1988;40(2):74.
d'Eril 2000 {published data only}
-
- d'Eril GM, Merlini G, Finazzi S, Bosoni T, Barakat B, Pezzilli R. Procalcitonin is not a reliable marker for the assessment of severity in acute pancreatitis without infectious complications. Clinical Chemistry 2000;46(3):428‐30. - PubMed
Dambrauskas 2010 {published data only}
-
- Dambrauskas Z, Gulbinas A, Pundzius J, Barauskas G. Value of the different prognostic systems and biological markers for predicting severity and progression of acute pancreatitis. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology 2010;45(7‐8):959‐70. - PubMed
Dammann 1979 {published data only}
-
- Dammann HG, Wichert P, Schreiber HW. Prognostic indices in acute pancreatitis. Zentralblatt Fur Chirurgie 1979;104(6):397‐404. - PubMed
Daniel 2010 {published data only}
-
- Daniel P, Lesniowski B, Mokrowiecka A, Jasinska A, Pietruczuk M, Malecka‐Panas E. Circulating levels of Visfatin, Resistin and pro‐inflammatory cytokine Interleukin‐8 in acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2010;10(4):477‐82. - PubMed
de Beaux 1996 {published data only}
-
- Beaux AC, Goldie AS, Ross JA, Carter DC, Fearon KC. Serum concentrations of inflammatory mediators related to organ failure in patients with acute pancreatitis. British Journal of Surgery 1996;83(3):349‐53. - PubMed
De la Pena 1991 {published data only}
-
- Pena J, las Heras G, Galo Peralta F, Casafont F, Pons Romero F. Prospective study of the prognostic value of C reactive protein, alpha 1‐antitrypsin and alpha 1‐acid glycoprotein in acute pancreatitis. Revista Espanola de Enfermedades Digestivas 1991;79(5):337‐40. - PubMed
Del Prete 2001 {published data only}
-
- Prete M, Castiglia D, Meli M, Perri S, Nicita A, Dalla Torre A, et al. Prognostic value of C reactive protein in acute pancreatitis. Chirurgia Italiana 2001;53(1):33‐8. - PubMed
Digalakis 2009 {published data only}
Duarte‐Rojo 2009 {published data only}
-
- Duarte‐Rojo A, Suazo‐Barahona J, Ramirez‐Iglesias MT, Uscanga LF, Robles‐Diaz G. Time frames for analysis of inflammatory mediators in acute pancreatitis: Improving admission triage. Digestive Diseases and Sciences 2009;54(10):2282‐7. - PubMed
Economou 1997 {published data only}
-
- Economou MS. The potential role of procalcitonin and interleukin‐8 in the prediction of infected necrosis in acute pancreatitis. Hellenic Journal of Gastroenterology 1997;10(3):248‐9.
Fan 1994 {published data only}
-
- Fan ST. Early recognition of severe acute‐pancreatitis. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 1994;9(3):289‐90. - PubMed
Ferguson 1990 {published data only}
-
- Ferguson CM, Bradley EL. Can markers for pancreatic necrosis be used as indicators for surgery?. American Journal of Surgery 1990;160(5):459‐61. - PubMed
Fisic 2013 {published data only}
Folch‐Puy 2007 {published data only}
-
- Folch‐Puy E. Markers of severity in acute pancreatitis. Medicina Clinica 2007;128(11):417‐8. - PubMed
Frasquet 2003 {published data only}
-
- Frasquet J, Saez J, Trigo C, Martinez J, Such J, Perez‐Mateo M. Early measurement of procalcitonin does not predict severity in patients with acute pancreatitis. British Journal of Surgery 2003;90(9):1129‐30. - PubMed
Frossard 2001 {published data only}
-
- Frossard JL, Hadengue A, Pastor CM. New serum markers for the detection of severe acute pancreatitis in humans. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2001;164(1):162‐70. - PubMed
Gao 2014 {published data only}
-
- Gao K, Zhang LJ, Wang GY, Li J, Zhang H. Role of serum IL‐6, IL‐8 and procalcitonin in diagnosis of secondary infection in severe acute pancreatitis. World Chinese Journal of Digestology 2014;22(16):2343‐6.
Garcia‐Cantu 2004 {published data only}
-
- Garcia‐Cantu DA, Gonzalez‐Gonzalez JA, Dominguez NR, Perez DOR, Maldonado‐Garza HJJ. A simple score plus serum C‐reactive protein at admission increase the positive predictive value for organ failure in severe acute pancreatitis. A prospective trial. Gastroenterology 2004;126(4):A227.
Garcia Lozano 1992 {published data only}
-
- Garcia Lozano A, Garcia‐Villanova J, Martin L, Martinez D, Mansilla D, Rodenas V, et al. The prediction of the severity of acute pancreatitis by C‐reactive protein. Revista Espanola de Enfermedades Digestivas 1992;82(4):231‐3. - PubMed
Gelfand 2005 {published data only}
-
- Gelfand B, Filimonov M, Burnevich S, Brazhnik T, Sergeyeva N. The procalcitonin test in the evaluation of clinical severity in patients with acute pancreatitis. Critical Care 2005;9(Supp 1):P171.
Geng 2014 {published data only}
-
- Geng P, Ding Y. Advances in studies on procalcitonin and acute pancreatitis. Chinese Journal of Gastroenterology 2014;19(7):439‐41.
Gluskina 1967 {published data only}
-
- Gluskina VM. On the differential diagnosis of edema and hemorrhagic necrosis of the pancreas. Vestnik Khirurgii Imeni I. I. Grekova 1967;99(9):69‐72. - PubMed
Gosling 1992 {published data only}
-
- Gosling P, Shearman CP. Can we predict disease severity in acute‐pancreatitis. Annals of Clinical Biochemistry 1992;29:9‐10. - PubMed
Gross 1990 {published data only}
-
- Gross V, Scholmerich J, Leser HG, Salm R, Lausen M, Ruckauer K, et al. Granulocyte elastase in assessment of severity of acute‐pancreatitis ‐ comparison with acute‐phase proteins C‐reactive protein, alpha‐1‐antitrypsin, and protease inhibitor alpha‐2‐macroglobulin. Digestive Diseases and Sciences 1990;35(1):97‐105. - PubMed
Guenther 2010 {published data only}
-
- Guenther A, Aghdassi AA, Nitsche CJ, Schulte J, Struck J, Lerch MM, et al. Comparison of peroxiredoxin‐4 with CRP as a severity marker for acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2010;10(2‐3):345.
Gurda‐Duda 2008 {published data only}
-
- Gurda‐Duda A, Kusnierz‐Cabala B, Nowak W, Naskalski JW, Kulig J. Assessment of the prognostic value of certain acute‐phase proteins and procalcitonin in the prognosis of acute pancreatitis. Pancreas 2008;37(4):449‐53. - PubMed
Gurleyik 2004 {published data only}
-
- Gurleyik G, Cirpici OZ, Aktekin A, Saglam A. The value of Ranson and APACHE II scoring systems, and serum levels of interleukin‐6 and C‐reactive protein in the early diagnosis of the severity of acute pancreatitis. Ulusal Travma Ve Acil Cerrahi Dergisi 2004;10(2):83‐8. - PubMed
Gurleyik 2005 {published data only}
-
- Gurleyik G, Emir S, Kilicoglu G, Arman A, Saglam A. Computed tomography severity index, APACHE II score, and serum CRP concentration for predicting the severity of acute pancreatitis. Journal of the Pancreas 2005;6(6):562‐7. - PubMed
Gvozdenovic 2001 {published data only}
-
- Gvozdenovic M, Lausevic Z, Ignjatovic S, Bukumirovic V. Significance of C‐reactive protein in the treatment of acute necrotizing pancreatitis. Acta Chirurgica Iugoslavica 2001;48(3):29‐34. - PubMed
Hamalainen 2002 {published data only}
-
- Hamalainen MT, Gronroos P, Gronroos JM. Do normal leucocyte count and C‐reactive protein on admission to hospital exclude a life‐threatening attack of acute pancreatitis?. Scandinavian Journal of Surgery 2002;91(Part 4):353‐6. - PubMed
Han 2011 {published data only}
-
- Han L, Lu S. Early predictive value of lactate dehydrogenase, serum creatinine and C‐reactive protein in severe acute pancreatitis. Chinese Journal of Critical Care Medicine 2011;31(Part 12):1058‐61.
Hjalmarsson 2009 {published data only}
-
- Hjalmarsson C, Stenflo J, Borgstrom A. Activated protein C‐protein C inhibitor complex, activation peptide of carboxypeptidase B and C‐reactive protein as predictors of severe acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2009;9(5):700‐7. - PubMed
Huang 2013 {published data only}
Huang 2015 {published data only}
-
- Huang J, Wu ZW, Lu SQ, Shen JQ, Kong XM, Shen YP. Soluble B7‐H2 as a novel marker in early evaluation of the severity of acute pancreatitis. Labmedicine 2015;46(2):109‐17. - PubMed
Imamura 2002a {published data only}
-
- Imamura T, Tanaka S, Yoshida H. Significance of measurement of high‐sensitivity C‐reactive protein in acute pancreatitis. Journal of Gastroenterology 2002;37(Part 11):935‐8. - PubMed
Imamura 2002b {published data only}
-
- Imamura T, Tanaka S, Yoshida H, Kitamura K, Takahashi A, Ikegami A, et al. Clinical significance of measurement of high‐sensitivity C‐reactive protein in acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2002;122(4):A368. - PubMed
Inagaki 1997 {published data only}
-
- Inagaki T, Hoshino M, Hayakawa T, Ohara H, Yamada T, Yamada H, et al. Interleukin‐6 is a useful marker for early prediction of the severity of acute pancreatitis. Pancreas 1997;14(1):1‐8. - PubMed
Isenmann 1993 {published data only}
-
- Isenmann R, Buchler M, Uhl W, Malfertheiner P, Martini M, Beger HG. Pancreatic necrosis: An early finding in severe acute pancreatitis. Pancreas 1993;8(3):358‐61. - PubMed
Isogai 1998 {published data only}
-
- Isogai M, Yamaguchi A, Hori A, Kaneoka Y. LDH to AST ratio in biliary pancreatitis ‐ a possible indicator of pancreatic necrosis: preliminary results. American Journal of Gastroenterology 1998;93(3):363‐7. - PubMed
Jia 2015 {published data only}
-
- Jia R, Tang M, Qiu L, Sun R, Cheng L, Ma X, et al. Increased interleukin‐23/17 axis and C‐reactive protein are associated with severity of acute pancreatitis in patients. Pancreas 2015;44(2):321‐5. - PubMed
Jiang 2004 {published data only}
-
- Jiang CF, Shiau YC, Ng KW, Tan SW. Serum interleukin‐6, tumor necrosis factor alpha and C‐reactive protein in early prediction of severity of acute pancreatitis. Journal of the Chinese Medical Association 2004;67(9):442‐6. - PubMed
Jimenez 2015 {published data only}
-
- Jimenez E, Moreno S, Guadiana LG, Pedregosa J, Jimenez R, Rebollo S, et al. Procalcitonin for predicting severity of acute pancreatitis. Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine 2015;53:S941.
Jimin 2015 {published data only}
-
- Jimin Z, Jian Z, Juncha G. Early evaluations of BISAP plus C‐reactive protein in predicting the severity of acute pancreatitis. Zhonghua Yi Xue za Zhi 2015;95(12):925‐8. - PubMed
Johnson 2003 {published data only}
-
- Johnson CD. Early severity indexes in acute pancreatitis. Acta Gastro‐Enterologica Belgica 2003;66(2):174‐6. - PubMed
Kaiyasah 2013 {published data only}
-
- Kaiyasah H, Alozaibi L, Anwar S, Al‐Jufairi F, Naim R. Can serum procalcitonin be a reliable single bio‐marker in predicting the severity of acute pancreatitis?. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2013;28:681.
Kaya 2007 {published data only}
Kazda 2002 {published data only}
-
- Kazda A, Brodska H, Valenta J, Uhrova I, Hendl J, Belohlavek J, et al. Procalcitonin in acute pancreatitis and in septic states. Klinicka Biochemie a Metabolismus 2002;10(1):32‐7.
Khanna 2013 {published data only}
-
- Khanna AK, Meher S, Prakash S, Tiwary SK, Singh U, Srivastava A, et al. Comparison of Ranson, Glasgow, MOSS, SIRS, BISAP, APACHE II, CTSI scores, IL‐6, CRP, and procalcitonin in predicting severity, organ failure, pancreatic necrosis, and mortality in acute pancreatitis. HPB Surgery 2013 Sep 24 [Epub ahead of print]:32‐7. [DOI: 10.1155/2013/367581] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Khvatova 1973 {published data only}
-
- Khvatova EA. Role of certain enzymatic systems in different forms of acute pancreatitis. Klinicheskaia Khirurgiia 1973;2:48‐53. - PubMed
Khvatova 1977 {published data only}
-
- Khvatova EA. Value of thermal fractionation of lactate dehydrogenase and the protein composition of the blood in the differential diagnosis of the phases of acute pancreatitis. Vestnik Khirurgii Imeni I. I. Grekova 1977;118(1):34‐7. - PubMed
Kibar 2016 {published data only}
Kim 2013a {published data only}
Kim 2013b {published data only}
-
- Kim KH, Kim BG, Ryu CH, Nam HS, Woo SM, Ryu SH, et al. Comparative analysis of BISAP system and serum procalcitonin for predicting severity of acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2013;13(Supp):S25‐7.
Kitsanou 2004 {published data only}
-
- Kitsanou M, Katsanos KH, Christodoulou D, Kalabokis G, Katsaraki A, Kontodimou N, et al. The role of PMN elastase and CRP on the diagnosis and assessment of severity of acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2004;126(4):A228.
Korczowski 2006 {published data only}
-
- Korczowski B. Diagnostic usefulness of procalcitonin in acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterologia Polska 2006;13(1):63‐5.
Kusnierz‐Cabala 2004 {published data only}
-
- Kusnierz‐Cabala B, Naskalski JW, Kedra B, Panek J. Comparison of sensitivity and specificity of serum poly‐C avid ribonuclease activity and C‐reactive protein concentration in detection of mild and severe acute pancreatitis. Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine 2004;42(5):549‐55. - PubMed
Kylanpaa‐Back 2001a {published data only}
-
- Kylanpaa‐Back ML, Takala A, Kemppainen E, Puolakkainen P, Haapiainen R, Repo H. Procalcitonin strip test in the early detection of severe acute pancreatitis. British Journal of Surgery 2001;88(2):222‐7. - PubMed
Kylanpaa‐Back 2001b {published data only}
-
- Kylanpaa‐Back ML, Takala A, Kemppainen EA, Puolakkainen PA, Haapiainen RK, Repo H. The strip test of procalcitonin in early detection of severe acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2001;120(5):A469. - PubMed
Kylanpaa‐Back 2001c {published data only}
-
- Kylanpaa‐Back ML, Takala A, Kemppainen EA, Puolakkainen PA, Leppaniemi AK, Karonen SL, et al. Procalcitonin, soluble interleukin‐2 receptor, and soluble E‐selectin in predicting the severity of acute pancreatitis. Critical Care Medicine 2001;29(1):63‐9. - PubMed
Leese 1987 {published data only}
-
- Leese T, Fuller M, Holliday M. C‐reactive protein and alpha‐2 macroglobulin in the assessment and monitoring of acute‐pancreatitis. Digestion 1987;38(1):35‐6.
Leese 1988 {published data only}
Lempinen 1999 {published data only}
-
- Lempinen M, Kylanpaa‐Back ML, Stenman UH, Puolakkainen P, Haapiainen R, Finne P, et al. Predicting the severity of acute pancreatitis by rapid measurement of trypsinogen‐2 in urine. Clinical Chemistry 1999;47(12):2103‐7. - PubMed
Lempinen 2005 {published data only}
-
- Lempinen M, Puolakkainen P, Kemppainen E. Clinical value of severity markers in acute pancreatitis. Scandinavian Journal of Surgery: SJS 2005;94(2):118‐23. - PubMed
Lewandowski 2007 {published data only}
-
- Lewandowski A, Kopec W, Diakowska D, Garbien M. Proinflammatory cytokines IL‐6, IL‐8 and C‐reactive protein in acute pancreatitis ‐ the role of IL‐8 in prognosing complications. Gastroenterologia Polska 2007;14(3):165‐72.
Li 2013 {published data only}
-
- Li Y, Li Y, Lu S. The value of lactate dehydrogenase combined with BISAP scoring in predicting the prognosis of acute pancreatitis. Chinese Journal of Critical Care Medicine 2013;33(Part 6):523‐6.
Liang 2014 {published data only}
-
- Liang K. Early predictive value of serum calcium, C‐reactive protein and serum amylase like protein A on severe acute pancreatitis. Chinese Journal of Critical Care Medicine 2014;34(Part 8):720‐3.
Lindner 1995 {published data only}
-
- Lindner J, Skokanova V. Acute phase proteins in acute pancreatitis. Rozhledy V Chirurgii 1995;74(1):21‐4. - PubMed
Lipsett 2001 {published data only}
-
- Lipsett PA. Serum cytokines, proteins, and receptors in acute pancreatitis: Mediators, markers, or more of the same?. Critical Care Medicine 2001;29(8):1642‐4. - PubMed
Liu 2008 {published data only}
-
- Liu C, Haldene C. C‐reactive protein or lactate dehydrogenase to assess the severity of pancreatic necrosis. Emergency Medicine Journal 2008;25(10):687‐8. - PubMed
Lobo 1999 {published data only}
-
- Lobo SM, Meirelles RF, Lupino P, Pires MD, Kuga ML, Beolchi G. Increased procalcitonin serum levels as predictive parameter of multiple organ failure and outcome in acute pancreatitis patients. Critical Care 1999;3(Supp 1):P93.
Lott 1991 {published data only}
-
- Lott JA. The value of clinical laboratory studies in acute‐pancreatitis. Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine 1991;115(4):325‐6. - PubMed
Ma 2013 {published data only}
-
- Ma J, Fan H, Kou JT, Li LX, He Q. Clinical significance for monitoring of serum ghrelin in acute pancreatitis severity assessment. National Medical Journal of China 2013;93(48):3864‐6. - PubMed
Machiedo 1974 {published data only}
-
- Machiedo GW, Brown CS, Rush BF Jr. Comparison of biochemical changes in blood and abdominal fluid during acute hemorrhagic pancreatitis. Review of Surgery 1974;31(1):60‐2. - PubMed
Makay 2003 {published data only}
-
- Makay R, Issekutz A, Banga P, Belagyi T, Olah A. Role of procalcitonin rapid test in the differential diagnosis of uninfected and infected forms of acute pancreatitis. Magyar Sebeszet 2003;56(1):31‐3. - PubMed
Makela 2007 {published data only}
-
- Makela JT, Eila H, Kiviniemi H, Laurila J, Laitinen S. Computed tomography severity index and C‐reactive protein values predicting mortality in emergency and intensive care units for patients with severe acute pancreatitis. American Journal of Surgery 2007;194(1):30‐4. - PubMed
Malfertheiner 1993 {published data only}
-
- Malfertheiner P, Dominguez‐Munoz JE. Prognostic factors in acute‐pancreatitis. International Journal of Pancreatology 1993;14(1):1‐8. - PubMed
Manabe 2004 {published data only}
-
- Manabe T, Okada Y. Serum markers for predicting the severity of acute pancreatitis. Journal of Gastroenterology 2004;39(5):504‐6. - PubMed
Mandi 2000a {published data only}
-
- Mandi Y, Farkas G, Takacs T, Boda K, Lonovics J. Diagnostic relevance of procalcitonin, IL‐6, and sICAM‐1 in the prediction of infected necrosis in acute pancreatitis. International Journal of Pancreatology 2000;28(1):41‐9. - PubMed
Mandi 2000b {published data only}
-
- Mandi Y, Farkas G, Skolak E, Takacs T. Relevance of procalcitonin in infected pancreatic necrosis. 5th World Congress on Trauma, Shock, Inflammation and Sepsis: Pathophysiology, Immune Consequences and Therapy; 2000 Feb 29‐Mar 4; Munich, Germany. Augusta (GA): BioMedical, 2000:419‐24.
Manes 1994 {published data only}
-
- Manes G, Rabitti PG, Laccetti M, Perrotti F, Cavallera A, Uomo G. Early prognostic assessment of acute pancreatitis with sterile necrosis. A perspective clinical study. Recenti Progressi in Medicina 1994;85(10):490‐3. - PubMed
Mantke 2002 {published data only}
-
- Mantke R, Pross M, Kunz D, Ebert M, Kahl S, Peters B, et al. Soluble thrombomodulin plasma levels are an early indication of a lethal course in human acute pancreatitis. Surgery 2002;131(4):424‐32. - PubMed
Marek 1996 {published data only}
-
- Marek TA, Nowak A, Dziurkowska‐Marek A, Nowakowska‐Dulawa E, Cholewka A, Kaczor R, et al. C‐reactive protein (CRP) in the early assessment of severity in acute biliary pancreatitis (ABP). Gastroenterology 1996;110(4):A415.
Mayer 1984 {published data only}
Mayer 2002 {published data only}
-
- Mayer JM, Raraty M, Slavin J, Kemppainen E, Fitzpatrick J, Hietaranta A, et al. Serum amyloid A is a better early predictor of severity than C‐reactive protein in acute pancreatitis. British Journal of Surgery 2002;89(2):163‐71. - PubMed
Melzi D'Eril 2000 {published data only}
-
- Melzi D'Eril GV, Merlini G, Finazzi S, Bosoni T, Barakat B, Pezzilli R. Procalcitonin is not a reliable marker for the assessment of severity in acute pancreatitis without infectious complications. Clinical Chemistry 2000;46(3):428‐30. - PubMed
Millat 1999 {published data only}
-
- Millat B. Acute pancreatitis. Etiology, diagnosis, prognosis. Revue du Praticien 1999;49(3):311‐9. - PubMed
Modrau 2005 {published data only}
-
- Modrau IS, Floyd AK, Thorlacius‐Ussing O. The clinical value of procalcitonin in early assessment of acute pancreatitis. American Journal of Gastroenterology 2005;100(7):1593‐7. - PubMed
Modzelewski 2005 {published data only}
-
- Modzelewski B, Holynski J. The role of selected enzymes and acute phase proteins in necrotizing pancreatitis. Polski Merkuriusz Lekarski 2005;18(106):412‐4. - PubMed
Mulholland 1996 {published data only}
-
- Mulholland MW, Eckhauser FE. Prognostic criteria in necrotizing pancreatitis. Problems in General Surgery 1996;13(4):29‐36.
Muller 1997 {published data only}
-
- Muller C, Uhl W, Printzen G, Friess K, Vogel R, Reber P, et al. Value of procalcitonin (PCT) and granulocyte colony‐stimulating factor (G‐CSF) in predicting infected pancreatic necrosis. Gut 1997;41:A134.
Muller 2000 {published data only}
Neoptolemos 2001 {published data only}
-
- Neoptolemos JP. Procalcitonin strip test in the early detection of severe acute pancreatitis. British Journal of Surgery 2001;88(10):1418. - PubMed
Nunes 2009 {published data only}
-
- Nunes QM, Gardner‐Thorpe J, Dajani K, Raraty M, Ghaneh P, Sutton R, et al. CRP as an indicator for using CT‐guided fine needle aspiration in the diagnosis of infected pancreatic necrosis. Pancreatology 2009;9(4):454.
Oezcueruemez‐Porsch 1998 {published data only}
-
- Oezcueruemez‐Porsch M, Kunz D, Hardt PD, Fadgyas T, Kress O, Schulz HU, et al. Diagnostic relevance of interleukin pattern, acute‐phase proteins, and procalcitonin in early phase of post‐ERCP pancreatitis. Digestive Diseases and Sciences 1998;43(8):1763‐9. - PubMed
Olah 2005 {published data only}
-
- Olah A, Belagyi T, Issekutz A, Makay R, Zaborszky A. Value of procalcitonin quick test in the differentiation between sterile and infected forms of acute pancreatitis. Hepato‐Gastroenterology 2005;52(61):243‐5. - PubMed
Omoto 2015 {published data only}
-
- Omoto S, Kitano M, Sakamoto H, Imai H, Yamao K, Kamata K, et al. Usefulness of serum procalcitonin for diagnosis of acute pancreatitis. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2015;30:141.
Ostrovskii 2012 {published data only}
-
- Ostrovskii VK, Rodionov PN, Makarov SV. Some of criteria in the evaluation of severity and prognosis with different forms of acute pancreatitis. Anesteziologiia i Reanimatologiia 2012, (3):56‐9. - PubMed
Paajanen 1995 {published data only}
-
- Paajanen H, Laato M, Jaakkola M, Pulkki K, Niinikoski J, Nordback I. Serum tumour necrosis factor compared with C‐reactive protein in the early assessment of severity of acute pancreatitis. British Journal of Surgery 1995;82(2):271‐3. - PubMed
Palani 1977 {published data only}
-
- Palani CK, Sehgal LR, Kraft AR, Duarte B, Dulski R, Levine H, et al. Predictive value of biochemical indexes in acute alcoholic pancreatitis. Surgical Forum 1977;28:441‐3. - PubMed
Pallisera 2014 {published data only}
-
- Pallisera A, Jorba R, Ramia JM, Rodriguez JA, Subirana H, Zarate LO, et al. Biological markers of severity in acute pancreatitis. Central European Journal of Medicine 2014;9(4):550‐5.
Park 2012 {published data only}
-
- Park JY, Jeon TJ, Hwang JT, Sinn DH, Oh TH, Shin WC, et al. Bedside index for severity in acute pancreatitis: an early marker of severity. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2012;27:355.
Park 2013 {published data only}
-
- Park JY, Jeon TJ, Ha TH, Hwang JT, Sinn DH, Oh TH, et al. Bedside index for severity in acute pancreatitis: Comparison with other scoring systems in predicting severity and organ failure. Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International 2013;12(6):645‐50. - PubMed
Petrov 2011 {published data only}
-
- Petrov MS. Predicting the severity of acute pancreatitis: Choose the right horse before hitching the cart. Digestive Diseases and Sciences 2011;56(12):3402‐4. - PubMed
Pezzilli 1994 {published data only}
-
- Pezzilli R, Billi P, Plate L, Barakat B, Bongiovanni F, Miglioli M. Human pancreatic secretory trypsin inhibitor in the assessment of the severity of acute pancreatitis. A comparison with C‐reactive protein. Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology 1994;19(2):112‐7. - PubMed
Pezzilli 1995a {published data only}
-
- Pezzilli R, Billi P, Miniero R, Fiocchi M, Cappelletti O, Sprovieri G, et al. Serum‐beta‐2 microglobulin in the early assessment of the severity of acute pancreatitis ‐ a comparative study with Interleukin‐6, Interleukin‐8 and C‐reactive protein. Gastroenterology 1995;108(4 Suppl):A384.
Pezzilli 1995b {published data only}
-
- Pezzilli R, Billi P, Miniero R, Fiocchi M, Cappelletti O, Morselli‐Labate AM, et al. Serum interleukin‐6, interleukin‐8, and beta 2‐microglobulin in early assessment of severity of acute pancreatitis. Comparison with serum C‐reactive protein. Digestive Diseases and Sciences 1995;40(11):2341‐8. - PubMed
Pezzilli 1997 {published data only}
-
- Pezzilli R, Billi P, Cappelletti O, Barakat B. Serum C‐positive protein in acute biliary pancreatitis. Is it a reliable marker for the early assessment of severity of the disease?. Italian Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 1997;29(6):554‐7. - PubMed
Pezzilli 1998a {published data only}
-
- Pezzilli R, Labate AMM, Barakat B, Fiocchi M, Cappelletti O, Miglio F. Is the association of serum lipase with beta 2‐microglobulin or with C‐reactive protein useful in simultaneously establishing the diagnosis and prognosis of patients with acute pancreatitis?. Gastroenterology 1998;114(4):A490‐1.
Pezzilli 1998b {published data only}
-
- Pezzilli R, Morselli‐Labate AM, Barakat B, Fiocchi M, Cappelletti O. Is the association of serum lipase with alpha‐2‐microglobulin or C‐reactive protein useful for establishing the diagnosis and prognosis of patients with acute pancreatitis?. Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine 1998;36(12):963‐8. - PubMed
Pezzilli 2000 {published data only}
-
- Pezzilli R, D'Eril GVM, Morselli‐Labate AM, Merlini G, Barakat B, Bosoni T. Serum amyloid A, procalcitonin, and C‐reactive protein in early assessment of severity of acute pancreatitis. Digestive Diseases and Sciences 2000;45(6):1072‐8. - PubMed
Pongprasobchai 2010 {published data only}
-
- Pongprasobchai S, Jianjaroonwong V, Charatcharoenwitthaya P, Komoltri C, Tanwandee T, Leelakusolvong S, et al. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C‐reactive protein for the prediction of severity of acute pancreatitis. Pancreas 2010;39(8):1226‐30. - PubMed
Puolakkainen 1987 {published data only}
Purkayastha 2006 {published data only}
-
- Purkayastha S, Chow A, Athanasiou T, Cambaroudis A, Panesar S, Kinross J, et al. Does serum procalcitonin have a role in evaluating the severity of acute pancreatitis? A question revisited. World Journal of Surgery 2006;30(9):1713‐21. - PubMed
Qiu 2014 {published data only}
-
- Qiu L, Yu Q, Yu J, Wang H, Zhou Y, Li Q, et al. The prognostic value of CD14+HLA‐DRlow/‐ for evaluating the severity of acute pancreatitis. Chinese Journal of Microbiology and Immunology 2014;34(8):620‐3.
Raraty 2002 {published data only}
-
- Raraty MGT, Mayer JM, Slavin M, Kemppainen E, Fitzpatrick J, Hietaranta A, et al. Serum amyloid A is a better early predictor of severity than C‐reactive protein in acute pancreatitis. British Journal of Surgery 2002;89(3):380. - PubMed
Rau 1997 {published data only}
Rau 2000 {published data only}
-
- Rau B, Steinbach G, Baumgart K, Gansauge F, Grunert A, Beger HG. The clinical value of procalcitonin in the prediction of infected necrosis in acute pancreatitis. Intensive Care Medicine 2000;26:S159‐64. - PubMed
Rau 2004 {published data only}
-
- Rau B, Kruger CM, Schilling MK. Procalcitonin: Improved biochemical severity stratification and postoperative monitoring in severe abdominal inflammation and sepsis. Langenbecks Archives of Surgery 2004;389(2):134‐44. - PubMed
Rau 2007 {published data only}
Ricardo 2011 {published data only}
-
- Ricardo L, Cardoso F, Oliveira A, Rodrigues C, Horta D, Figueiredo A, et al. Comparison of BISAP, Ranson's, and CTSI scores, and C‐reactive protein in predicting organ failure, complications and mortality in acute pancreatitis. Pancreas 2011;40(8):1351.
Riche 2003 {published data only}
-
- Riche FC, Cholley BP, Laisne MJ, Vicaut E, Panis YH, Lajeunie EJ, et al. Inflammatory cytokines, C reactive protein, and procalcitonin as early predictors of necrosis infection in acute necrotizing pancreatitis. Surgery 2003;133(3):257‐62. - PubMed
Ruzafa 1991 {published data only}
-
- Ruzafa A, Granada ML, Gener J, Manterola JM, Oller B, Mesalles E, et al. C reactive protein concentrations, measured by a latex slide test, as a prognostic factor in acute pancreatitis. Revista de la Sociedad Espanola de Quimica Clinica 1991;10(5):372‐6.
Samso 2002 {published data only}
-
- Samso CT. Early assessment of severity in acute pancreatitis. Revista Espanola De Enfermedades Digestivas 2002;94(9):519‐22. - PubMed
Sanchez‐Lozada 2005 {published data only}
-
- Sanchez‐Lozada R, Camacho‐Hernandez MI, Vega‐Chavaje RG, Garza‐Flores JH, Campos‐Castillo C, Gutierrez‐Vega R. Acute pancreatitis: Five year experience at the hospital general de Mexico. Gaceta Medica de Mexico 2005;141(2):123‐7. - PubMed
Santotoribio 2015 {published data only}
-
- Santotoribio JD, Canavate‐Solano C, Garcia‐De La Torre A, Arce‐Matute F, Perez‐Ramos S. C‐reactive protein for diagnosis of severe acute pancreatitis. Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine 2015;53:S1250.
Sato 2004 {published data only}
-
- Sato N, Endo S, Kasai T, Inoue Y, Fujino Y, Onodera M, et al. Relationship of the serum procalcitonin level with the severity of acute pancreatitis. Research Communications in Molecular Pathology & Pharmacology 2004;115‐116:243‐9. - PubMed
Savel'ev 2002 {published data only}
-
- Savel'ev VS, Gel'fand BR, Filimonov MI, Burnevich SZ, Sergeeva NA, Brazhnik TB, et al. Clinical significance of the procalcitonin test in differential diagnosis of systemic inflammatory reaction in pancreatonecrosis. Anesteziologiia i Reanimatologiia 2002, (1):25‐9. - PubMed
Schaffler 2010 {published data only}
-
- Schaffler A, Hamer O, Dickopf J, Goetz A, Landfried K, Voelk M, et al. Admission resistin levels predict peripancreatic necrosis and clinical severity in acute pancreatitis. American Journal of Gastroenterology 2010;105(11):2474‐84. - PubMed
Schaffler 2011 {published data only}
-
- Schaffler A, Hamer OW, Dickopf J, Goetz A, Landfried K, Voelk M, et al. Admission visfatin levels predict pancreatic and peripancreatic necrosis in acute pancreatitis and correlate with clinical severity. American Journal of Gastroenterology 2011;106(5):957‐67. - PubMed
Sharma 2011 {published data only}
-
- Sharma M, Goswami B. C reactive protein, PCV and CT scan in assessing severity of acute pancreatitis. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2011;26(Supp 5):232.
Stimac 2010 {published data only}
-
- Stimac D, Fisic E, Zulle LB, Zrnic IK, Milic S. Clinical value of C‐reactive protein and elastase in assessment of acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2010;10(2‐3):347.
Stimac 2012 {published data only}
Stimac 2013 {published data only}
Stoelben 1996 {published data only}
-
- Stoelben E, Nagel M, Ockert D, Quintel M, Scheibenbogen C, Klein B, et al. Clinical relevance of cytokines IL‐6, IL‐8, and C‐reactive protein in the blood of patients with acute pancreatitis. Chirurg 1996;67(12):1231‐6. - PubMed
Sugumar 2011 {published data only}
-
- Sugumar A, Alkubeyyer M, Erickson B, Vege SS. Can machine learning predict the severity of acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2011;1:S853.
Tao 2013 {published data only}
-
- Tao J, Li L, Wu B. The value of combining earlier period C reactive protein and hematocrit level in acute pancreatitis. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2013;28:455.
Teerenhovi 1988 {published data only}
-
- Teerenhovi O, Nordback I. C‐reactive protein (CRP) and pancreatic necrosis in acute necrotizing pancreatitis. Annales Chirurgiae Et Gynaecologiae 1988;77(2):61‐3. - PubMed
Tesinsky 2008 {published data only}
-
- Tesinsky P, Holubec L. P016 predictive value of procalcitonin and cytokines in ERCP induced acute pancreatitis. Clinical Nutrition Supplements 2008;3(Supp 1):35.
Trunin 1985 {published data only}
-
- Trunin MA, Khvatova EA. Lactate dehydrogenase enzymes and isoenzymes in the diagnosis of forms of acute and postoperative pancreatitis. Khirurgiia 1985, (1):50‐5. - PubMed
Uhl 1991 {published data only}
-
- Uhl W, Buchler M, Malfertheiner P, Martini M, Beger HG. PMN‐elastase in comparison with CRP, antiproteases, and LDH as indicators of necrosis in human acute pancreatitis. Pancreas 1991;6(3):253‐9. - PubMed
Uomo 1995 {published data only}
-
- Uomo G, Rabitti PG, Laccetti M, Manes G, Carraturo I, Esposito P, et al. Predictive evaluation of acute necrotizing pancreatitis: Results of a prospective study. Presse Medicale 1995;24(5):263‐6. - PubMed
Vaz 2013 {published data only}
-
- Vaz PS, Caldeira A, Sousa R, Gouveia A, Banhudo A, Loureiro A. The value of procalcitonin, antithrombin III and BISAP score at predicting the severity of acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology: Abstracts presented at the 45th Annual Meeting of the European Pancreatic Club, 2013 June 26‐29, Zurich, Switzerland 2013;13(Supp):S34‐5.
Vesentini 1993 {published data only}
-
- Vesentini S, Bassi C, Talamini G, Cavallini G. Prospective comparison of C‐reactive protein level, Ranson score and contrast‐enhanced computed tomography in the prediction of septic complications of acute pancreatitis. British Journal of Surgery 1993;80(6):755. - PubMed
Viedma 1992 {published data only}
Viedma 1994 {published data only}
Vlachos 2014 {published data only}
-
- Vlachos S, Tsaroucha AK, Konstantoudakis G, Papachristou F, Trypsianis G, Schizas D, et al. Serum profiles of M30, M65 and Interleukin‐17 compared with C‐reactive protein in patients with mild and severe acute pancreatitis. Journal of Hepato‐Biliary‐Pancreatic Sciences 2014;21(12):911‐8. - PubMed
Wei 2013 {published data only}
-
- Wei H, Wang YX. Significance of C‐reactive protein to prediction and severity evaluation of acute pancreatitis. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2013;28(Suppl 3):885‐6.
Wetherill 2012 {published data only}
-
- Wetherill C, Melling J, Jones M. C‐reactive protein accurately predicts severity of acute pancreatitis in children. Pancreas 2012;41(8):1412‐3. - PubMed
Wetherill 2013a {published data only}
-
- Wetherill C, Melling J, Jones M. 48 hour C‐reactive protein accurately predicts severity of acute pancreatitis in children. Pancreatology 2013;13(1):e6. - PubMed
Wetherill 2013b {published data only}
-
- Wetherill C, Melling J, Jones M. C‐reactive protein accurately predicts severity of acute pancreatitis in children. Pancreatology 2013;13(2):e84. - PubMed
Wilson 1987 {published data only}
-
- Wilson C, Fraser WD, Gardner MD, Imrie CW. Source of lactate‐dehydrogenase elevation in acute‐pancreatitis. Digestion 1987;38(1):64.
Wilson 1988 {published data only}
-
- Wilson C, Shenkin A, Imrie CW. Value of C‐reactive protein and antiproteases in the objective monitoring of acute pancreatitis. Gut 1988;29(2):A269.
Wilson 1989a {published data only}
-
- Wilson C, Heads A, Shenkin A, Imrie CW. C‐reactive protein, antiproteases and complement factors as objective markers of severity in acute pancreatitis. British Journal of Surgery 1989;76(2):177‐81. - PubMed
Wilson 1989b {published data only}
-
- Wilson C, Shenkin A, Imrie C. C‐reactive protein and acute pancreatitis ‐ reply. British Journal of Surgery 1989;76(8):877. - PubMed
Wong 1993 {published data only}
-
- Wong ECC, Butch AW, Rosenblum JL, Ladenson JH, Scott MG. (Washington University Case Conference) The clinical chemistry laboratory and acute pancreatitis. Clinical Chemistry 1993;39(2):234‐43. - PubMed
Woo 2011 {published data only}
-
- Woo SM, Noh MH, Kim BG, Hsing CT, Han JS, Ryu SH, et al. Comparison of serum procalcitonin with Ranson, APACHE II, Glasgow and Balthazar CT severity index scores in predicting severity of acute pancreatitis. Korean Journal of Gastroenterology 2011;58(1):31‐7. - PubMed
Xu 2015 {published data only}
-
- Xu YH, Yan L, Bian C, Tian ZB, Jing X. Value of procalcitonin in assessing severity of acute pancreatitis. World Chinese Journal of Digestology 2015;23(30):4898‐904.
Yadav 2015a {published data only}
-
- Yadav A, Rafferty S, Rasool J, Keohane J, Sengupta S. C reactive protein ‐ a rapid and cost effective marker of severity of acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2015;148(4):S684.
Yadav 2015b {published data only}
-
- Yadav A, Rafferty S, Rasool J, Keohane J, Sengupta S. C‐reactive protein: A rapid and cost effective marker of acute pancreatitis severity. Irish Journal of Medical Science 2015;184:S217.
Yasuda 2011 {published data only}
-
- Yasuda H, Suzaki S. Is procalcitonin useful to the diagnosis of infected pancreatic necrosis and pancreatic abscess?. Critical Care Medicine 2011;39:104.
Yin 2014 {published data only}
-
- Yin G, Hu G, Cang X, Yu G, Hu Y, Xing M, et al. C‐reactive protein: Rethinking its role in evaluating the severity of hyperlipidemic acute pancreatitis. Pancreas 2014;43(8):1323‐8. - PubMed
Yu 2011 {published data only}
-
- Yu YH, Han DS, Kim EK, Park HS, Kim TY, Eun CS, et al. Prevalence, mortality rate and predictive factors for severe acute pancreatitis according to the revised Atlanta classification. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2011;26:235.
Zhu 2013 {published data only}
-
- Zhu GF. Early predictive values of the combined detection of serum calcium and CRP in the severity of acute pancreatitis. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2013;28:891‐2.
Zrnic 2007 {published data only}
-
- Zrnic IK, Milic S, Fisic E, Radic M, Stimac D. C‐reactive protein and lactate dehydrogenase as single prognostic factors of severity in acute pancreatitis. Lijecnicki Vjesnik 2007;129(1):1‐3. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Djurasinovic 2013 {published data only}
-
- Djurasinovic T, Subota V, Vujanic S, Andjelic T, Pejovic J, Bezmarevic M. Prognostic values of procalcitonin and CRP in acute pancreatitis. Biochimica Clinica 2013;37:S663.
Grenier 1968 {published data only}
-
- Grenier JF, Gillet M, Sava G, Crevoisier R, Weiss AG. Acute pancreatitis. Anatomo‐clinical and biological confrontations; diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic deductions. Apropos of a statistic of 37 cases. Presse Medicale 1968;76(29):1481‐4. - PubMed
Issekutz 2003 {published data only}
-
- Issekutz A, Belagy T, Olah A. Clinical value of procalcitonin test in severe acute pancreatitis. Hpb 2003;5, SUPP 1:140.
Pindak 2003 {published data only}
-
- Pindak D, Parrak V, Pechan J, Vavrecka A, Kuzela L, Fuchs D, et al. The clinical value of the procalcitonin in prediction of severity and outcome in acute pancreatitis. Hepato‐Gastroenterology 2003;50(Suppl 2):ccviii‐ccix. - PubMed
Additional references
Ayub 2004
Bakker 2012
-
- Bakker OJ, Santvoort HC, Brunschot S, Geskus RB, Besselink MG, Bollen TL, et al. Endoscopic transgastric vs surgical necrosectomy for infected necrotizing pancreatitis: a randomized trial. JAMA 2012;307(10):1053‐61. - PubMed
Banks 2013
-
- Banks PA, Bollen TL, Dervenis C, Gooszen HG, Johnson CD, Sarr MG, et al. Classification of acute pancreatitis ‐ 2012: revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Gut 2013;62(1):102‐11. - PubMed
Becker 2010
Bradley 1993
-
- Bradley EL 3rd. A clinically based classification system for acute pancreatitis. Summary of the International Symposium on Acute Pancreatitis; 1992 September 11‐13; Atlanta, GA. Archives of Surgery 1993;128(5):586‐90. - PubMed
Buscemi 2006
-
- Buscemi N, Hartling L, Vandermeer B, Tjosvold L, Klassen TP. Single data extraction generated more errors than double data extraction in systematic reviews. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2006;59(7):697‐703. - PubMed
Cannon 2009
-
- Cannon JW, Callery MP, Vollmer CM Jr. Diagnosis and management of pancreatic pseudocysts: What is the evidence?. Journal of the American College of Surgeons 2009;209(3):385‐93. - PubMed
Cheruvu 2003
Chu 2006
-
- Chu H, Cole SR. Bivariate meta‐analysis of sensitivity and specificity with sparse data: a generalized linear mixed model approach. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2006;59(12):1331‐2. - PubMed
Doust 2005
-
- Doust JA, Pietrzak E, Sanders S, Glasziou PP. Identifying studies for systematic reviews of diagnostic tests was difficult due to the poor sensitivity and precision of methodologic filters and the lack of information in the abstract. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2005;58(5):444‐9. - PubMed
Eloubeidi 2001
-
- Eloubeidi MA, Wade SB, Provenzale D. Factors associated with acceptance and full publication of GI endoscopic research originally published in abstract form. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy 2001;53(3):275‐82. - PubMed
Ghekiere 2007
-
- Ghekiere O, Lesnik A, Hoa D, Laffargue G, Uriot C, Taourel P. Value of computed tomography in the diagnosis of the cause of nontraumatic gastrointestinal tract perforation. Journal of Computer Assisted Tomography 2007;31(2):169‐76. - PubMed
Grassi 2004
-
- Grassi R, Romano S, Pinto A, Romano L. Gastro‐duodenal perforations: conventional plain film, US and CT findings in 166 consecutive patients. European Journal of Radiology 2004;50(1):30‐6. - PubMed
Gurusamy 2013
Gurusamy 2014
-
- Gurusamy KS, Davidson BR. Gallstones. BMJ 2014;348:g2669. - PubMed
Gurusamy 2016
Johnson 2009
-
- Johnson MD, Walsh RM, Henderson JM, Brown N, Ponsky J, Dumot J, et al. Surgical versus nonsurgical management of pancreatic pseudocysts. Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology 2009;43(6):586‐90. - PubMed
Larson 2006
-
- Larson SD, Nealon WH, Evers BM. Management of gallstone pancreatitis. Advances in Surgery 2006;40:265‐84. - PubMed
Moayyedi 2006
-
- Moayyedi P, Talley NJ, Fennerty MB, Vakil N. Can the clinical history distinguish between organic and functional dyspepsia?. JAMA 2006;295(13):1566‐76. - PubMed
Mouli 2013
-
- Mouli VP, Sreenivas V, Garg PK. Efficacy of conservative treatment, without necrosectomy, for infected pancreatic necrosis: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Gastroenterology 2013;144(2):333‐40.e2. - PubMed
Muddana 2009
-
- Muddana V, Whitcomb DC, Khalid A, Slivka A, Papachristou GI. Elevated serum creatinine as a marker of pancreatic necrosis in acute pancreatitis. American Journal of Gastroenterology 2009;104(1):164‐70. - PubMed
NCBI 2014a
-
- NCBI. MeSH. NLM Controlled Vocabulary. Pancreas. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/68010179 2014 (accessed 4 July 2014).
NCBI 2014b
-
- NCBI. MeSH. NLM Controlled Vocabulary. C‐reactive protein. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/68010179 2014 (accessed 2 August 2014).
NCEPOD 2016
-
- NCEPOD. National Confidential Enquiry Into Patient Outcome and Death. Acute pancreatitis: Treat the cause (2016). www.ncepod.org.uk/2016ap.html 2016 (accessed 19 September 2016).
Peery 2012
Petrov 2010
-
- Petrov MS, Shanbhag S, Chakraborty M, Phillips AR, Windsor JA. Organ failure and infection of pancreatic necrosis as determinants of mortality in patients with acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2010;139(3):813‐20. - PubMed
Reitsma 2005
-
- Reitsma JB, Glas AS, Rutjes AW, Scholten RJ, Bossuyt PM, Zwinderman AH. Bivariate analysis of sensitivity and specificity produces informative summary measures in diagnostic reviews. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology. 2005/09/20 2005; Vol. 58, issue 10:982‐90. - PubMed
Roberts 2013
Rutter 2001
-
- Rutter CM, Gatsonis CA. A hierarchical regression approach to meta‐analysis of diagnostic test accuracy evaluations. Statistics in Medicine 2001;20(19):2865‐84. - PubMed
Sampson 2008
-
- Sampson M, Shojania KG, McGowan J, Daniel R, Rader T, Iansavichene AE, et al. Surveillance search techniques identified the need to update systematic reviews. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2008;61(8):755‐62. - PubMed
Sanabria 2013
Schmid 1999
Takwoingi 2015
Tenner 2013
-
- Tenner S, Baillie J, DeWitt J, Vege SS. American College of Gastroenterology guideline: management of acute pancreatitis. American Journal of Gastroenterology 2013;108(9):1400‐15. - PubMed
van Brunschot 2014
-
- Brunschot S, Fockens P, Bakker OJ, Besselink MG, Voermans RP, Poley JW, et al. Endoscopic transluminal necrosectomy in necrotising pancreatitis: a systematic review. Surgical Endoscopy 2014;28(5):1425‐38. - PubMed
van Santvoort 2010
-
- Santvoort HC, Besselink MG, Bakker OJ, Hofker HS, Boermeester MA, Dejong CH, et al. A step‐up approach or open necrosectomy for necrotizing pancreatitis. New England Journal of Medicine 2010;362(16):1491‐502. - PubMed
van Santvoort 2011
-
- Santvoort HC, Bakker OJ, Bollen TL, Besselink MG, Ahmed Ali U, Schrijver AM, et al. A conservative and minimally invasive approach to necrotizing pancreatitis improves outcome. Gastroenterology 2011;141(4):1254‐63. - PubMed
Varadarajulu 2008
-
- Varadarajulu S, Christein JD, Tamhane A, Drelichman ER, Wilcox CM. Prospective randomized trial comparing EUS and EGD for transmural drainage of pancreatic pseudocysts (with videos). Gastrointestinal Endoscopy 2008;68(6):1102‐11. - PubMed
Varadarajulu 2013
-
- Varadarajulu S, Bang JY, Sutton BS, Trevino JM, Christein JD, Wilcox CM. Equal efficacy of endoscopic and surgical cystogastrostomy for pancreatic pseudocyst drainage in a randomized trial. Gastroenterology 2013;145(3):583‐90. - PubMed
Vissers 1999
-
- Vissers RJ, Abu‐Laban RB, McHugh DF. Amylase and lipase in the emergency department evaluation of acute pancreatitis. Journal of Emergency Medicine 1999;17(6):1027‐37. - PubMed
Whiting 2006
Whiting 2011
-
- Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME, Mallett S, Deeks JJ, Reitsma JB, et al. QUADAS‐2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Annals of Internal Medicine 2011;155(8):529‐36. - PubMed
Yadav 2006
-
- Yadav D, Lowenfels AB. Trends in the epidemiology of the first attack of acute pancreatitis: a systematic review. Pancreas 2006;33(4):323‐30. - PubMed
Yang 2008
-
- Yang AL, Vadhavkar S, Singh G, Omary MB. Epidemiology of alcohol‐related liver and pancreatic disease in the United States. Archives of Internal Medicine 2008;168(6):649‐56. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Gurusamy 2015
-
- Gurusamy KS, Davidson BR. Serum amylase and lipase and urinary trypsinogen and amylase for diagnosis of acute pancreatitis and serum C‐reactive protein, procalcitonin and lactate dehydrogenase for the diagnosis of pancreatic necrosis. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2015, Issue 12. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD012010] - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

