Small molecules targeting histone demethylase genes (KDMs) inhibit growth of temozolomide-resistant glioblastoma cells
- PMID: 28432280
- PMCID: PMC5471020
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.16820
Small molecules targeting histone demethylase genes (KDMs) inhibit growth of temozolomide-resistant glioblastoma cells
Abstract
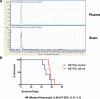
In glioblastoma several histone demethylase genes (KDM) are overexpressed compared to normal brain tissue and the development of Temozolomide (TMZ) resistance is accompanied by the transient further increased expression of KDM5A and other KDMs following a mechanism that we defined as "epigenetic resilience". We hypothesized that targeting KDMs may kill the cells that survive the cytotoxic therapy.We determined the effect of JIB 04 and CPI-455, two KDM inhibitors, on glioblastoma cells and found that both molecules are more effective against TMZ-resistant rather than native cells.Because of its lower IC50, we focused on JIB 04 that targets KDM5A and other KDMs as well. We have shown that this molecule activates autophagic and apoptotic pathways, interferes with cell cycle progression, inhibits cell clonogenicity and dephosphorylates Akt thus inactivating a potent pro-survival pathway. We performed combination temozolomide/JIB 04 in vitro treatments showing that these two molecules, under certain conditions, have a strong synergic effect and we hypothesize that JIB 04 intercepts the cells that escape the G2 block exerted by TMZ. Finally we studied the permeability of JIB 04 across the blood-brain barrier and found that this molecule reaches bioactive concentration in the brain; furthermore a pilot in vivo experiment in an orthotopic GB xenograft model showed a trend toward longer survival in treated mice with an Hazard Ratio of 0.5.In conclusion we propose that the combination between cytotoxic drugs and molecules acting on the epigenetic landscape may offer the opportunity to develop new therapies for this invariably lethal disease.
Keywords: drug resistance; epigenetics; glioblastoma; histone demethylase; temozolomide.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the Authors has any conflicts of interest that could have biased the work and the funding agencies had no role in the conduction of the experimental work neither in the interpretation of the results.
Figures
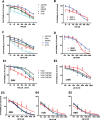
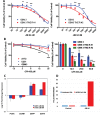
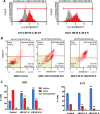
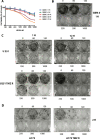

References
-
- Florio T, Barbieri F. The status of the art of human malignant glioma management: the promising role of targeting tumor-initiating cells. Drug Discov Today. 2012;17:1103–1110. - PubMed
-
- Friedman HS, Kerby T, Calvert H. Temozolomide and treatment of malignant glioma. Clin Cancer Res. 2000;6:2585–2597. - PubMed
-
- Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn U, Curschmann J, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, et al. European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Brain Tumor and Radiotherapy Groups, and National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:987–996. - PubMed
-
- Hegi ME, Diserens AC, Gorlia T, Hamou MF, de Tribolet N, Weller M, Kros JM, Hainfellner JA, Mason W, Mariani L, Bromberg JE, Hau P, Mirimanoff RO, et al. MGMT gene silencing and benefit from temozolomide in glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:997–1003. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

