Maternal low-protein diet decreases brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in the brains of the neonatal rat offspring
- PMID: 28432877
- PMCID: PMC5466833
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2017.03.005
Maternal low-protein diet decreases brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in the brains of the neonatal rat offspring
Abstract
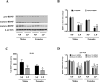
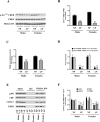
Prenatal exposure to a maternal low-protein (LP) diet has been known to cause cognitive impairment, learning and memory deficits. However, the underlying mechanisms have not been identified. Herein, we demonstrate that a maternal LP diet causes, in the brains of the neonatal rat offspring, an attenuation in the basal expression of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a neurotrophin indispensable for learning and memory. Female rats were fed either a 20% normal protein (NP) diet or an 8% LP 3 weeks before breeding and during the gestation period. Maternal LP diet caused a significant reduction in the Bdnf expression in the brains of the neonatal rats. We further found that the maternal LP diet reduced the activation of the cAMP/protein kinase A/cAMP response element binding protein (CREB) signaling pathway. This reduction was associated with a significant decrease in CREB binding to the Bdnf promoters. We also show that prenatal exposure to the maternal LP diet results in an inactive or repressed exon I and exon IV promoter of the Bdnf gene in the brain, as evidenced by fluxes in signatory hallmarks in the enrichment of acetylated and trimethylated histones in the nucleosomes that envelop the exon I and exon IV promoters, causing the Bdnf gene to be refractory to transactivation. Our study is the first to determine the impact of a maternal LP diet on the basal expression of BDNF in the brains of the neonatal rats exposed prenatally to an LP diet.
Keywords: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor; Cyclic adenosine monophosphate; Histone acetylation; Histone methylation; Maternal low-protein diet; cAMP response element binding protein.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Flores O, Perez H, Valladares L, Morgan C, Gatica A, Burgos H, et al. Hidden prenatal malnutrition in the rat: role of beta(1)-adrenoceptors on synaptic plasticity in the frontal cortex. J Neurochem. 2011;119:314–23. - PubMed
-
- Morgane PJ, Austin-LaFrance R, Bronzino J, Tonkiss J, Diaz-Cintra S, Cintra L, et al. Prenatal malnutrition and development of the brain. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1993;17:91–128. - PubMed
-
- Morgane PJ, Mokler DJ, Galler JR. Effects of prenatal protein malnutrition on the hippocampal formation. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2002;26:471–83. - PubMed
-
- Tonkiss J, Galler J, Morgane PJ, Bronzino JD, Austin-LaFrance RJ. Prenatal protein malnutrition and postnatal brain function. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1993;678:215–27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

