In vitro susceptibility of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from skin and soft tissue infections to vancomycin, daptomycin, linezolid and tedizolid
- PMID: 28432878
- PMCID: PMC9425527
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bjid.2017.03.010
In vitro susceptibility of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from skin and soft tissue infections to vancomycin, daptomycin, linezolid and tedizolid
Abstract
Introduction: Treatment of multidrug-resistant Gram-positive infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus remains as a clinical challenge due to emergence of new resistance mechanisms. Tedizolid is a next-generation oxazolidinone, recently approved for skin and soft tissues infections. We conducted a study to determine in vitro susceptibility to vancomycin, daptomycin, linezolid and tedizolid in MRSA clinical isolates from adult patients with skin and soft tissue infections.
Material and methods: Methicillin-resistant S. aureus isolates were collected in three tertiary-care hospitals of Medellin, Colombia, from February 2008 to June 2010 as part of a previous study. Clinical characteristics were assessed by medical records and MIC values were determined by Epsilometer test. Genotypic analysis included spa typing, MLST, and SCCmec typing.
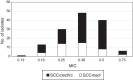
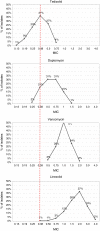
Results: A total of 150 MRSA isolates were evaluated and tedizolid MIC values obtained showed higher in vitro activity than other antimicrobials, with MIC values ranging from 0.13μg/mL to 0.75μg/mL and lower values of MIC50 and MIC90 (0.38μg/mL and 0.5μg/mL). In contrast, vancomycin and linezolid had higher MIC values, which ranged from 0.5μg/mL to 2.0μg/mL and from 0.38μg/mL to 4.0μg/mL, respectively. Tedizolid MICs were 2- to 5-fold lower than those of linezolid. Clinical characteristics showed high previous antimicrobial use and hospitalization history. The majority of the strains belong to the CC8 harboring the SCCmec IVc and were associated with the spa t1610 (29.33%, n=44).
Conclusion: In vitro effectiveness of tedizolid was superior for isolates from skin and soft tissue infections in comparison with the other antibiotics evaluated. The above added to its less toxicity, good bioavailability, daily dose and unnecessity of dosage adjustment, make tedizolid in a promising alternative for the treatment of infections caused by MRSA.
Keywords: Daptomycin; Linezolid; MRSA; Skin and soft tissues infections; Tedizolid; Vancomycin.
Copyright © 2017 Sociedade Brasileira de Infectologia. Published by Elsevier Editora Ltda. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Aires de Sousa M., de Lencastre H. Bridges from hospitals to the laboratory: genetic portraits of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clones. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2004;40:101–111. - PubMed
-
- Ruef C. Epidemiology and clinical impact of glycopeptide resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Infection. 2004;32:315–327. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical