The genetics of Wilson disease
- PMID: 28433102
- PMCID: PMC5648646
- DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-444-63625-6.00003-3
The genetics of Wilson disease
Abstract
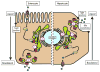
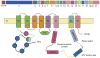
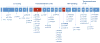
Wilson disease (WD) is an autosomal-recessive disorder of hepatocellular copper deposition caused by pathogenic variants in the copper-transporting gene, ATP7B. Early detection and treatment are critical to prevent lifelong neuropsychiatric, hepatic, and systemic disabilities. Due to the marked heterogeneity in age of onset and clinical presentation, the diagnosis of Wilson disease remains challenging to physicians today. Direct sequencing of the ATP7B gene is the most sensitive and widely used confirmatory testing method, and concurrent biochemical testing improves diagnostic accuracy. More than 600 pathogenic variants in ATP7B have been identified, with single-nucleotide missense and nonsense mutations being the most common, followed by insertions/deletions, and, rarely, splice site mutations. The prevalence of Wilson disease varies by geographic region, with higher frequency of certain mutations occurring in specific ethnic groups. Wilson disease has poor genotype-phenotype correlation, although a few possible modifiers have been proposed. Improving molecular genetic studies continue to advance our understanding of the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and screening for Wilson disease.
Keywords: ATP7B; Wilson disease; copper metabolism; molecular diagnosis.
© 2017 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Abdelghaffar TY, Elsayed SM, Elsobky E, et al. Mutational analysis of ATP7B gene in Egyptian children with Wilson disease: 12 novel mutations. J Hum Genet. 2008;53(8):681–687. - PubMed
-
- Aggarwal A, Bhatt M. Update on Wilson disease. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2013;110:313–348. - PubMed
-
- Aggarwal A, Chandhok G, Todorov T, et al. Wilson disease mutation pattern with genotype–phenotype correlations from Western India: confirmation of p.C271* as a common Indian mutation and identification of 14 novel mutations. Ann Hum Genet. 2013;77(4):299–307. - PubMed
-
- Al Jumah M, Majumdar R, Al Rajeh S, et al. A clinical and genetic study of 56 Saudi Wilson disease patients: identification of Saudi-specific mutations. Eur J Neurol. 2004;11(2):121–124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

