Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is a potential therapeutic target for EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 28433633
- PMCID: PMC7092918
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.04.102
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is a potential therapeutic target for EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
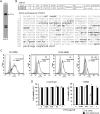
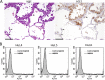
EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinomas contain a subpopulation of cells that have undergone epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and can grow independently of EGFR. To kill these cancer cells, we need a novel therapeutic approach other than EGFR inhibitors. If a molecule is specifically expressed on the cell surface of such EGFR-independent EGFR-mutant cancer cells, it can be a therapeutic target. We found that a mesenchymal EGFR-independent subline derived from HCC827 cells, an EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma cell line, expressed angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) to a greater extent than its parental cells. ACE2 was also expressed at least partially in most of the primary EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinomas examined, and the ACE2 expression level in the cancer cells was much higher than that in normal lung epithelial cells. In addition, we developed an anti-ACE2 mouse monoclonal antibody (mAb), termed H8R64, that was internalized by ACE2-expressing cells. If an antibody-drug conjugate consisting of a humanized mAb based on H8R64 and a potent anticancer drug were produced, it could be effective for the treatment of EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinomas.
Keywords: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2); Antibody-drug conjugate (ADC); EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma; Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT); Monoclonal antibody (mAb); Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs).
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Polyphyllin I Overcomes EMT-Associated Resistance to Erlotinib in Lung Cancer Cells via IL-6/STAT3 Pathway Inhibition.Biol Pharm Bull. 2017 Aug 1;40(8):1306-1313. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b17-00271. Epub 2017 May 18. Biol Pharm Bull. 2017. PMID: 28515374
-
Enhanced YAP expression leads to EGFR TKI resistance in lung adenocarcinomas.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 10;8(1):271. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-18527-z. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29321482 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced autophagy is required for survival in EGFR-independent EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma cells.Lab Invest. 2013 Oct;93(10):1137-46. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2013.102. Epub 2013 Aug 12. Lab Invest. 2013. PMID: 23938604
-
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and its role in EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Pathol Int. 2017 Aug;67(8):379-388. doi: 10.1111/pin.12553. Epub 2017 Jul 5. Pathol Int. 2017. PMID: 28678431 Review.
-
Fighting cancer drug resistance: Opportunities and challenges for mutation-specific EGFR inhibitors.Drug Resist Updat. 2015 May;20:12-28. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2015.05.002. Epub 2015 May 12. Drug Resist Updat. 2015. PMID: 26021435 Review.
Cited by
-
Decipering the Molecular Mechanism of ACE2 Regulating A549 Cells.Front Genet. 2021 Jul 19;12:653725. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.653725. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34354732 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring cellular plasticity and resistance mechanisms in lung cancer: Innovations and emerging therapies.J Pharm Anal. 2025 May;15(5):101179. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2024.101179. Epub 2025 Jan 3. J Pharm Anal. 2025. PMID: 40496071 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemotherapy induces ACE2 expression in breast cancer via the ROS-AKT-HIF-1α signaling pathway: a potential prognostic marker for breast cancer patients receiving chemotherapy.J Transl Med. 2022 Nov 5;20(1):509. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03716-w. J Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36335375 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of limbal epithelial proliferation is partly controlled by the ACE2-LCN2 pathway.iScience. 2024 Jul 18;27(8):110534. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110534. eCollection 2024 Aug 16. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39175771 Free PMC article.
-
From ACE2 to COVID-19: A multiorgan endothelial disease.Int J Infect Dis. 2020 Nov;100:425-430. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.08.083. Epub 2020 Sep 5. Int J Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32896660 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Sakuma Y., Matsukuma S., Nakamura Y. Enhanced autophagy is required for survival in EGFR-independent EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma cells. Lab. Invest. 2013;93:1137–1146. - PubMed
-
- Sakuma Y., Nishikiori H., Hirai S. Prolyl isomerase Pin1 promotes survival in EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma cells with an epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotype. Lab. Invest. 2016;96:391–398. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

