Emerging potential of gene silencing approaches targeting anti-chondrogenic factors for cell-based cartilage repair
- PMID: 28434038
- PMCID: PMC11107620
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-017-2531-z
Emerging potential of gene silencing approaches targeting anti-chondrogenic factors for cell-based cartilage repair
Abstract
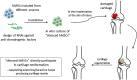
The field of cartilage repair has exponentially been growing over the past decade. Here, we discuss the possibility to achieve satisfactory regeneration of articular cartilage by means of human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) depleted of anti-chondrogenic factors and implanted in the site of injury. Different types of molecules including transcription factors, transcriptional co-regulators, secreted proteins, and microRNAs have recently been identified as negative modulators of chondroprogenitor differentiation and chondrocyte function. We review the current knowledge about these molecules as potential targets for gene knockdown strategies using RNA interference (RNAi) tools that allow the specific suppression of gene function. The critical issues regarding the optimization of the gene silencing approach as well as the delivery strategies are discussed. We anticipate that further development of these techniques will lead to the generation of implantable hMSCs with enhanced potential to regenerate articular cartilage damaged by injury, disease, or aging.
Keywords: Anti-chondrogenic regulators; Cartilage repair; Chondrogenesis; Gene silencing; Mesenchymal stem cells; MicroRNA; RNA interference.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Silencing of Antichondrogenic MicroRNA-221 in Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promotes Cartilage Repair In Vivo.Stem Cells. 2016 Jul;34(7):1801-11. doi: 10.1002/stem.2350. Epub 2016 Mar 27. Stem Cells. 2016. PMID: 26930142
-
Suppressing mesenchymal stem cell hypertrophy and endochondral ossification in 3D cartilage regeneration with nanofibrous poly(l-lactic acid) scaffold and matrilin-3.Acta Biomater. 2018 Aug;76:29-38. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.06.027. Epub 2018 Jun 22. Acta Biomater. 2018. PMID: 29940371 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-based articular cartilage repair: the link between development and regeneration.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015 Mar;23(3):351-62. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2014.11.004. Epub 2014 Nov 11. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015. PMID: 25450846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Zinc-finger protein 145, acting as an upstream regulator of SOX9, improves the differentiation potential of human mesenchymal stem cells for cartilage regeneration and repair.Arthritis Rheum. 2011 Sep;63(9):2711-20. doi: 10.1002/art.30430. Arthritis Rheum. 2011. PMID: 21547890
-
Mesenchymal stem cells and cartilage in situ regeneration.J Intern Med. 2009 Oct;266(4):390-405. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.2009.02153.x. J Intern Med. 2009. PMID: 19765182 Review.
Cited by
-
Women's contribution to stem cell research for osteoarthritis: an opinion paper.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Dec 19;11:1209047. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1209047. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 38174070 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Intra-articular drug delivery systems for joint diseases.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2018 Jun;40:67-73. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2018.03.013. Epub 2018 Apr 3. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29625332 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-193b-3p regulates chondrogenesis and chondrocyte metabolism by targeting HDAC3.Theranostics. 2018 Apr 15;8(10):2862-2883. doi: 10.7150/thno.23547. eCollection 2018. Theranostics. 2018. PMID: 29774080 Free PMC article.
-
Long noncoding RNA expression profiles in chondrogenic and hypertrophic differentiation of mouse mesenchymal stem cells.Funct Integr Genomics. 2017 Nov;17(6):739-749. doi: 10.1007/s10142-017-0569-5. Epub 2017 Jul 22. Funct Integr Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28735352
-
Engineering gene-activated bioprinted scaffolds for enhancing articular cartilage repair.Mater Today Bio. 2024 Nov 19;29:101351. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2024.101351. eCollection 2024 Dec. Mater Today Bio. 2024. PMID: 39649247 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

