The mTOR Signaling Pathway in Myocardial Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- PMID: 28434143
- PMCID: PMC8219468
- DOI: 10.1007/s11892-017-0865-4
The mTOR Signaling Pathway in Myocardial Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
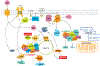
Purpose of review: T2DM (type 2 diabetes mellitus) is a risk factor for heart failure. The mTOR (mechanistic target of rapamycin) is a key mediator of the insulin signaling pathway. We will discuss the role of mTOR in myocardial dysfunction in T2DM.
Recent findings: In T2DM, chronically activated mTOR induces multiple pathological events, including a negative feedback loop that suppresses IRS (insulin receptor substrate)-1. While short-term treatment with rapamycin, an mTOR inhibitor, is a promising strategy for cardiac diseases such as acute myocardial infarction and cardiac hypertrophy in T2DM, there are many concerns about chronic usage of rapamycin. Two mTOR complexes, mTORC1 and mTORC2, affect many molecules and processes via distinct signaling pathways that regulate cardiomyocyte function and survival. Understanding mechanisms underlying mTOR-mediated pathophysiological features in the heart is essential for developing effective therapies for cardiac diseases in the context of T2DM.
Keywords: Cardiovascular disease; Cell signaling; Diabetes mellitus; Heart failure; Rapamycin; mTOR.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
Tomohiro Suhara, Yuichi Baba, Briana K. Shimada, Jason K. Higa, and Takashi Matsui declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting mTOR Signaling in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Diabetes Complications.Curr Drug Targets. 2022;23(7):692-710. doi: 10.2174/1389450123666220111115528. Curr Drug Targets. 2022. PMID: 35021971 Review.
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin signaling in cardiac physiology and disease.Circ Res. 2014 Jan 31;114(3):549-64. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.114.302022. Circ Res. 2014. PMID: 24481845 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rapamycin inhibits activation of AMPK-mTOR signaling pathway-induced Alzheimer's disease lesion in hippocampus of rats with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Int J Neurosci. 2019 Feb;129(2):179-188. doi: 10.1080/00207454.2018.1491571. Epub 2018 Nov 5. Int J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 29962282
-
The Role of Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) in Insulin Signaling.Nutrients. 2017 Oct 27;9(11):1176. doi: 10.3390/nu9111176. Nutrients. 2017. PMID: 29077002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Insights Into the Role of mTOR Signaling in the Cardiovascular System.Circ Res. 2018 Feb 2;122(3):489-505. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.311147. Circ Res. 2018. PMID: 29420210 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
mTOR-mediated calcium transients affect cardiac function in ex vivo ischemia-reperfusion injury.Physiol Rep. 2021 Mar;9(6):e14807. doi: 10.14814/phy2.14807. Physiol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33769701 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of the Long Non-coding RNA LINC01480 Is Associated With Immune Infiltration in Coronary Artery Disease Based on an Immune-Related lncRNA-mRNA Co-expression Network.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Apr 26;9:724262. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.724262. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35557532 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulated inflammation, oxidative stress, and protein quality control in diabetic HFpEF: unraveling mechanisms and therapeutic targets.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 May 14;24(1):211. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02734-4. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 40369521 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics Analysis of Next Generation Sequencing Data Identifies Molecular Biomarkers Associated With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Clin Med Insights Endocrinol Diabetes. 2023 Feb 20;16:11795514231155635. doi: 10.1177/11795514231155635. eCollection 2023. Clin Med Insights Endocrinol Diabetes. 2023. PMID: 36844983 Free PMC article.
-
Brain insulin resistance linked Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease pathology: An undying implication of epigenetic and autophagy modulation.Inflammopharmacology. 2023 Apr;31(2):699-716. doi: 10.1007/s10787-023-01187-z. Epub 2023 Mar 23. Inflammopharmacology. 2023. PMID: 36952096 Review.
References
-
- Shimobayashi M, Hall MN. Making new contacts: the mTOR network in metabolism and signalling crosstalk. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15(3):155–62. doi:10.1038/nrm3757. - DOI - PubMed
-
A comprehensive review of mTOR pathways, especially in metabolism and signaling crosstalk, providing new insight into the modulation of mTOR by other pathways.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

